Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Sharks are not mammals, but fish, as they live underwater and breathe using gills.
- Sharks are classified as elasmobranchs, a type of fish with cartilage skeletons, including skates, rays, and sawfish.
- Mammals have specific traits such as hair, mammary glands, and a neocortex, which sharks lack.
- Around 60% of shark species give birth to live young, while the rest lay eggs known as “mermaid’s purses.”
- Some marine mammals include otters, seals, sea lions, whales, dolphins, manatees, and polar bears.

The animal kingdom is divided into six main groups: mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and insects. Each group has defining traits and characteristics. Only a few animals are outliers of these traits, and these generally fall between categories.
But where do sharks fit into these classifications? And most importantly, are sharks mammals?
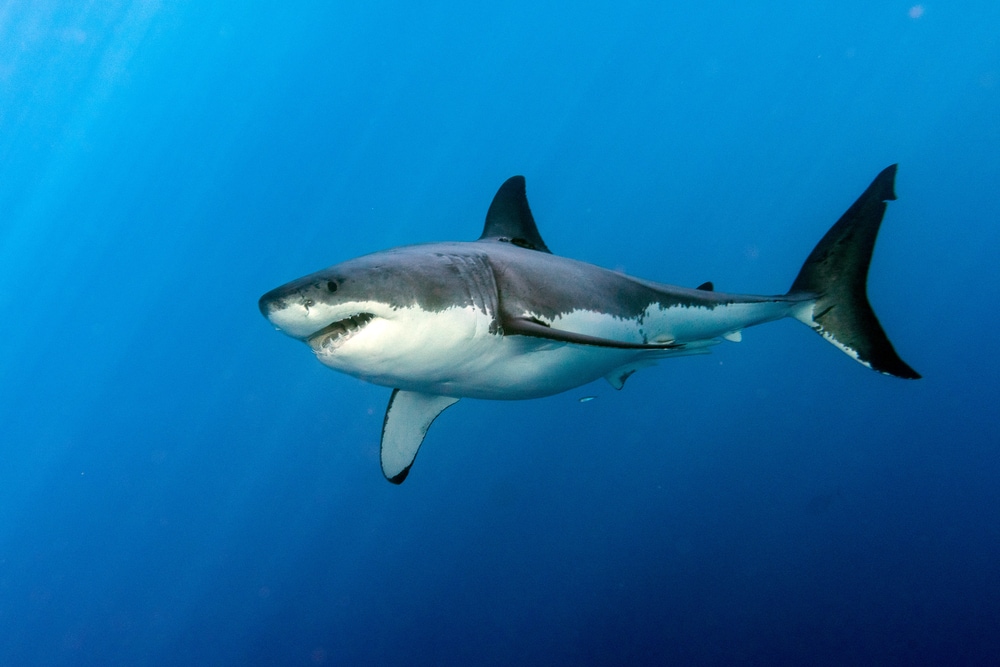
Sharks aren’t mammals like some people may believe. They lack almost all mammalian traits but fit well into the fish category. Sharks live underwater and breathe using gills to filter oxygen out of the water.

share this image on your site
<a href="https://outforia.com/are-sharks-mammals/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/are-sharks-mammals-infographics-683x1024.jpg"></a><br>are sharks mammals by <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>You May Also Like: How Long Do Sharks Live? Far Longer Than You’d Think
What Makes A Shark A Shark?
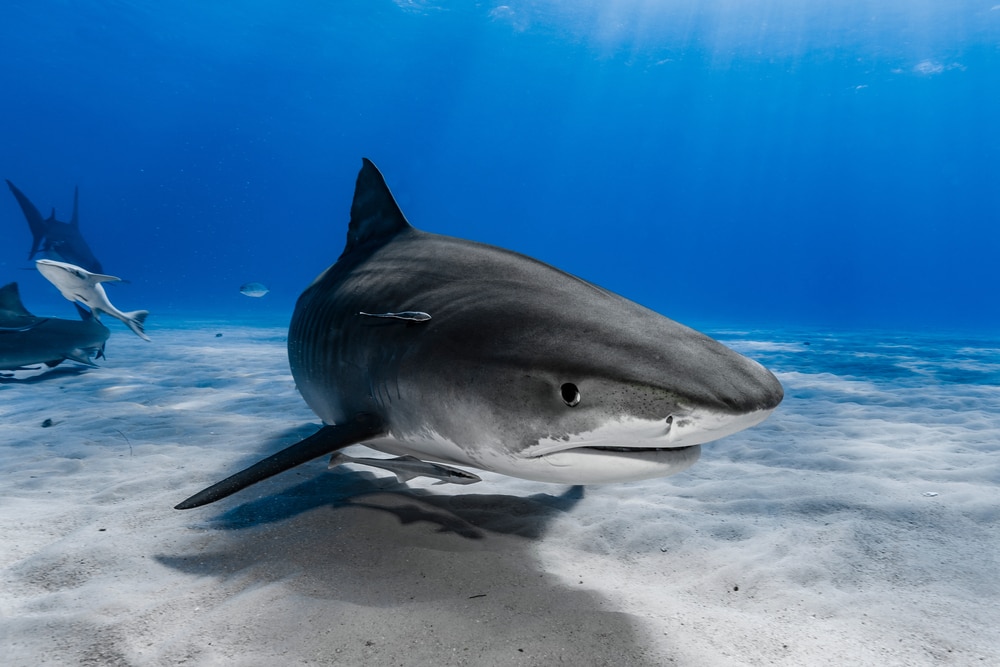

To fully understand what a shark is, we must look at its traits.
Sharks are fish. But what exactly is a fish?
Fish are vertebrate animals, which means they have a backbone and a spinal cord. They live underwater and filter oxygen from the water with gills. These function kind of like our lungs do.
Included in the definition of fish is the lack of limbs. Instead, they have fins that help propel them through the water and keep them upright.
Most fish are ectothermic, which is the scientific name for cold-blooded. They can’t generate heat on their own, meaning their body temperature is dependent on the water temperature.
However, this isn’t the case for all fish, as some can keep themselves warm despite colder water.
Fish are perhaps the most diverse group of vertebrates in the world. There are more different fish species than mammals, birds, or reptiles. You can find fish in nearly every body of water, from small pools and streams to the deepest parts of the ocean.
So how do sharks fit into the fish category?
Sharks live exclusively underwater. They breathe by filtering oxygen from the water with their gills. One distinct feature of sharks is that they usually have five to seven gills slits, while most fish only have one.
Sharks also have fins, not limbs. Most sharks have a fairly similar body shape to other sharks. It inspires terror in people and is one of the most recognizable animal outlines.
But just because sharks are fish, that doesn’t mean they are a complete match to the majority of fish species.
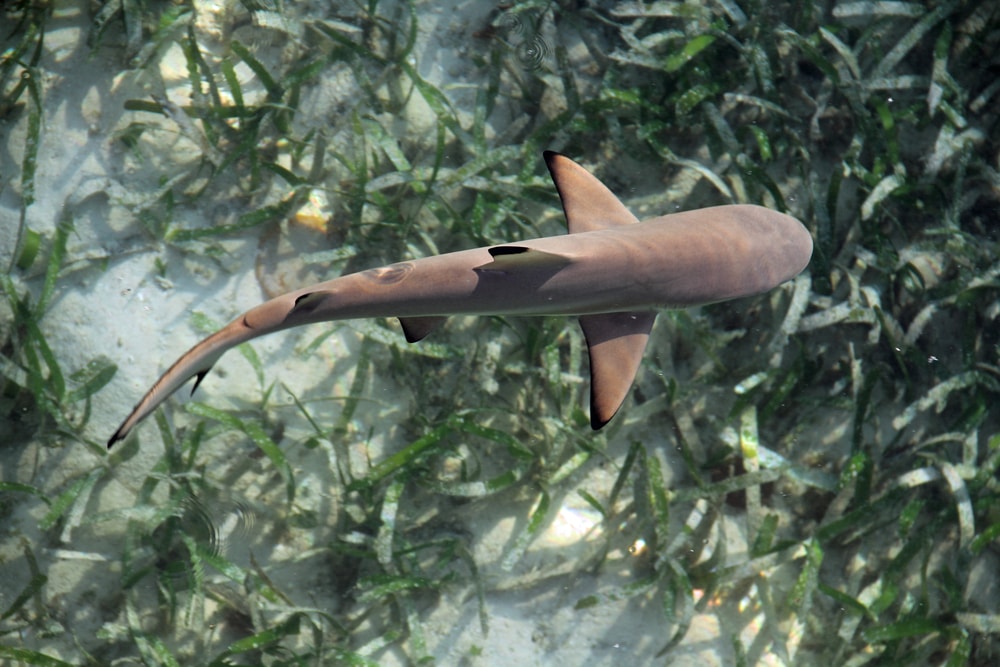

A few shark species give birth to live young. A few shark species are even warm-blooded like mammals.
Despite these extra abilities, all sharks are fish. In fact, they’re an extraordinary type of fish. Instead of hard bones, most of a shark’s skeleton is made up of cartilage. Cartilage is a softer, more flexible material than bone.
Humans have cartilage in their bodies as well. For us, it’s used to protect your bones. It acts as a cushion and lets you flex your joints without grinding the bones. Arthritis pain is usually caused by the lack or decay of cartilage.
Shark’s cartilage skeleton classifies them as their own branch of fish called the elasmobranchs. This includes sharks, skates, rays, and sawfish.
Sharks also don’t have an inflatable air bladder like bony fish. Instead, they have an extra oily liver that helps them maintain neutral buoyancy.
All sharks have teeth. They use them to grab onto prey and rip chunks of meat off. Even the massive and docile whale shark has teeth, though theirs are very small and are more like sandpaper than steak knives.
For the most part, sharks don’t chew their food. All sharks feed mostly on meat, making them carnivores. Some sharks can and will eat plants to sustain themselves if they can’t find enough food.
Essentially, sharks lack all of the things that make a mammal a mammal.
- Hair or fur
- Glands that produce milk
- Neocortex region of the brain
- Sweat glands
- A four-chambered heart
- Three middle ear bones
Then What’s A Mammal?
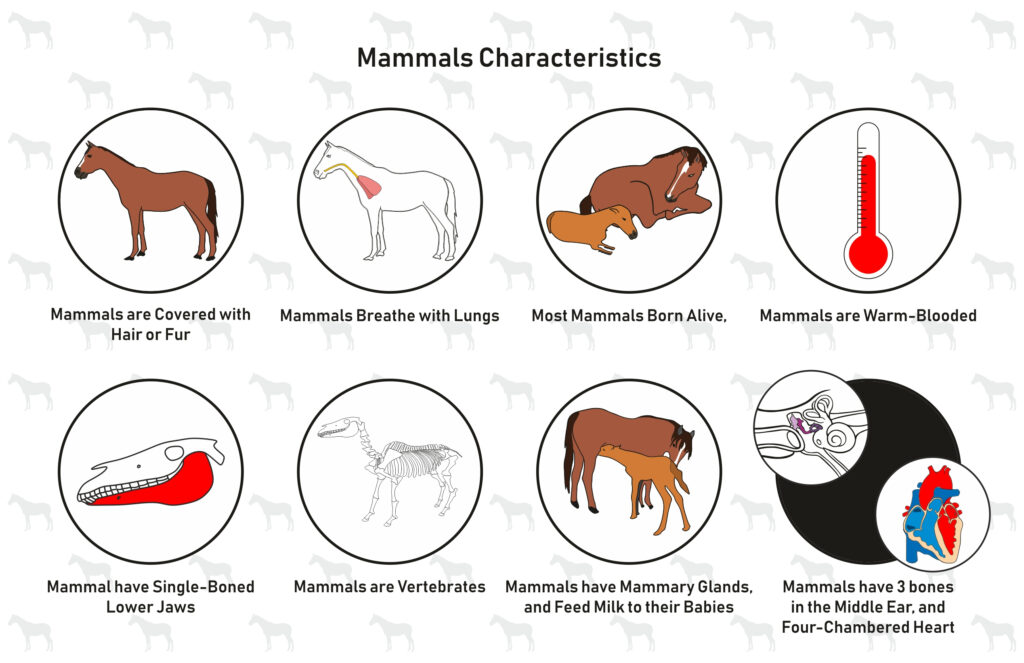
Since the real question is whether or not sharks are mammals, it’s appropriate to address why sharks don’t fit in that category.
Mammals, like fish, have specific, defining characteristics that help group them together.
Mammals are also vertebrate animals. The biggest indicator of mammals is the presence of mammary glands. Simply put, these glands produce milk, which is used to feed offspring.
Generally, mammals also have some kind of fur or hair, a specific region of the brain called the neocortex, and three bones in their middle ears.
We, as humans, are mammals, as are all kinds of primates and apes. Rodents, whales, elephants, dogs, cats, and bats are also mammals.
Just based on traits, you could technically argue a coconut is a mammal. It has hair and milk. But even if you have heard that joke before, coconuts are not mammals. Just the fruit of a plant.
You may also like: Animals That Lay Eggs: The World’s Most Eggs-Ellent Creatures!
Do Sharks Give Live Birth Or Lay Eggs?

Part of the reason sharks might get confused as mammals is the way they give birth.
Only about 40% of sharks lay eggs. The other 60% of the 500 known shark species give birth to live young.
Shark eggs look very different from the typical bird eggs we see. They don’t even look like caviar or fish eggs on sushi. Instead, shark eggs look kind of like purses. This gained them the nickname of mermaid’s purse.
A shark egg is usually a flat pouch with two upturned and curled “horns” near the top. It also usually has some threads sticking off it that help anchor it. Sharks like to attach their eggs to kelp, seaweed, or rocks.
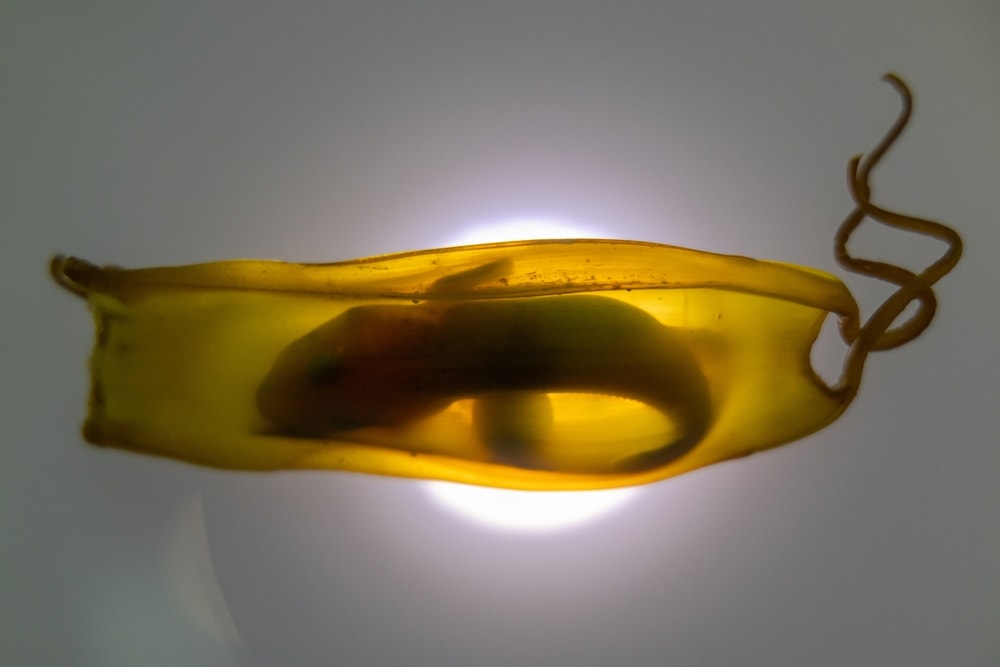

For sharks that give live birth, the number of babies varies a lot. Sharks don’t produce milk as mammals do. In many cases, a female shark will carry multiple babies in her belly at one time. Some sharks even have multiple uteri for carrying babies.
For certain species, like sand tiger sharks, the strongest baby will eat the other embryos in the womb. Fertilized or not, it doesn’t matter. They give birth to two pups at a time.
When a shark is born, it’s completely independent. There aren’t any sharks that care for their young once they are born. Once the umbilical cord comes off, the baby sharks fend for themselves.
They exit the womb or the egg, fully able to hunt, swim, and hide. Baby sharks rely on natural instincts to survive.
You may also like: How Do Sharks Mate? It Might Surprise You
Which Sea Creatures Are Mammals?
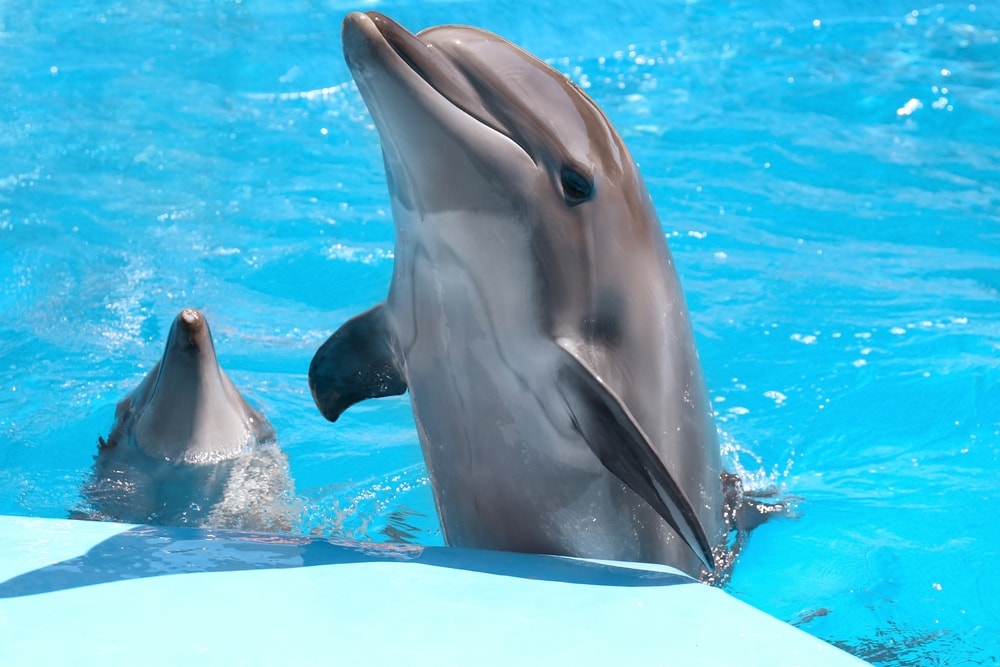

While most mammals today live on land, there are still mammals in our planet’s oceans, rivers, and lakes. Some are fully aquatic, while others are amphibious and often move between land and water.
Unlike fish, mammals don’t have gills to breathe underwater. They must return to the surface to breathe air like us.
Otters

Otters are a great example of an amphibious mammal. They’re incredibly well adapted for life in the ocean or along rivers. Despite this, they breathe air with their lungs, are warm-blooded, and are covered in fur.
Seals and Sea Lions
Seals and sea lions are almost completely aquatic. They can move on land but are usually fairly slow and awkward. Seals and sea lions swim amazingly, coming to the surface to breathe and resting on beaches.
Whales and Dolphins
All whales and dolphins are mammals. They have hair, breathe air, are warm-blooded, and produce milk for their offspring. While they never leave the water, they don’t need to. Whales actually still have bones in their bodies where their limbs and fingers used to be!
Manatees

Manatees fit in with seals and sea lions, but they’re fully aquatic. They prefer to stay in slow-moving water and feed almost exclusively on vegetation.
Polar Bears

Polar bears are also marine mammals. They spend most of their time living atop ice, not on land. They’re some of the largest bears in the world. Polar bears hunt by waiting on top of the ice for seals to surface to breathe. They then attack and eat the seals.
You may also like: 14 Of Our Favorite Ocean Animals Listed: A World Of Wonders
Shark Fun Facts


Sharks have very sensitive organs that let them sense other animals in the water. All life gives off faint electrical impulses. Sharks use their lateral line and special organs called the ampullae of Lorenzini to detect prey.

It’s a myth that sharks are always hungry. Many go for weeks without eating. Sharks only hunt when their body needs fuel. They aren’t bloodthirsty monsters or killing machines, despite what movies might have tried telling us.

Cartilage doesn’t fossilize the way bone does, at least not naturally. So how do we have shark fossils from millions of years ago? The answer is that we don’t have many. As sharks age, they deposit minerals in their cartilage that can help it fossilize. This mostly happens with the jaws.

Shark teeth are the one part of their body that will consistently fossilize. The only fossils we have of the famous megalodon sharks are their teeth and sometimes some of their vertebrae.

Most sharks aren’t dangerous to humans. Shark attacks are extremely rare, to the point that you’re more likely to be struck by lightning or killed by a cow than a shark. Some sharks are more dangerous than others, though. Great whites, bull sharks, tiger sharks, and nurse sharks are the most common ones that bite people.

Sharks can actually go into a trance when flipped upside down. This state is called tonic immobility. It’s a great tool for scientists to keep sharks calm when collecting data. It should be said, though, do not try to do this at home.
You may also like: How Do Whales Sleep? All About Their Surprising Ways To Slumber
Sharks FAQs

Why do people think sharks are mammals?
There are a couple of reasons why someone might mistakenly think sharks are mammals.
The first is that the majority of sharks give live birth. Many people think fitting that criteria automatically classifies sharks with mammals. But this is not true. Up to 40% of shark species also lay eggs.
It’s also possible that people lump sharks in with dolphins and orcas. This is because they have similar body shapes and sit near the top of their food chains. Unfortunately, a similar body shape does not make a shark a mammal.
Thanks to the general criteria for fish and mammals, it’s pretty clear that sharks fit in the fish category much better.
What makes a mammal a mammal?
The defining characteristics of mammals are:
1. Hair or fur on the body
2. Mammary glands to produce milk for offspring
3. Almost all give live birth
4. Most feed embryos with a placenta when in the womb
5. Mammals tend to be warm-blooded and able to burn energy to heat themselves
6. Many mammals have self-awareness, are intelligent, and have higher brain functions than other animals.
7. Three bones in their middle ear
8. A special region of the brain called a neocortex
Remember, there are always exceptions to these rules. Don’t think of them as hard-and-fast. Instead, use them as a general guide. Most mammals adhere to most of these, even if they ignore some.
What makes a fish a fish?
The defining characteristics of fish are:
1. Aquatic or marine animals
2. They use gills to breathe
3. They are vertebrates with a backbone and spine\
4. They lack limbs with digits, as in, they don’t have arms or legs with fingers or toes
5. Most fish are cold-blooded
6. They tend to be streamlined to swim faster
7. Most have scales and lay eggs
8. Keep in mind that there are exceptions to every one of those criteria. The term fish is a wide category, though most creatures residing inside of it adhere to a majority of them.













