Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Elephants are herbivores and eat vegetation like grasses, leaves, tree branches, bark, and fruit.
- African and Asian elephants have different diets based on their native habitats and available plant species.
- Elephants do not eat peanuts or meat; their teeth are designed for grinding plant matter.
- Elephants eat 200-600 pounds (91-272 kg) of food daily and spend 12-18 hours a day eating.
- Elephants do not get drunk from consuming fermented fruit; they would need an unrealistic large amount to become intoxicated.
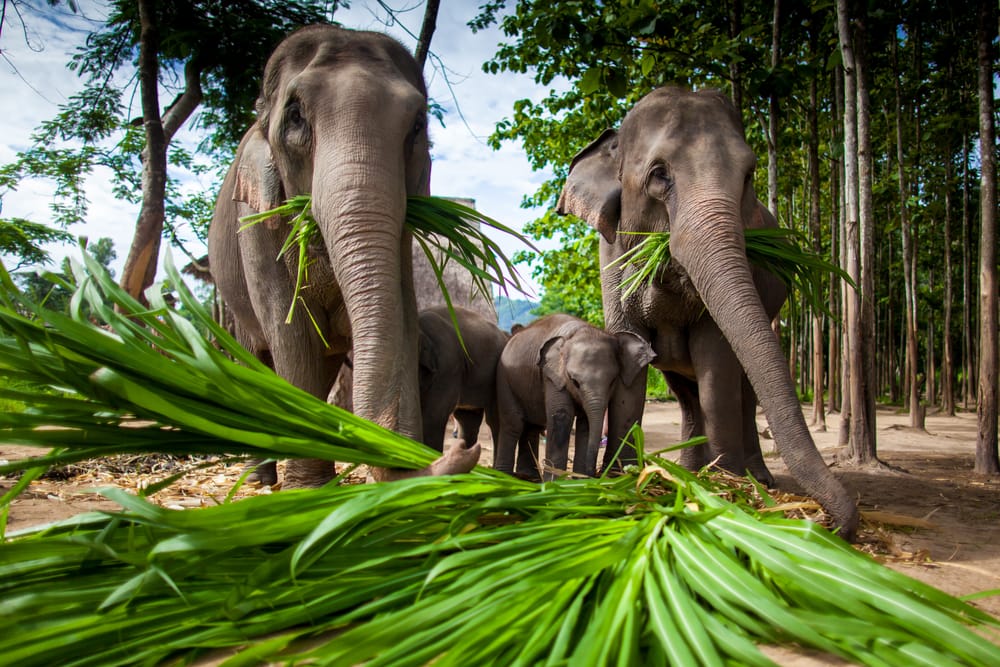

In captivity, most of an elephant’s diet is made up of hay. Some elephants are fed 100 pounds (45 kg) of hay a day or more, depending on their size.
You might be wondering, what do elephants eat in the wild? Elephants eat a wide variety of vegetation in the wild. This includes grasses, leaves, tree branches and bark, fruit, and other plant matter.
Elephants are strictly herbivores. They eat a wide variety of vegetation native to their range. Elephants have teeth in their mouths designed for mashing and grinding down vegetation. They don’t have canine teeth, which carnivores have for ripping apart meat.
What Are Elephants?
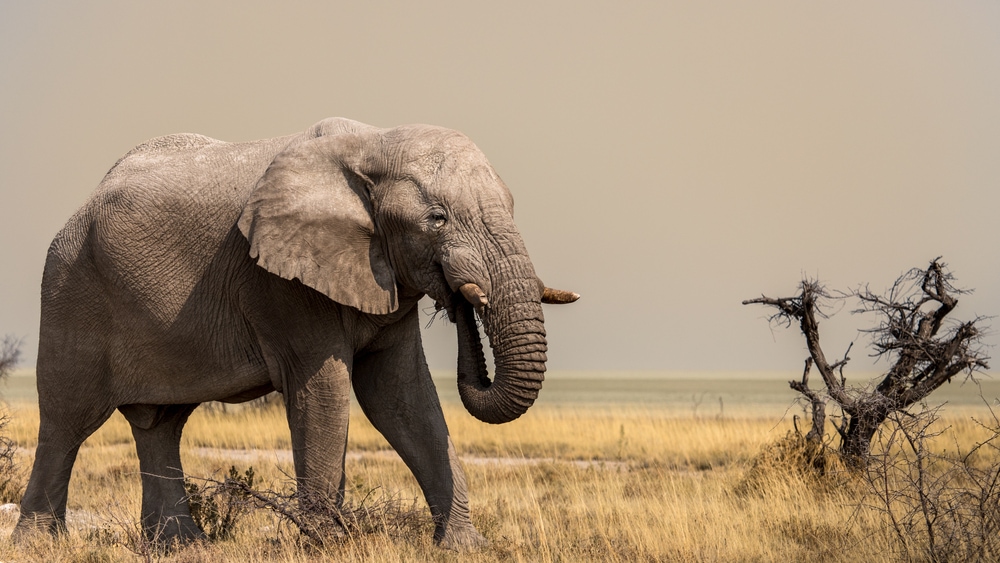

The elephant (Loxodonta) is the largest living land mammal on Earth. An elephant can weigh anywhere between 4,409 and 13,448 pounds (2,000 and 6,100 kg). That equals about 2-7 tons!
These large mammals have long trunks made of muscle that allow them to grab things. Their large ears help them regulate body heat and are also useful for hearing and communication.
Elephants have two tusks, which evolved from teeth. They use their trunks for various things, such as gathering food, digging, defending, and lifting objects.
Elephants belong to the superfamily Elephantoidea, which falls under the order Proboscidea. The superfamily includes elephants species and their closest extinct relatives.
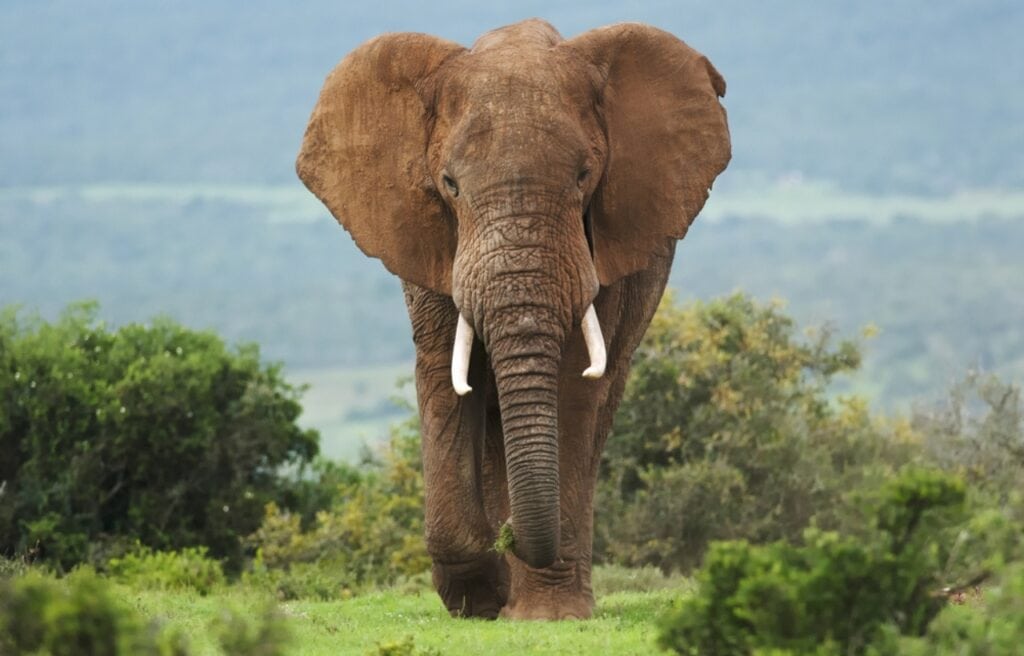
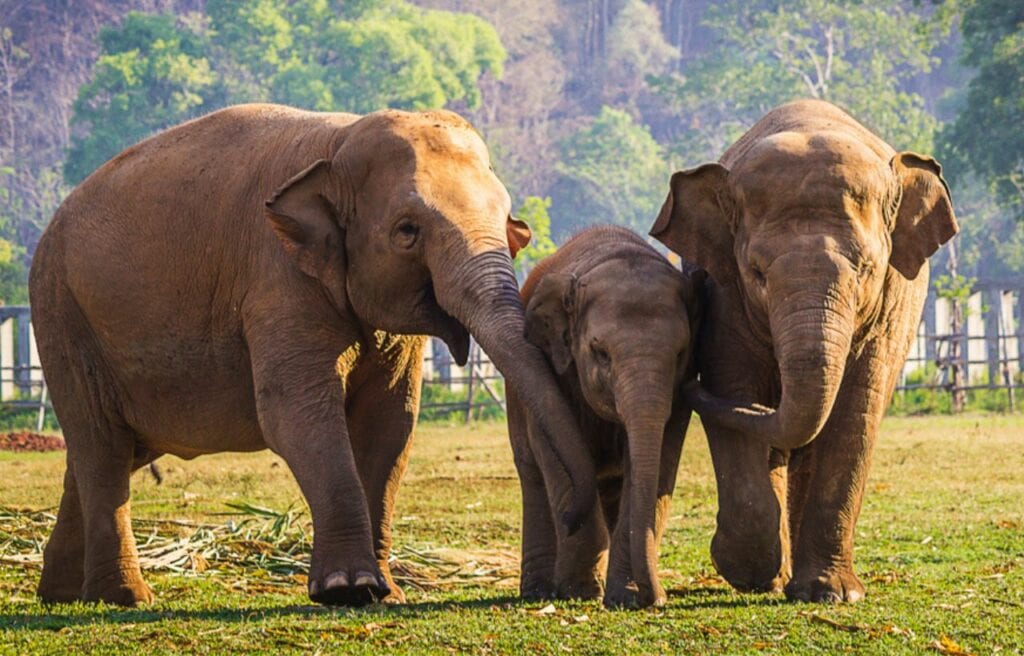


There are two main living elephant species recognized in the family Elephantidae. These species include the African elephant and the Asian elephant.
The two species of African elephants include the African bush elephant and the African forest elephant. The three subspecies of Asian elephants include the Indian, Sumatran, and Sri Lankan elephants.
Animals within the order Proboscidea appeared in Africa about 60 million years ago.
The modern elephants alive today share a common ancestor with woolly mammoths, which appeared during the Pleistocene Epoch. This is the period when the Ice Age began about 2.5 million years ago.
Modern elephants that roam the Earth today are native to Africa and Asia. African elephants are found in sub-Saharan Africa and the tropical forests of Central and West Africa. The range of Asian elephants includes 13 countries in South and Southeast Asia.

SHARE THIS IMAGE ON YOUR SITE
<a href="https://outforia.com/what-do-elephants-eat/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/what-do-elephants-eat-infographic-683x1024.jpg"></a><br>what do elephants eat <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>What Do Elephants Eat?
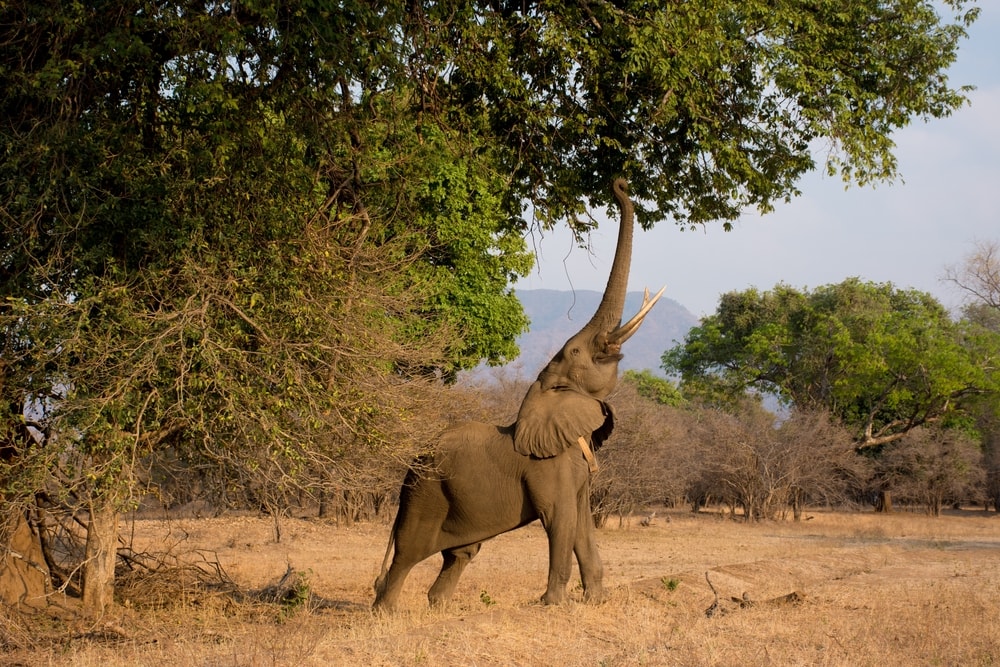

Elephants are herbivores. They’re foragers that spend most of their time eating grasses, leaves, fruits, bark, and tree foliage. They also enjoy eating bananas, sugarcane, and rice. The type of vegetation that an elephant eats depends upon where it lives.
The African bush elephant feeds on various savanna grasses and other vegetation in sub-Saharan Africa. The African forest elephant feeds on various tropical plants and trees in Central and West Africa.
Asian elephants feed on plants and trees native to their country and range. All elephants have an herbivorous diet. The specific type of food they eat ultimately depends on the country they live in and what food is naturally readily available to them.
Elephants use their long trunks to grab leaves and fruits and place them in their mouths. They also use their tusks to tear the bark off of trees to eat.
List of Food Elephants Eat
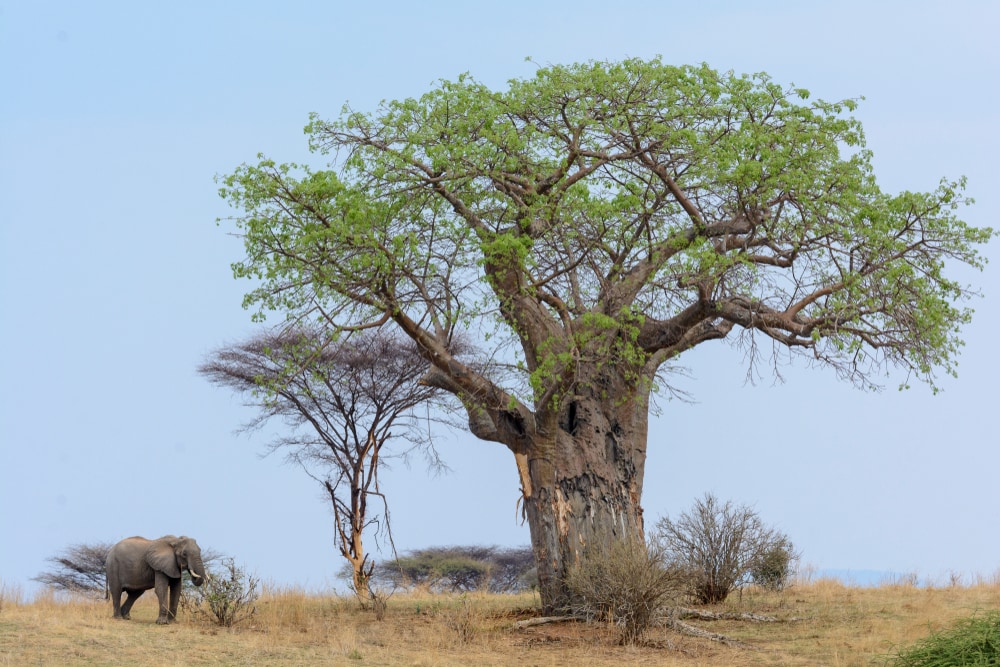

Trees are an important part of an elephant’s diet in the wild. African elephants enjoy eating a variety of trees, grasses, and shrubs in their native range. Some trees that African elephants favor in the wild include:
- Baobab trees (Adansonia digitata)
- Umbrella tree (Acacia tortilis)
- Sausage tree (Kigelia africana)
- Savanna grass
Baobab trees are a key food source for many animal species in Africa. These trees produce fruit and seed pods.
African elephants enjoy eating the spongy bark of baobab trees. The bark has a lot of moisture in it. This provides elephants with a water source, especially when migrating.
African elephants also eat fruit. This helps with seed dispersal. The baobab tree is also significant to the people of Africa. They can use various tree parts to make drinks and useful materials like baskets and cloth.
The Acacia tortilis, known as the umbrella tree, is a keystone tree species native to Africa. It can be found in arid ecosystems on the African continent and in the Middle East. It’s an important food source for African elephants and other animals. It promotes biodiversity and also helps with soil fertility.
Elephants eat the leaves of sausage trees found in tropical Africa. This tree produces a unique sausage-looking fruit that gives the tree its name.
The fruit of the sausage tree is a food source for some wildlife. However, it can be poisonous when it’s not ripe.
The Seneca Park Zoo in New York, US, says that their elephants favor a variety of maple trees and willow. They snack on the leaves, small branches, and bark.
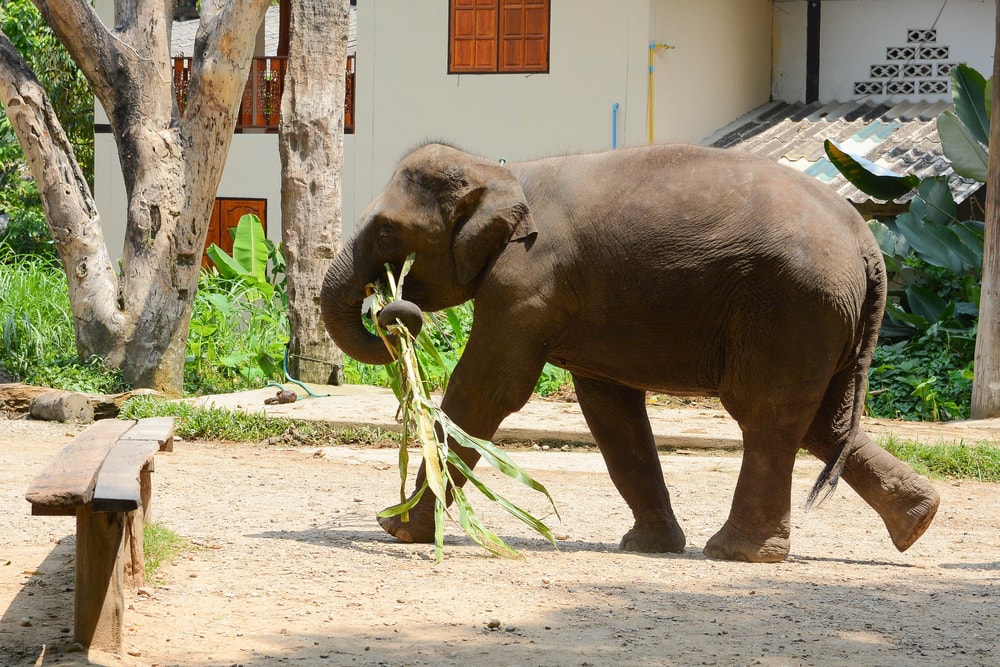

Asian elephants have similar diets to African elephants. Both species eat various trees and other vegetation. However, their diets differ because of where they live and the native plants available in their habitats.
Most of the Asian elephant diet in Nepal consists of the following plants:
- Bando lata (Spatholobus parviflorus)
- Wild sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum)
- Sal tree (Shorea robusta)
- Red kamala or kumkum tree (Mallotus philippensis)
- Garuga tree (Garuga pinnata)
A study conducted on the feeding preferences of Asian elephants in Nepal showed that they eat 57 species of plants. They eat 37 species of trees and 12 species of grasses. The rest of their diet consists of shrubs, climbing plants, and herbs.
The woody Bando lata plant takes up the largest portion of the Asian elephant diet in Nepal.
The second greatest portion of their diet is wild sugarcane. Browsing plants are an important part of Asian elephants’ diets during the dry season.
Various grasses are important food sources during the wet season. Asian elephants are considered grazers rather than browsers like their African elephant counterparts.
You may also like: 21+ Types Of Plants: From The Dinosaur Age To The Present (ID Guide, Pictures, And Facts)
Do Elephants Eat Peanuts?
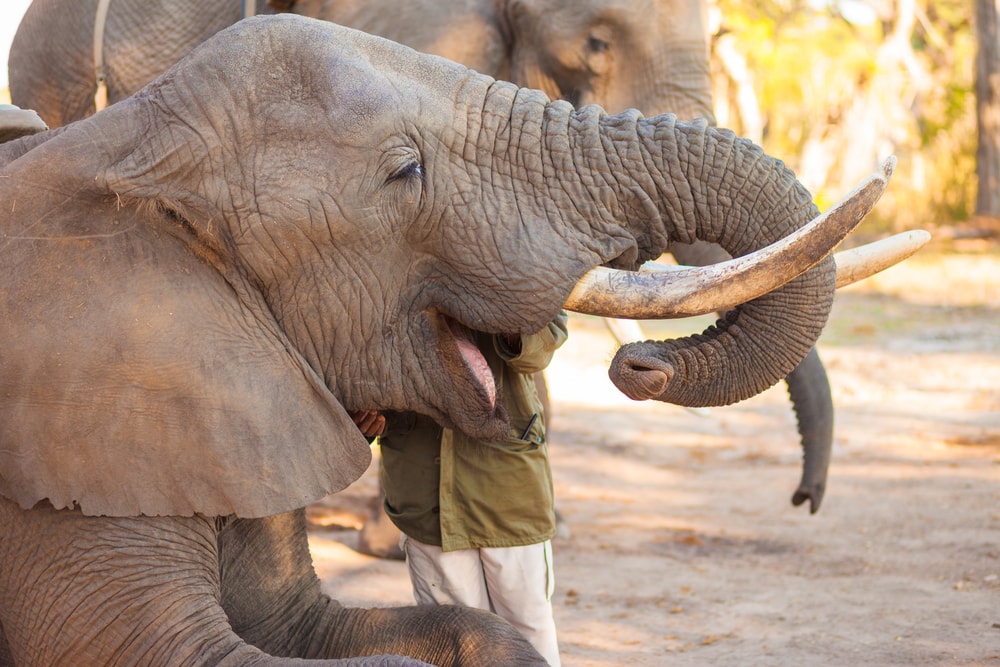

Contrary to popular belief, elephants don’t eat peanuts. It’s not a part of their diet in the wild, and it’s not a common food source for elephants in captivity.
The myth may have derived from elephants becoming a popular attraction in circuses and zoos in the 19th century. Visitors were given bags of peanuts to feed the animals. Thus, the myth of elephants being peanut lovers was born.
Do Elephants Ever Eat Meat?
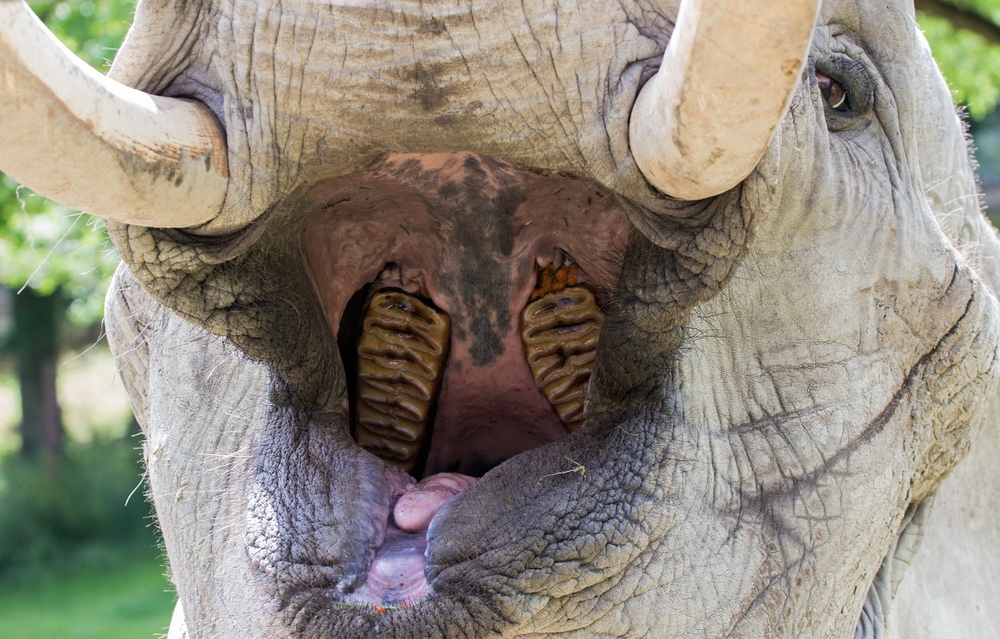
Elephants aren’t carnivorous or omnivorous. They have a strict herbivorous diet consisting of various types of vegetation.
An elephant’s large size makes it capable of killing other animals. However, they may only do so in defense or when competing for food against other animals, such as rhinos.
Aside from its tusks, an elephant only has molars inside its mouth. These teeth are flat and wide. They’re designed to help elephants grind down plant and tree matter. Their teeth aren’t designed to rip through flesh like the teeth of carnivores.
You may also like: How Long Do Elephants Live & How Humans Factor In
How Much Do Elephants Eat Every Day?
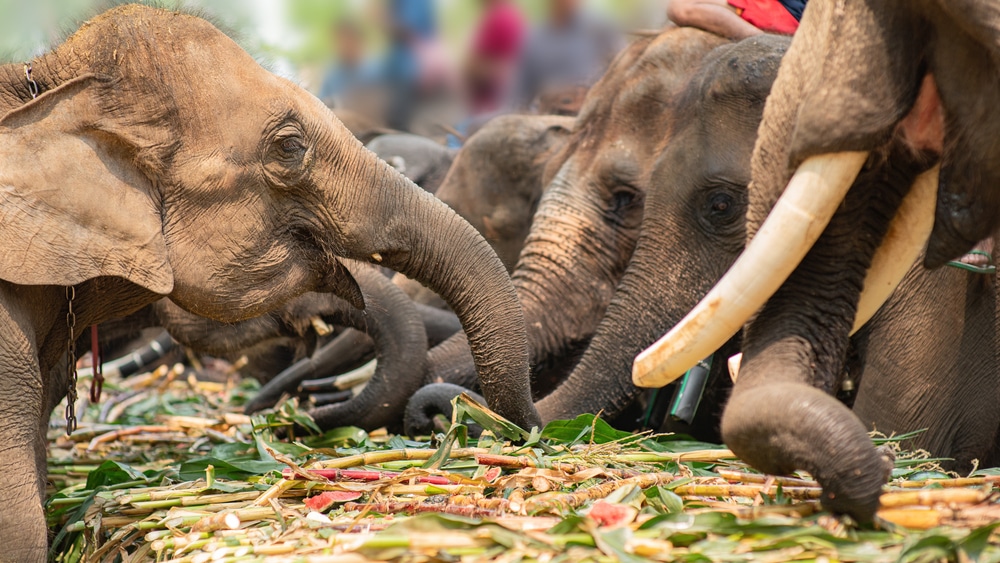

Elephants spend most of their day browsing for leaves, fruit, and tree bark or grazing on grasses. They can spend anywhere between 12-18 hours a day eating. Elephants eat approximately 200-600 pounds (91-272 kg) of food each day.
The Cleveland Metroparks Zoo says that their elephants eat 100-400 pounds (45-181 kg) of hay daily, depending on the elephant. If you’ve ever visited a zoo and seen elephants, you may have witnessed food being suspended high in the air.
The Saint Louis Zoo also feeds their elephants hay and other snacks. Zookeepers feed the elephants pellets for vitamins and minerals and fruits and veggies for special snacks. They also feed them trees and shrubs.
Elephants in zoos are often given food suspended in the air to mimic their natural feeding environment. This allows them to browse for their food as if they were browsing trees in the wild.
Why Do Elephants Eat So Much?
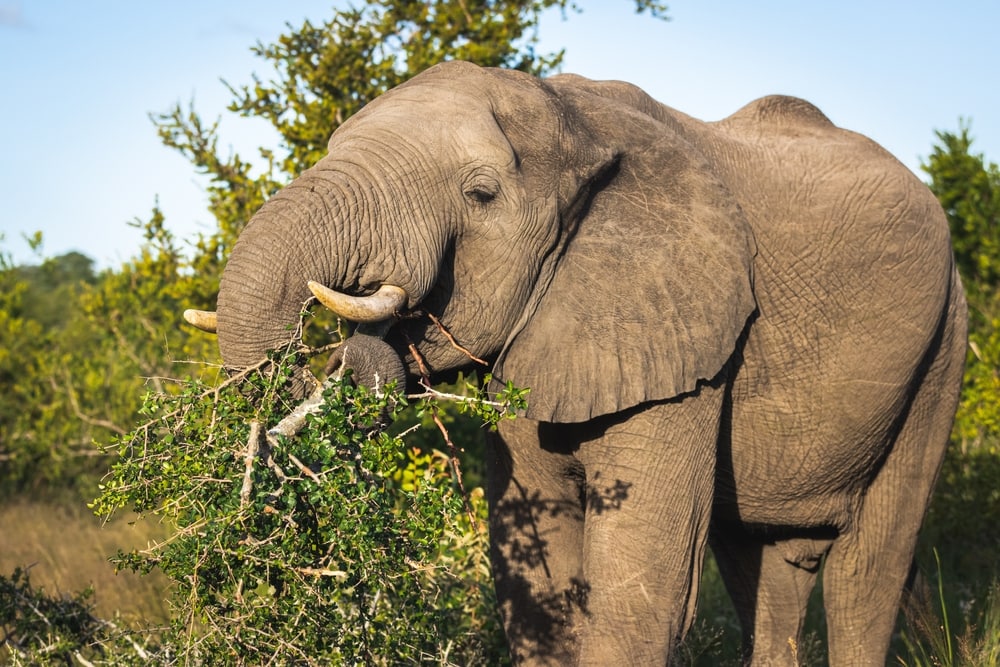

Elephants are large animals that weigh thousands of pounds. It takes a lot of vegetation for elephants to receive the proper nutrients they need to survive.
Wild and captive elephants don’t digest all of the food they eat. They only digest about 30-60% of what they eat, which means they eat a lot to get the necessary amount of nutrients. Wild elephants travel up to 12.4 miles (20 km) a day just to take in all the vegetation they need.
You may also like: 10 Types Of Habitats Around The World That Animals & Plants Call Home
Can Elephants Get Drunk?
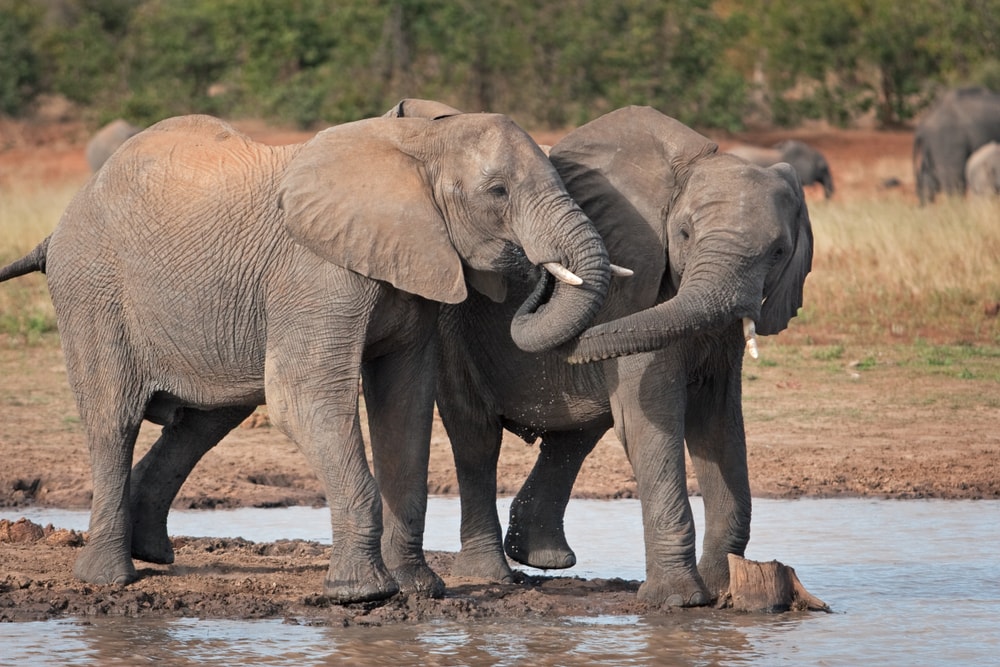

Whether elephants can get drunk or not is a debated topic. Some researchers suggest that elephants can get drunk because of their lack of the ADH7 gene. Humans have this gene, which allows us to metabolize ethanol pretty quickly.
A study conducted to determine genetic variations related to ethanol metabolism attempts to disprove that elephants may be able to get drunk from rotting fruit.
The study suggests that elephants and other mammals may be able to get drunk off fermenting fruits. This is because elephants lack the ADH7 gene to metabolize ethanol.
The main fruit that could get elephants drunk comes from the marula tree. Marula fruits are consumed by elephants and can be intoxicating when overripe. However, research suggests that elephants would need to consume a hefty amount of marula fruit to get drunk.
A study conducted by Steve Morris from the University of Bristol attempts to disprove the myth that elephants get drunk off fermented marula fruit. The average weight of humans and elephants was considered part of the study.
The metabolic rates of elephants versus humans were also considered. Additionally, the amount of ethanol in fermented marula was taken into account.

It was determined that elephants would need to consume 1.9 liters of pure ethanol to get drunk. This equals 27 liters of marula fruit juice. There is about 22 ml of juice in one marula fruit. Therefore, it would take about 1,500 fermented marula fruits to get an elephant drunk.
The amount of food that an elephant consumes in a day was considered. Based on the average amount of food an elephant eats in a day, elephants would likely only eat about 714 marulas in a day.
It should be noted that this number is also based on the assumption that an elephant only ate marulas for a day.
The number of marulas an elephant could consume in a day is significantly less than the amount it would take to cause intoxication. This means that it’s unlikely for elephants to become intoxicated through eating fermented marulas.
Elephants sometimes exhibit strange behaviors that may resemble intoxication. There are theories that this strange behavior could be caused by other things. For example, elephants eat beetle pupae living under the bark of marula trees.
The indigenous San people of southern Africa traditionally used these beetle pupae as poison for their arrow tips. Theories suggest the beetle pupae could be the cause of changes in elephant behaviors through consumption.
Based on the average diet of an elephant, it’s very unlikely that elephants get drunk by eating fermented marula. Further research may be needed to explore the topic to determine if elephants are capable of getting drunk due to their differing metabolic rate.
Conservation Status of Elephants

Elephants are considered a keystone species because they help the ecosystems they live in.
For example, African forest elephants use their tusks to dig in the ground to reach water. This creates watering holes that other animals, such as zebras, can drink from.
They also promote plant biodiversity. As elephants trample overgrown vegetation, it allows lower plants to grow because they can get sunlight.
The conservation status of elephants in the last few decades has been a concern. Illegal poaching and habitat loss pose a risk to African and Asian elephant populations.
Poachers go after elephants for their tusks. Elephant tusks are ivory. Ivory is considered a highly valuable item.
An international commercial trade ban was placed on ivory in 1989 by the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES). The ban was lifted for some African countries that exhibited healthy and well-managed African elephant populations.

In 2007, select African countries were given permission by CITES to take part in single sales of ivory. However, there were restrictions on how much ivory could be sold.
The legal sale of ivory comes from elephants who have died of natural causes. Yet, the illegal ivory trade still brings in around $1.44 billion a year.
African forest elephants were listed as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
African savanna elephants were listed as endangered. The Asian elephant population was last assessed in September 2019 as endangered. In 2016, there was an estimated global African elephant population of 415,000.
The estimated global Asian elephant population was between 48,000 and 52,000 individuals in 2018. India houses more than half of the global Asian elephant population. Some populations have become stabilized due to conservation efforts in certain areas.
You may also like: How Many Rhinos Are Left In The World Today?
Elephant Fun Facts


You can tell elephant species apart by their ears and trunks.
African elephants and Asian elephants can be distinguished by the appearance of their ears and trunks. African elephant ears are larger than the ears of Asian elephants.
African elephants have two prehensile fingers at the tips of their trunks. This allows them to firmly grasp things. Asian elephants only have one prehensile finger on the tip of their trunk.

Elephant trunks are super strong.
An elephant’s trunk contains around 40,000 muscles and about 150,000 muscle fascicles. It’s also one of the most sensitive organs that any mammal has. An elephant’s trunk can hold up to 8 liters of water. It can also help elephants breathe when they swim.

Elephants have protective skin.
Elephant skin is about 2.5 cm thick. This gives them extra protection. The wrinkles and folds in their skin also help retain water to cool down.
Elephants frequently take dust and mud baths to keep their skin clean and protect themselves from sunburn.

Elephants communicate in several ways.
You may have heard elephants make noise by letting out trumpet calls. This is just one way they communicate.
They also communicate through body language, touch, and scent. Elephants also use seismic signals. These signals are vibrations elephants create that other elephants can feel.

Elephants cannot grow their tusks back.
An elephant only has two tusks. It’s similar to adult teeth. If you lose or break one, it can’t grow back or be repaired naturally. Elephant tusks are teeth that can’t grow back or be repaired once removed or damaged. This is why ivory elephant tusks are considered highly valuable.

Elephants have a long gestation period.
Elephants have the longest gestation period out of any other mammal. The gestation period for Asian elephants is 18-22 months.
African elephants have a gestation period of about 22 months. Females only give birth to one baby every 4-5 years. This long reproductive process contributes to diminishing population issues.
Elephant FAQs

Do tigers eat elephants?
Elephants aren’t a typical part of a tiger’s diet. Only Asian elephants can be vulnerable to tigers because of where tigers live in the world. However, it’s uncommon for tigers to prey on Asian elephants.
Elephants are very large and wouldn’t be an easy target for tigers to take down. Baby elephants may be more vulnerable to tiger predation
What is an elephant’s favorite fruit?
Elephants love to snack on fruits. In captivity, elephants enjoy eating bananas, mangos, papayas, and watermelons. In the wild, elephants eat a variety of fruits found in the trees they eat.
How many stomachs does an elephant have?
An elephant only has one stomach. However, they have multiple chambers within their stomach. The different stomach chambers help elephants digest their high-fiber diet.
How do elephants drink?
Elephants drink water by using their trunks. However, they don’t consume water through their trunks like a straw. They suck up the water in the trunk and hold it. Then, they deliver the water from their trunk to their mouth.









