Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Subsidence is the sinking of Earth’s surface, often caused by human activity such as groundwater removal, which negatively affects the environment, infrastructure, and economy.
- Groundwater pumping, removal of underground resources, and draining organic soils are common causes of subsidence.
- Effects of subsidence include reduced aquifer capacity, damaged infrastructure, changes in drainage and water systems, increased coastal flooding, and habitat deterioration.
- Notable areas affected by subsidence include Hampton Roads, the western U.S., and Jakarta, with the latter losing up to 9.8 inches (25 cm) of land surface yearly.
What is Subsidence?

Subsidence is the abrupt or gradual sinking of the Earth’s surface. Typically, human action is the cause. But groundwater removal is one of the biggest causes.
This natural disaster has many negative effects on the environment, infrastructure, and economy. It’s known to have a serious impact on many populated coastal areas. For instance, housing and other infrastructure can crack and even become unusable.
But this is often overlooked by other issues such as climate change. In fact, it’s a serious problem that leads to permanent damage around the world.
What Causes Subsidence?

Subsidence is mainly caused by human activity. But in some cases, it can also be influenced by natural disasters. Although the damage is permanent, sinking land can be avoided if properly monitored.
The most common cause of sinking land is the use of groundwater. Over 80% of land in the US is affected as a result of groundwater usage.
Removing other underground resources and draining organic soils are other notable causes.
Groundwater Pumping
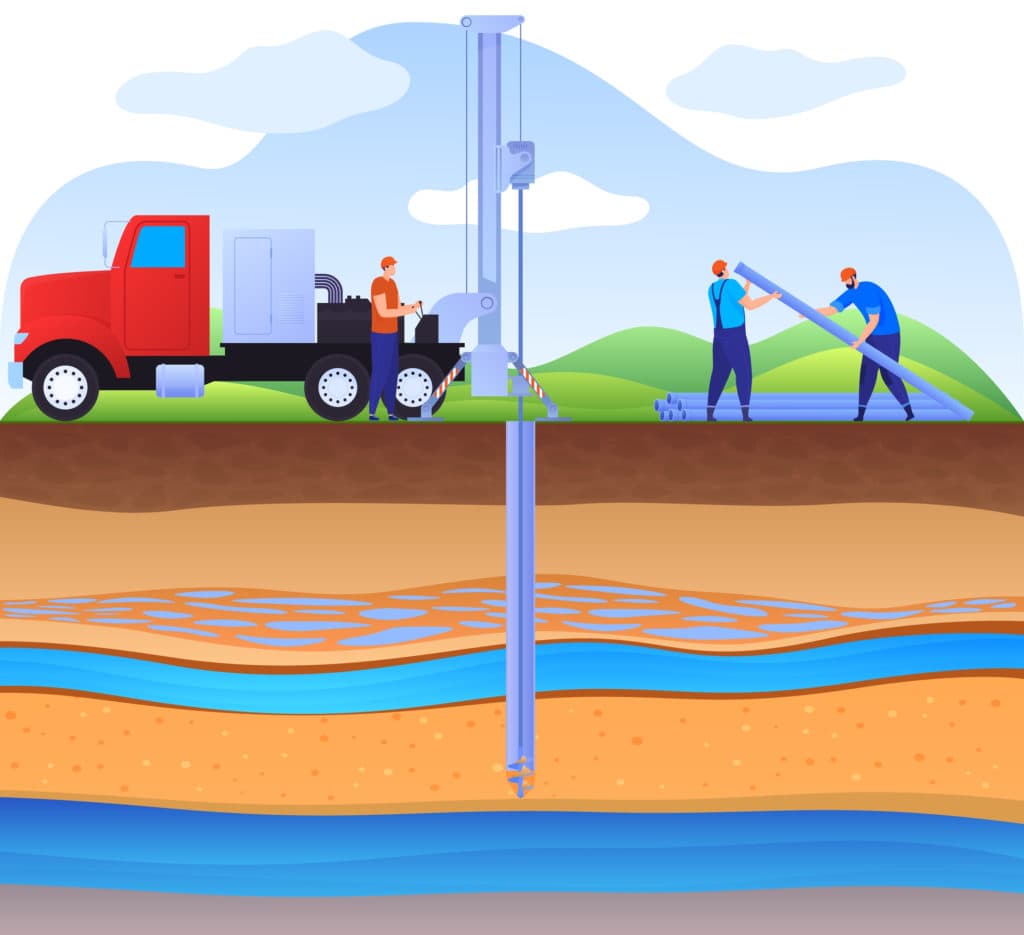

Groundwater is located beneath the water table boundary. The water table is the line that separates the unsaturated zone from the saturated zone. In the saturated zone, you can find groundwater, rocks, and sediment. This is called an aquifer.
Rocks and sediments help hold groundwater in place. When it rains, water is restored back into the saturated zone. But if groundwater is used faster than it can replenish itself, it can lead to subsidence.
Humans use groundwater for many different things. Some of the greatest uses for groundwater are drinking water and irrigation.
Overpumping of groundwater is common in heavily populated areas. The more people in one area, the more groundwater is used to meet the water demand.
Removal of Underground Resources
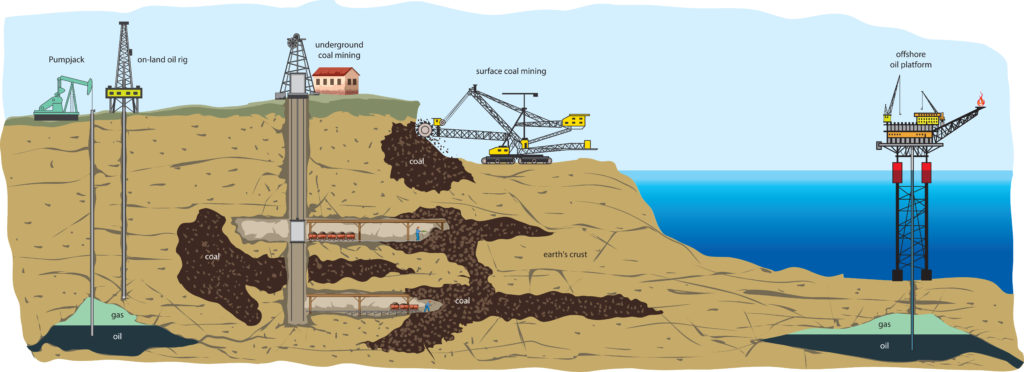
Upon removal, groundwater can cause the land to sink. Resources such as gas or oil also causes subsidence when removed from the ground.
Underground rocks and sediments compact when gas or oil is taken from reservoirs. This is often a result of mining activities. These activities can cause further harm when mines aren’t closed properly.
Draining Organic Soils

Organic soil is a type of soil that has higher amounts of organic matter. It has more than 50% organic matter compared to non-organic soil. Organic soil refers to soil types such as peat, muck, or bog.
This soil is found in swamp or wetland areas and drained for agricultural purposes. Since organic soils are very porous, this can cause them to compact when drained.
Compacted organic soil causes the land to sink. Another cause is oxidation. This is the imbalance between the accumulation and decomposition of plant matter.
Draining organic soils can also cause other harmful things besides subsidence. It releases carbon dioxide into the Earth’s atmosphere. Large amounts of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere highly contribute to climate change.

SHARE THIS IMAGE ON YOUR SITE
<a href="https://outforia.com/subsidence/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/subsidence-infographics.jpg"></a><br>subsidence <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>
You may also like: Man Vs Nature: Understanding What Causes Wildfires And How We Contribute
What Are the Effects?
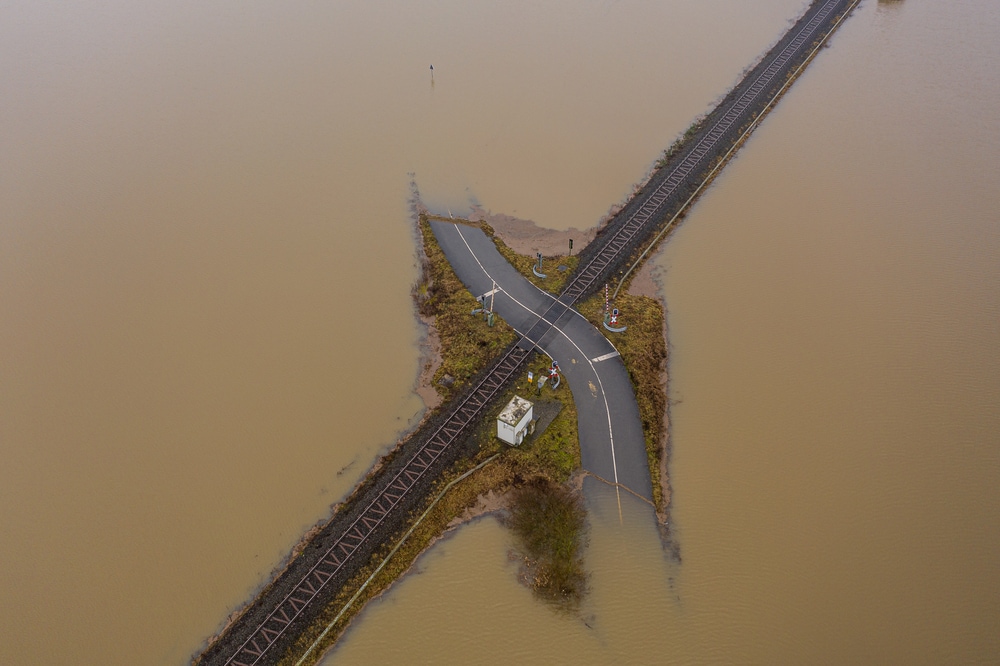

Subsidence has many social, environmental, and economic effects. For example, damaged infrastructure can have a negative economic impact. Sinking land can also affect the area’s quality of life.
It can even prevent aquifers from holding as much water. Unattended, this can greatly alter an area’s water systems.
Moreover, vulnerable regions can experience coastal flooding more often. In fact, entire coastal communities can sink due to this disaster.
Reduction of Aquifer Capacity
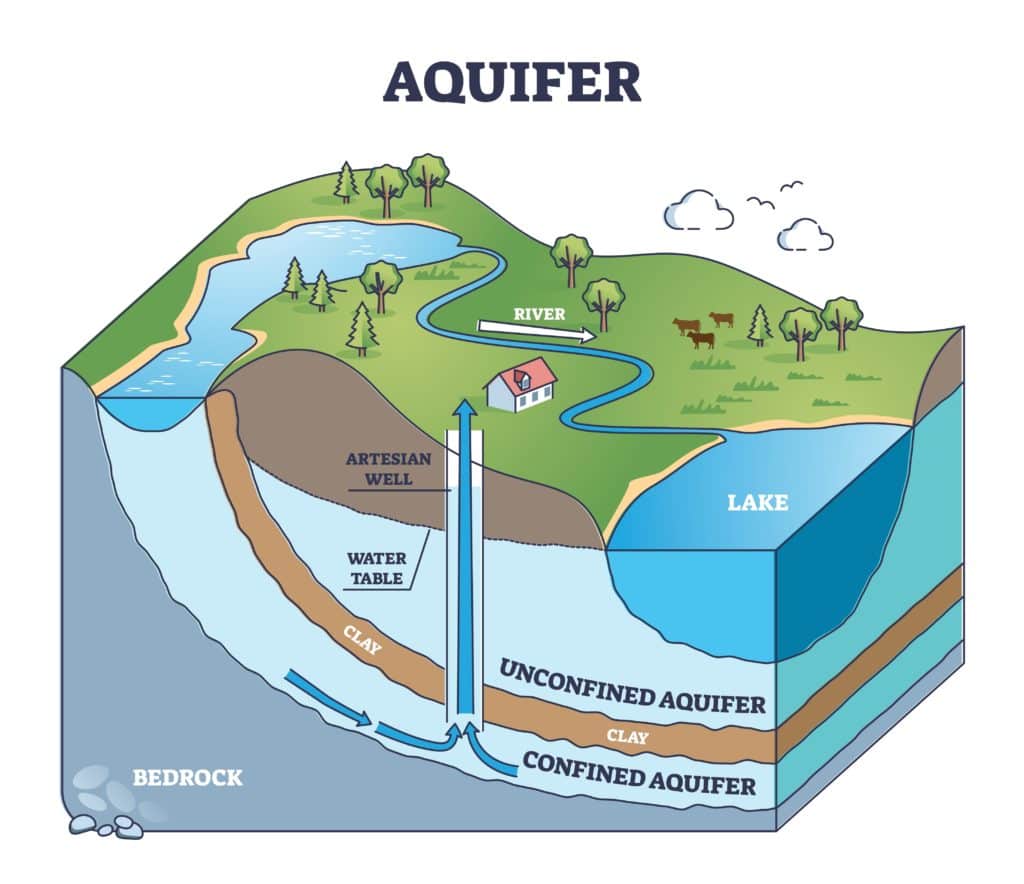
Subsidence affects the amount of water an aquifer can hold. Resources removed from reservoirs shrink the space between rocks and sediment.
An aquifer can’t hold much water when the spaces between rocks and sediments get smaller. If it can’t hold as much water, it’ll run out quicker when used. This can cause irreversible damage to an aquifer and an area’s water system.
Damage to Infrastructure
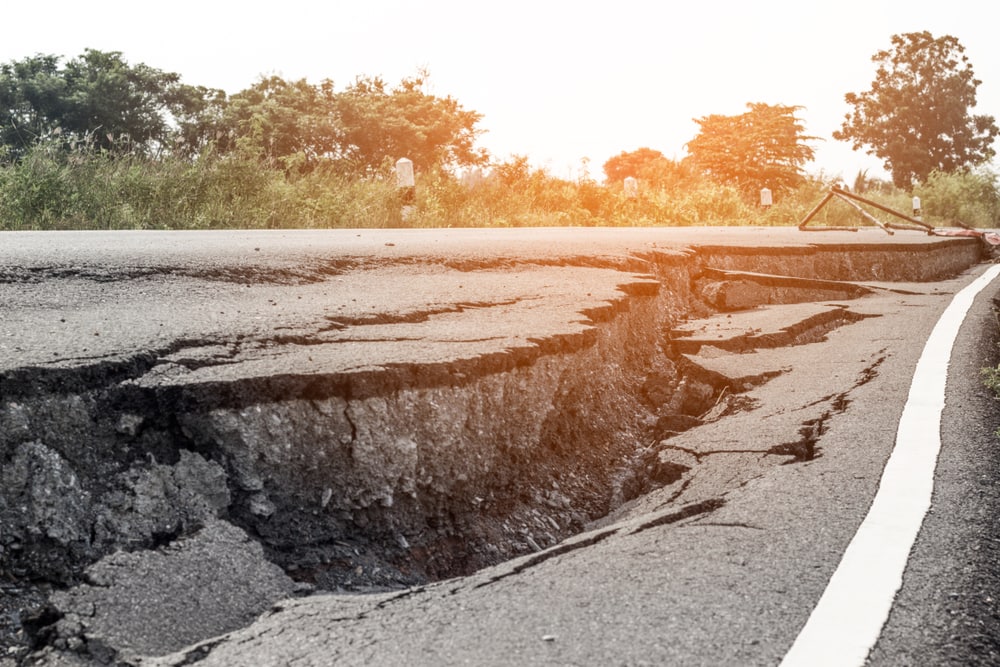

Subsidence can damage buildings, roads, and drainage systems.
Groundwater removal causes rocks and sediments beneath the water table to compact. This process is called aquifer compaction, which occurs in aquifers made of clay and silt.
Groundwater plays a key role in helping surface land stay together. When the saturated zone doesn’t have enough water, the land surface sinks.
When an aquifer loses more water than it takes in, it starts to shift.
As surface land moves around and changes, it damages infrastructure. Buildings tend to tilt due to the ground sinking beneath them. This can cause foundations to crack, and roads to be damaged.
Large-scale sinking affects the structure of entire communities or even regions. Frequent flooding causes structural damage to homes.
Coastal cities aren’t the only areas susceptible to major flooding. Inland areas also experience major floods because of subsidence.
Changes in Drainage and Water Systems
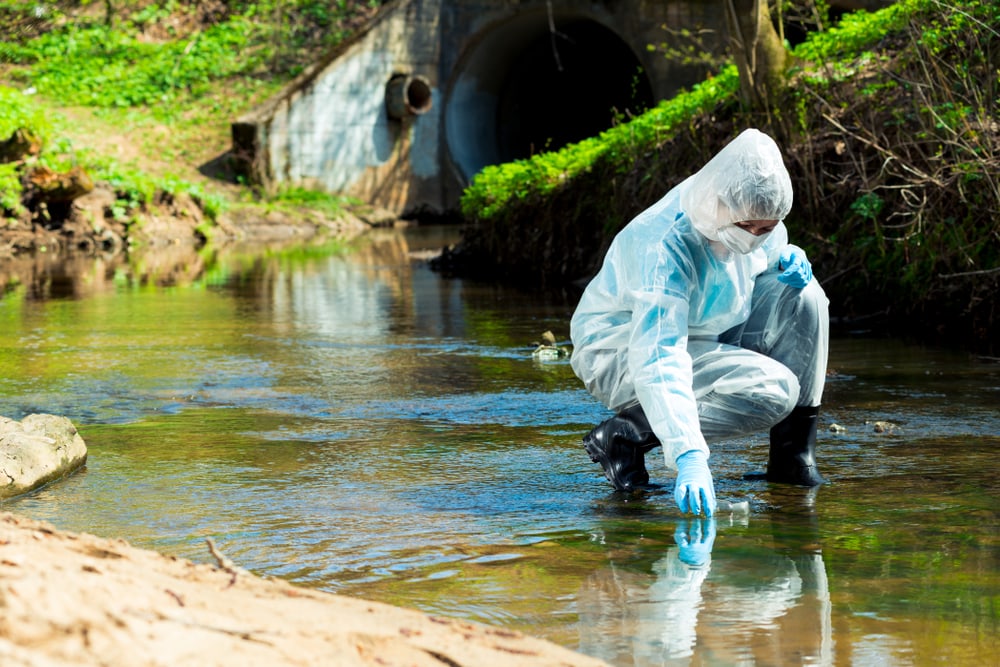

Excessive groundwater pumping can reduce water quality and flow. It increases the chances of contaminated water trickling down into deeper groundwater areas. This can cause drinking water to have harmful chemicals.
Other changes in a water system due to subsidence can include:
- Deterioration of ecosystems
- Changes in drainage flow
- Expansion of flood areas
When the land sinks, many coastal ecosystems are affected. Changes in the water system and coastal flooding can damage habitats. This can force local species out of their homes.
Subsidence also increases the possibility of inland flooding, which damages foundations and other infrastructure.
Increased Coastal Flooding
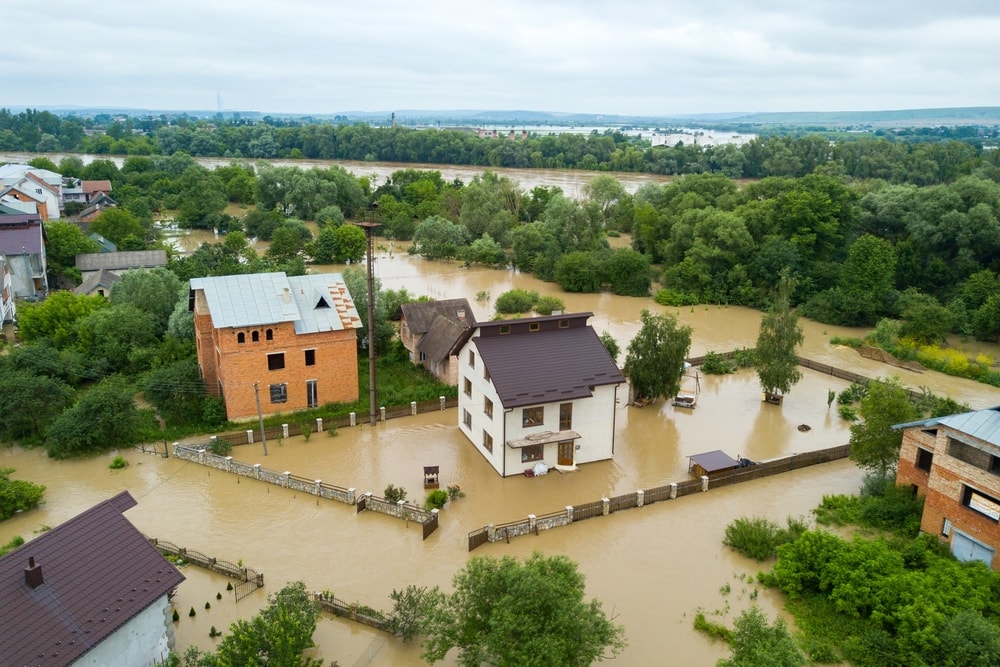

Coastal flooding can become more frequent during high tides when subsidence occurs. This can affect housing and other infrastructure that sits along a coast.
Global sea level rising also contributes to coastal flooding. Concerningly, sea levels have been rising for decades. Some regions experience rising sea levels and sinking lands more than others. It also causes many coastal cities to sink.
Some cities are discussing building sea walls to combat coastal flooding. But this doesn’t address the root of the issue, and can be very costly.
Habitat Deterioration

Coastal ecosystems are very vulnerable to subsidence. It also affects areas with increased inland flooding
Many animals and plants are unable to withstand major ecosystem and habitat changes. Flooding can harm or destroy wildlife habitats in the area. This forces some animals to move more inland or outside of their range.
Decreased water quality also harms wildlife. This is especially true if the waters are polluted with man-made chemicals.
You may also like: How Are Metamorphic Rocks Formed? (Full Explanation)
Records & History
Subsidence has affected over 17,000 square miles throughout the States. Many coastal areas or islands are harmed by this natural disaster across the globe.
Here are some major examples which took place in the U.S. and worldwide.
Hampton Roads
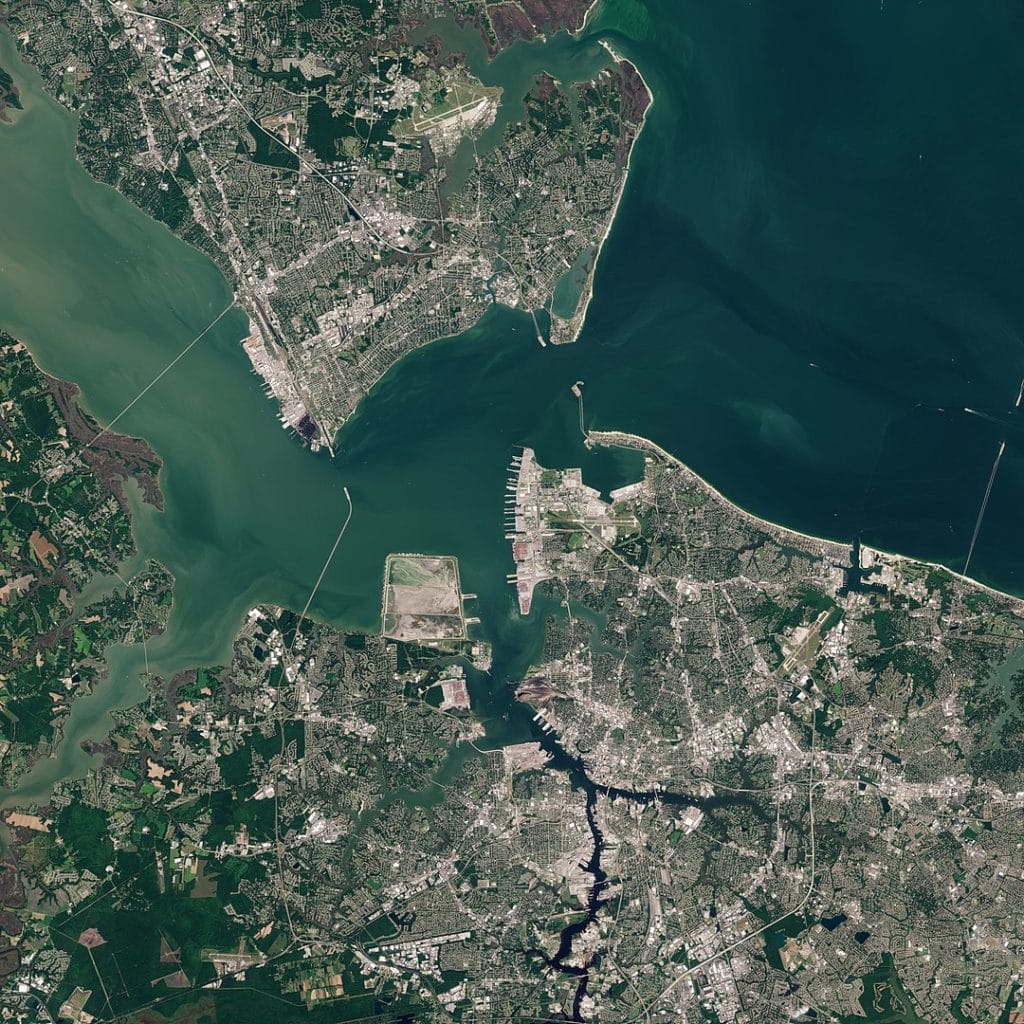

Copernicus Sentinel-2, ESA – https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home / CC BY-SA 3.0 igo / Wikimedia commons
Hampton Roads is a region in southeastern Virginia bordered by the Chesapeake Bay.
Many waterways travel throughout this coastal region. They then empty out into the Chesapeake and Atlantic Ocean.
The Hampton Roads is vulnerable to sinking land and sea level rising. The average amount of high tide flood days in the Hampton Roads region in 2022 was 10-15. Flood days are expected to increase significantly to 85 or more by 2050.
Old Dominion University studied the sinking of the Hampton Roads area. This was in partnership with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. They found that Norfolk and Virginia Beach sank at least 3.5 millimeters yearly.
Western U.S.

States in the southwestern and western portions of the U.S. are victim to subsidence. Clay and silt make up most of the region’s saturated zone.
As groundwater usage rises, the population in the western and southwestern regions grows. This allows fine-grained sediments to compact at a faster rate.
San Joaquin Valley is already experiencing the effects of groundwater overuse. Farming and decreases in surface-water availability have contributed to sinking lands.
Some areas in the San Joaquin Valley sank by more than 29 ft (8.5 m) between 1926 and 1970. California and other states in the west are susceptible to droughts. Groundwater usage and long droughts can cause the land surface to sink at dramatic rates.
Jakarta
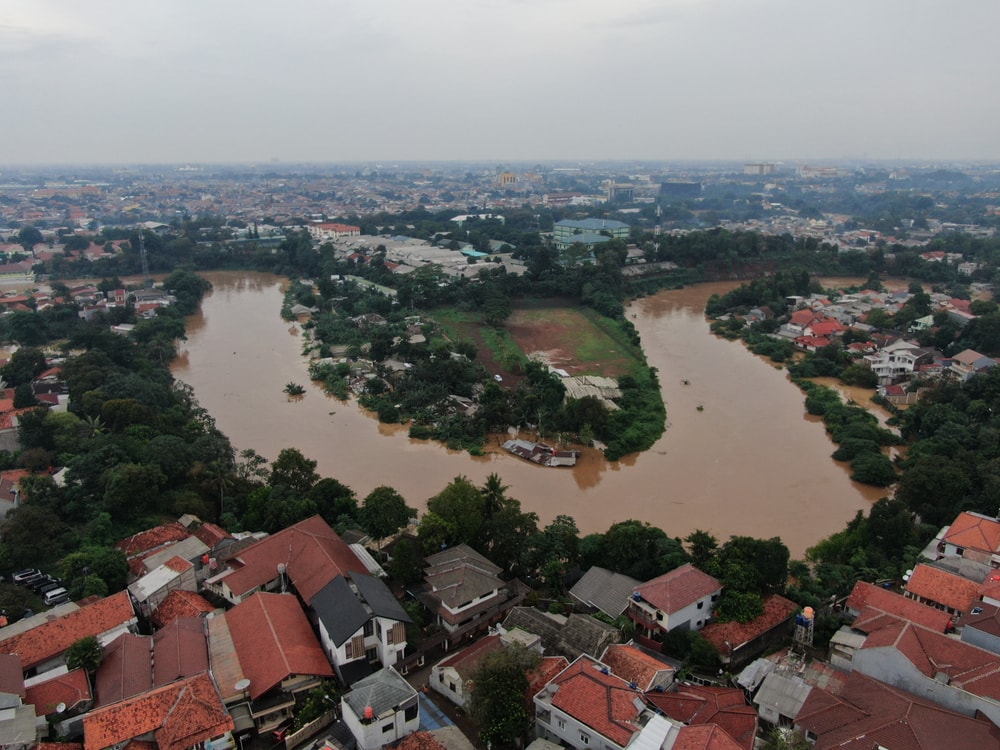

Jakarta is a metropolitan city and capital of Indonesia. It’s also one of the largest cities in the Southeast Asia region. It’s home to a little over 10 million people.
Due to its high population and groundwater usage, Jakarta is sinking at an alarming rate. It loses up to 9.8 inches (25 cm) of land surface yearly to subsidence.
Severe coastal flooding is causing costly damage to buildings and other infrastructure. Some portions of the city are expected to be underwater within the next century. For example, most of North Jakarta may be underwater within the next half-century.
You may also like: How Are Deltas Formed? Full Explanation With Examples
What Are the Common Signs?
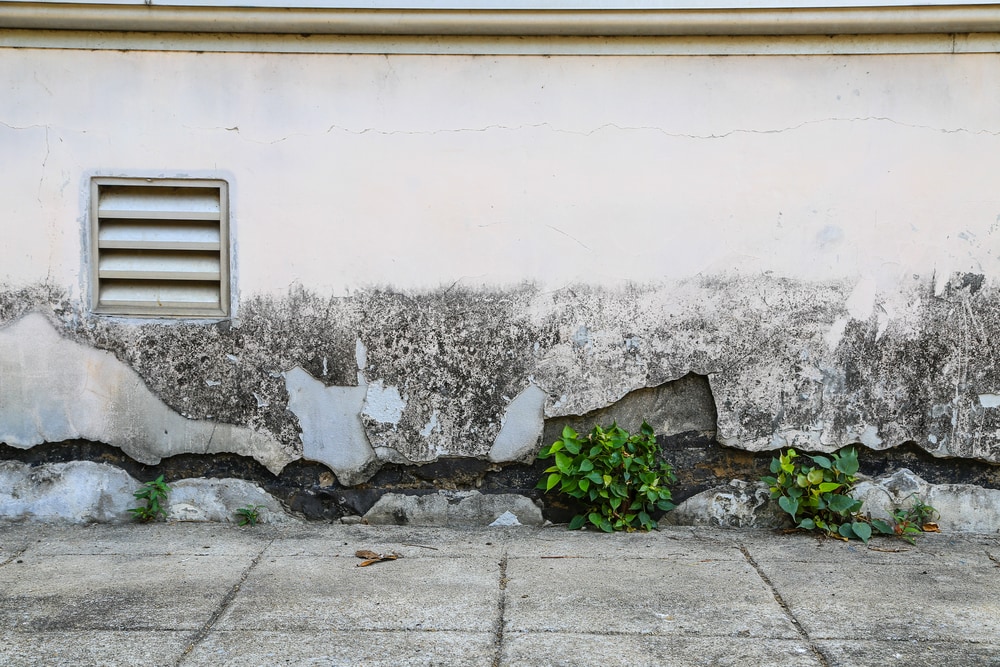

Signs of subsidence can be seen more easily in infrastructure. But when it occurs over large areas, it’s hard to identify.
The affected infrastructure may experience the following:
Though these are primary signs, they can also be caused by other things.
Large-scale signs aren’t as easy to detect. Still, you should look out for common signs in larger areas, which includes:
Signs of large-scale sinking are easier to track by monitoring areas. When monitored properly, prevention is proven to be more possible.
Subsidence Prevention

Because subsidence can’t be undone, avoidance is crucial.
To prevent it, small and big areas must be watched carefully. Spotting the main causes is the first step of prevention.
Aside from GPS surveys, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) is another reliable measuring tool. Using radar signals and satellites in orbit, it can measure changes in the land surface. Thanks to this system’s photographs, we can better grasp how Earth’s land evolves.
Preserving groundwater resources also counts as prevention. To achieve this, we need to reuse water and reduce groundwater pumping.
In agriculture, reusing surface water can help reduce excessive groundwater pumping. Lessening water usage around the house can also lessen groundwater use.
Artificial groundwater recharge is another method used to increase aquifer water levels. This can work because groundwater shifts from other areas to preserve healthy water levels.
What’s the Difference Between Sinkholes and Subsidence?
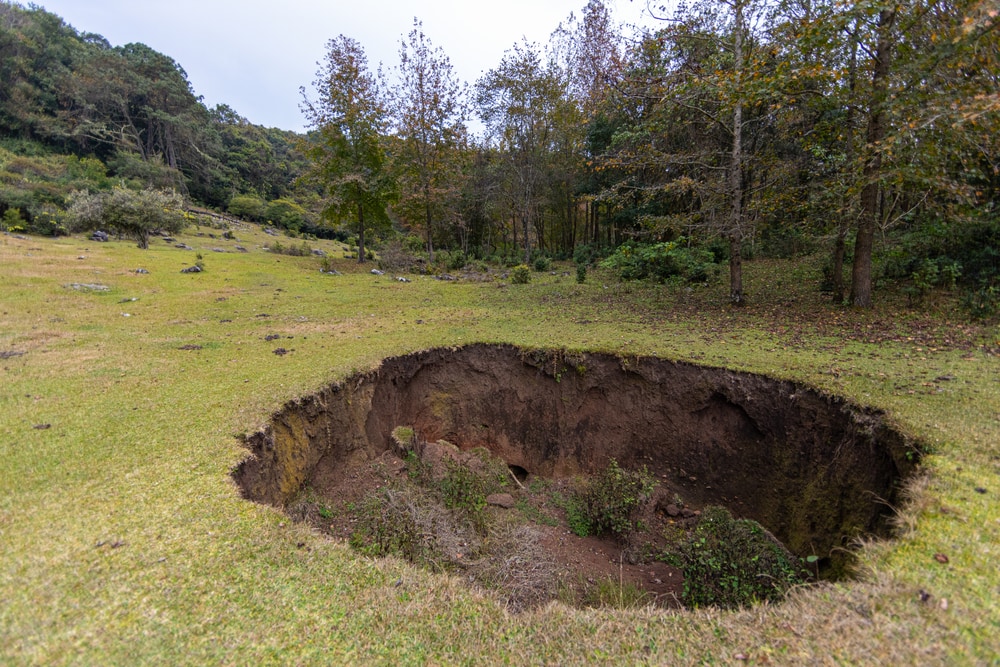

A sinkhole is a type of subsidence. It’s a sudden collapse of the land surface when the ground underneath can’t handle it. Sinkholes don’t have external surface drainage. This means it holds water, which is released in the unsaturated zone.
Sometimes sinkholes are difficult to notice until they collapse. They can be as small as a few feet or as big as hundreds of acres.
A variety of things can cause sinkholes to happen. They develop when groundwater naturally dissolves certain types of rocks. This includes salt beds, limestone, and carbonate rock.
When groundwater dissolves the rock, spaces form underneath. If the spaces get big enough, they may not be able to support the surface land.
The biggest difference between the two is that sinkholes are simply the collapse of land. On the other hand, subsidence is when land sinks. Although the two have many similarities, they’re not the same.
You may also like: 12 Types of Ecosystems and Why They’re Important
Subsidence Fun Facts
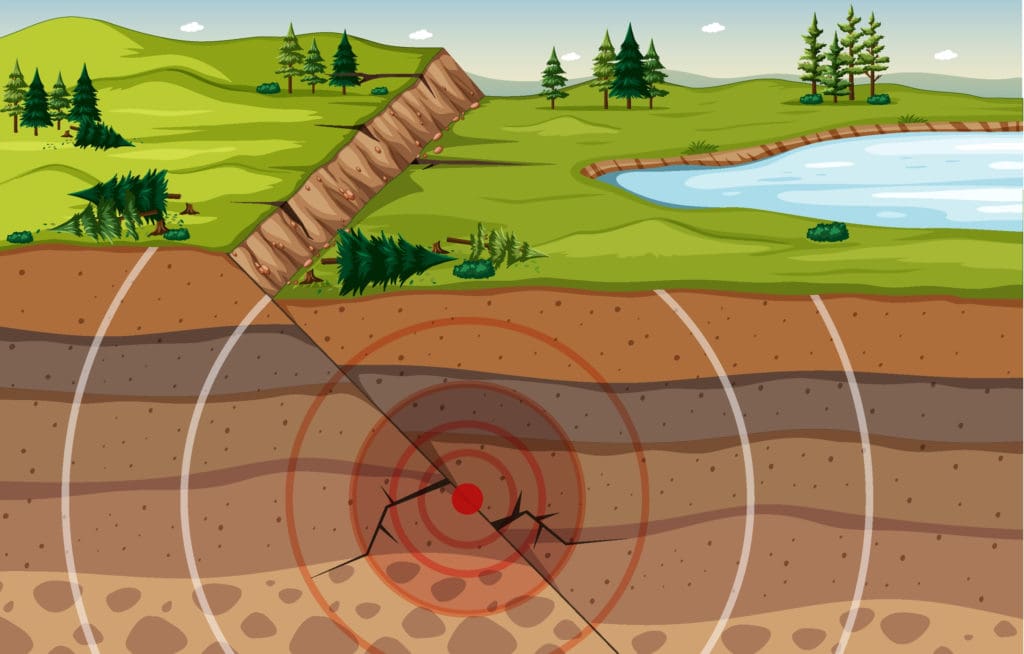
Earthquakes Can Cause Subsidence

Although human activity is the main cause behind subsidence, earthquakes can sink the land, too! This is due to rocks and sediments beneath the Earth being displaced during earthquakes. The changes underground can increase chances of subsidence occurring.
Urbanization Affects Subsidence

Urbanization is linked to subsidence because of population and the use of resources. As cities expand, more infrastructure is needed. Many metropolitan coastal cities struggle with subsidence as a result of urbanization.
Groundwater pumping increases when more people are using the water. Heavily populated cities risk subsidence when preventative measures are not taken.
Slow Subsidence is Sinking Venice

Slow subsidence is when water in the saturated zone is pushed out due to overlying weight. Venice, Italy is sinking due to the weight of the city and groundwater usage.
You may also like: What Is An Avalanche? Know The Conditions, Causes & Dangers
FAQ

What is the most well-known example of subsidence?
Jakarta, Indonesia is one of the most well-known cases of sinking land.
Rising sea levels and flooding during the monsoon season have harmed the city. These events, paired with groundwater usage, are causing the city to sink at rapid rates.
What happens if you ignore subsidence?
On a small scale, subsidence can cause costly damages to housing and infrastructure. Coastal cities and regions can end up underwater over long periods of time if subsidence is ignored.
What are the most common problems caused by subsidence?
Infrastructural issues and significant land changes are common subsidence problems. Land surface changes can lead to many other problems. These problems are mainly flooding and changes in the water system.









