Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- The red-shanked douc is a diurnal Old World monkey, known for its vibrant colors and stark features unique to the species.
- It dwells in the Southeast Asian rainforests, particularly in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia.
- With a diverse diet of leaves, fruits, flowers, and seeds, these primates lead an arboreal lifestyle, skillfully navigating the treetops.
- Their lifespan can reach up to 25 years in the wild, although various factors such as habitat and diet can impact this.
- Despite their captivating appearance and intriguing lifestyle, the red-shanked douc finds itself critically endangered due to habitat loss, hunting, and the illegal pet trade.
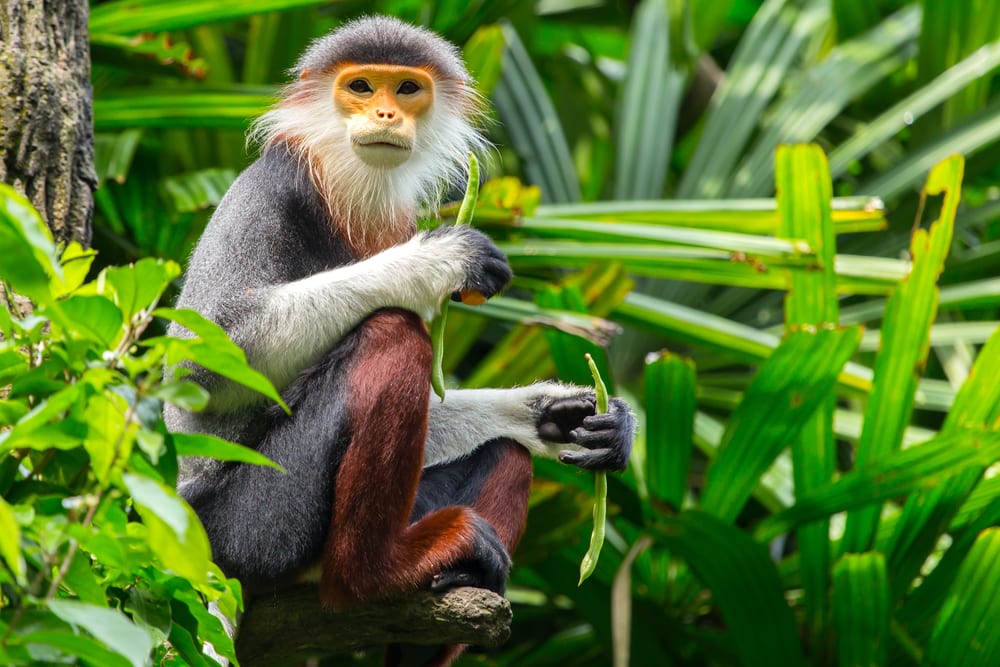
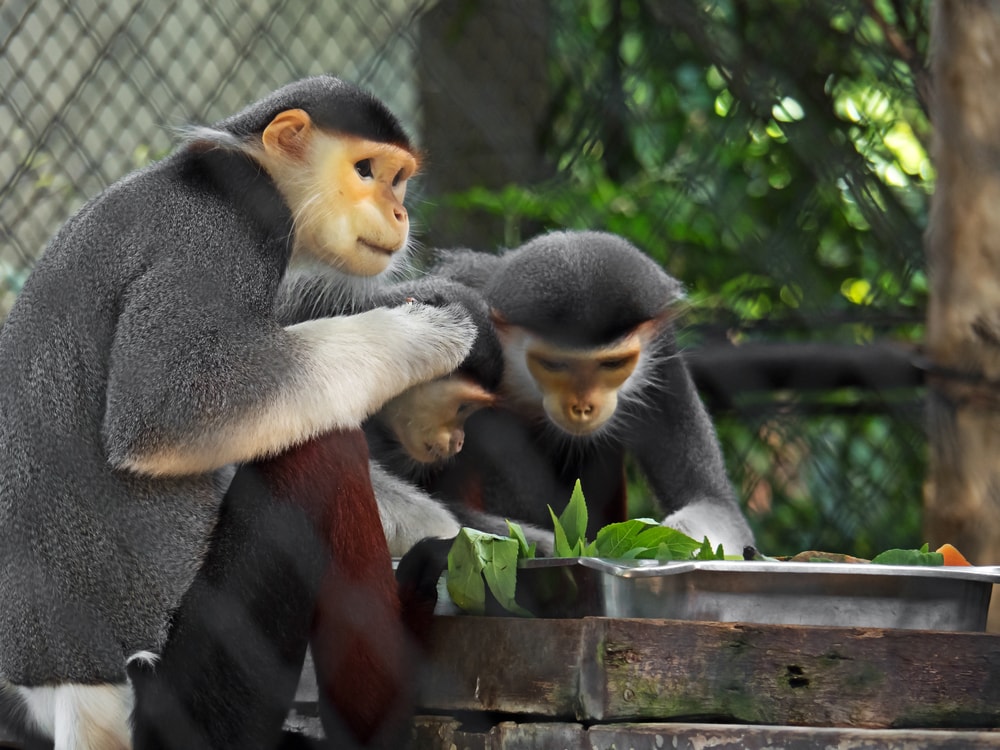
The red-shanked douc (Pygathrix nemaeus) is an Old World monkey that captivates onlookers with its bright red colors.
This rare and elusive primate is renowned for its acrobatic prowess. However, behind their vibrance is a vulnerability, as these creatures find themselves in the critical zone of endangered species.
So, what else should you know about this colorful creature?
Appearance and Physical Description
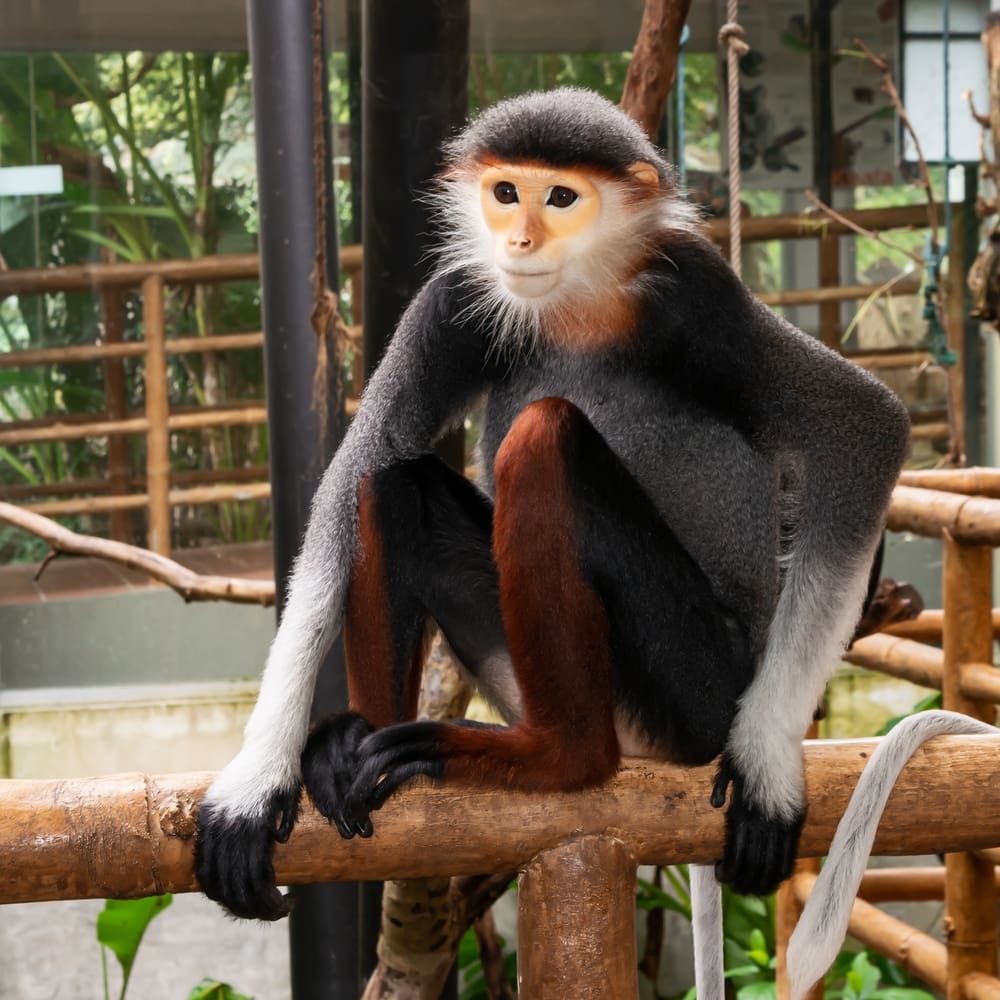

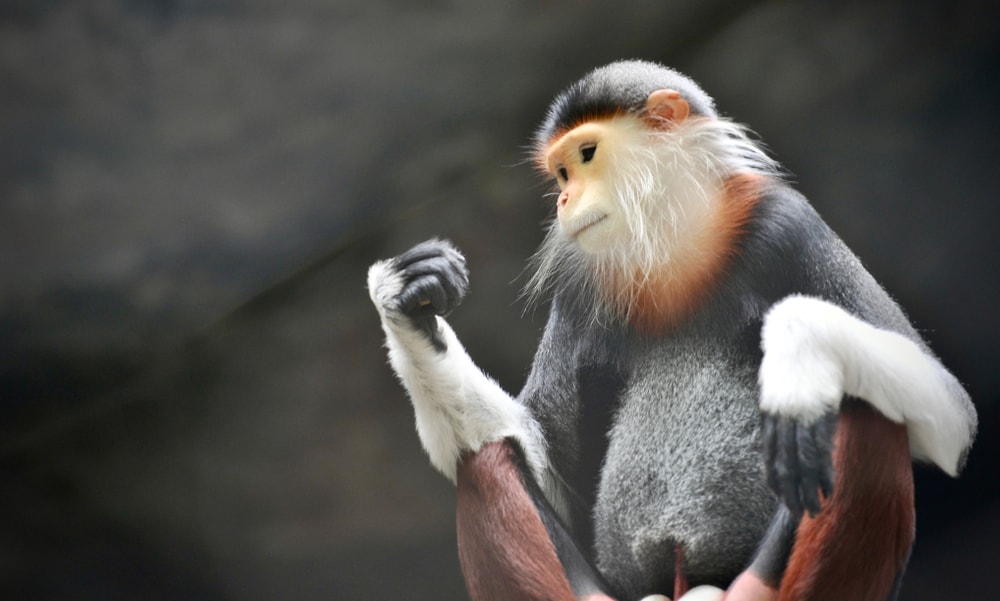
These monkeys bear a golden face, which is accentuated by orange hues on the nose and between the eyes. It has a white chin and dark hands and feet.
Distinct Features of the Red-Shanked Douc
It’s known for its vibrant, maroon-red “stockings” that run from its knees to its ankles, giving it an unmistakable look.
The patches around their eyes also exhibit a bright maroon shade, which stands in stark contrast to their dappled gray body.
In terms of size, the species exhibits sexual dimorphism. Males have a head and body length ranging from 22-32 in (55-82 cm) coupled with a tail that measures 22-29 in (56-74 cm) long.
Females, on the other hand, are slightly smaller, with a head and body length of 24-25 in (60-63 cm) and a tail measuring 17-24 in (44-60 cm) long.
Another noteworthy aspect of this species is its tail, which is long and white. They even have a distinctive white triangle of fur around the base of the tail.
Geographic Range and Distribution
This arboreal monkey species is native to Indochina. Their distribution ranges from Vietnam to Laos and Cambodia.
Biome and Climate Zones
The red-shanked douc thrives in tropical rainforests. These forests receive abundant rainfall and have stable temperatures throughout the year, providing an ideal environment for a variety of plant and animal species.
The dense foliage offers shelter and plenty of food sources for the douc, making this biome a perfect fit for their needs.
Habitat and Ecology
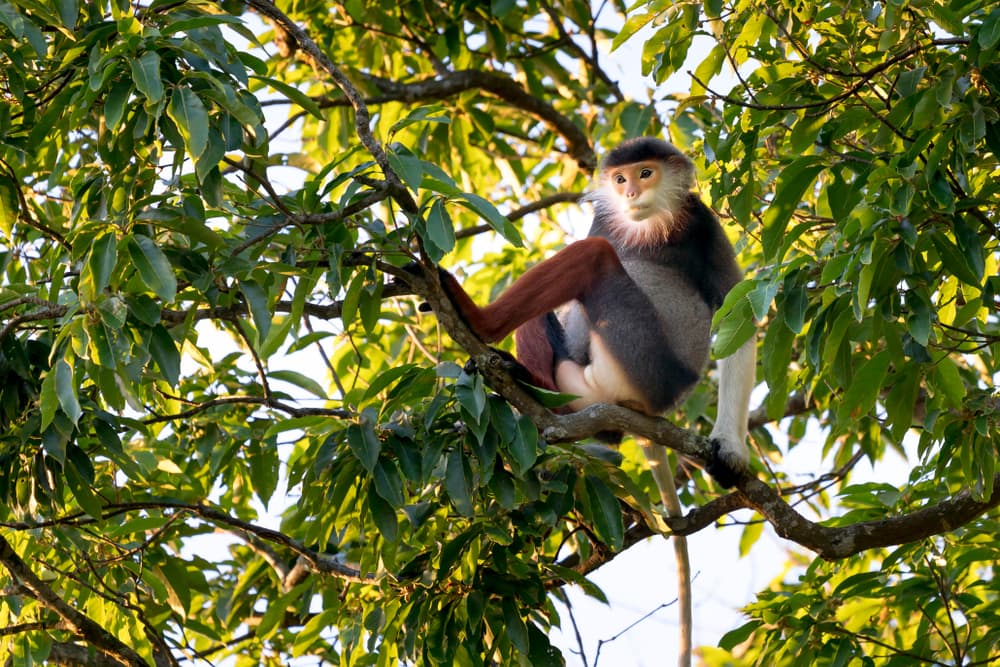

This species is found at a range of altitudes. They inhabit both primary and secondary forests, where they skillfully navigate the treetops in search of fruit, leaves, and flowers.
They thrive in the tropical rainforests of these countries, displaying impressive acrobatic skills as they traverse the treetops.
The availability of food and shelter has a significant impact on their habitat choice, ensuring their survival in lush environments.
Diet and Nutrition
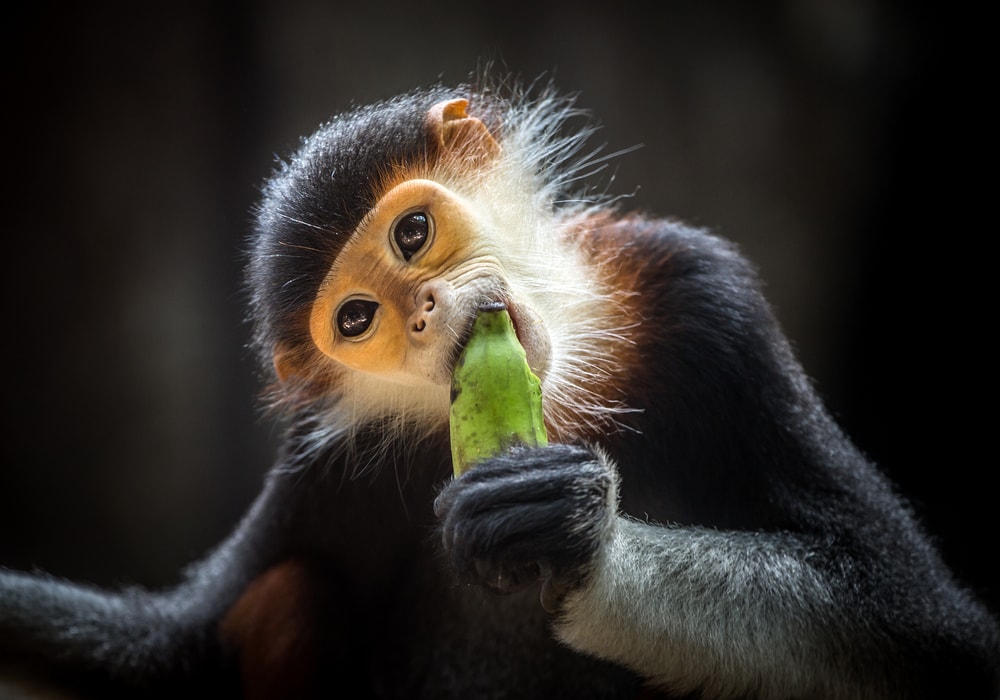

The red-shanked douc has a diverse diet, primarily consisting of leaves, fruits, buds, flowers, and seeds, making it both an herbivore and a folivore. When searching for food, you’ll often see these primates preferring young, tender leaves over older ones.
An important aspect of their diet is the high fiber content of the leaves they eat, which is vital for their digestive processes.
With the help of a four-chambered stomach, they can efficiently break down the fiber in their diet through bacterial fermentation, utilizing resident bacteria to extract nutrients and energy from their high-fiber diet.
Their diet may vary seasonally due to the availability of food sources. However, some common plant species that they have been observed to feed on include:
- Acacia pruinescens
- Ficus racemosa
- Millettia nigrescens Zanthoxylum avicennae, and
- Castanopsis ceratacantha.
This varied diet not only helps them meet their nutritional requirements but also assists in maintaining the health of their gastrointestinal system.
Behavior and Lifestyle
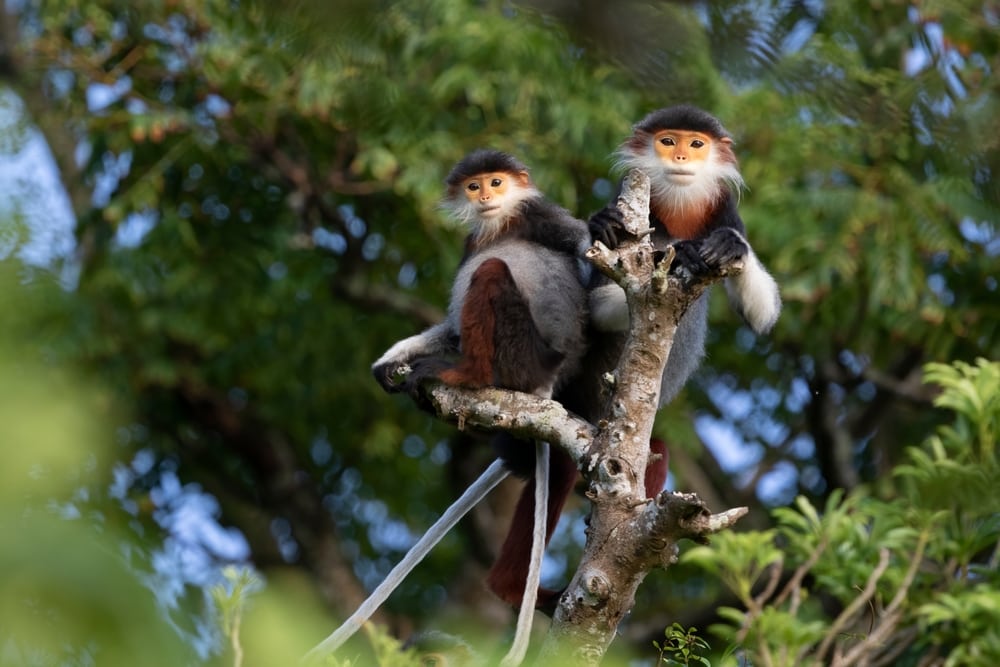

As diurnal animals, they are active during the daytime and rest at night.
These monkeys predominantly live in multi-male and multi-female groups, which can vary in size depending on their habitat and human disturbance. So far, the recorded group sizes are between 3 and 50 individuals.
In these social groups, communication and perception play a critical role. Doucs utilize a combination of vocalizations, gestures, and body postures to convey messages.
They establish a social hierarchy within their group, typically with a dominant male at the top. This dominance is essential for maintaining order and ensuring the group’s survival.
Fission-fusion and multilevel societies are two specific types of social structures that you might observe among this species.
Fission-fusion refers to a social structure where groups frequently split and merge, often based on the availability of resources.
Multilevel societies consist of several smaller subgroups or units within a larger group, allowing for more complex social relationships and dynamics.
Reproduction and Mating Habits
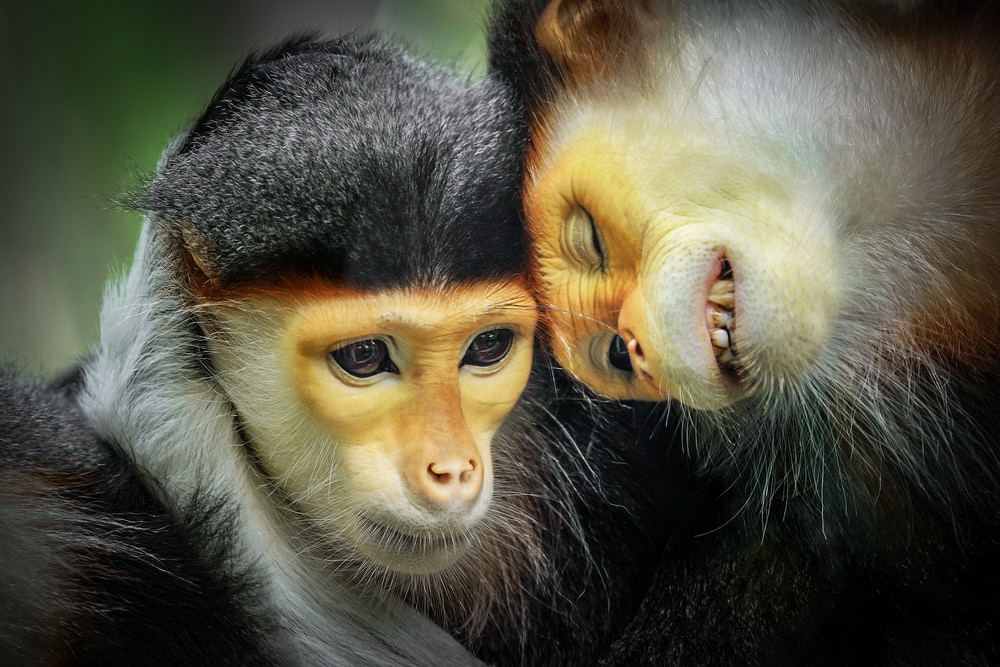

This particular species exhibits unique reproductive and mating habits. During mating season, which happens from, they engage in courtship displays.
Females are receptive to mating when they reach four years of age, while males become ready between four and five years old.
For these Old World monkeys, the mating process begins with a display of communication. They drop their jaws, wave their eyebrows, and shake their heads at each other.
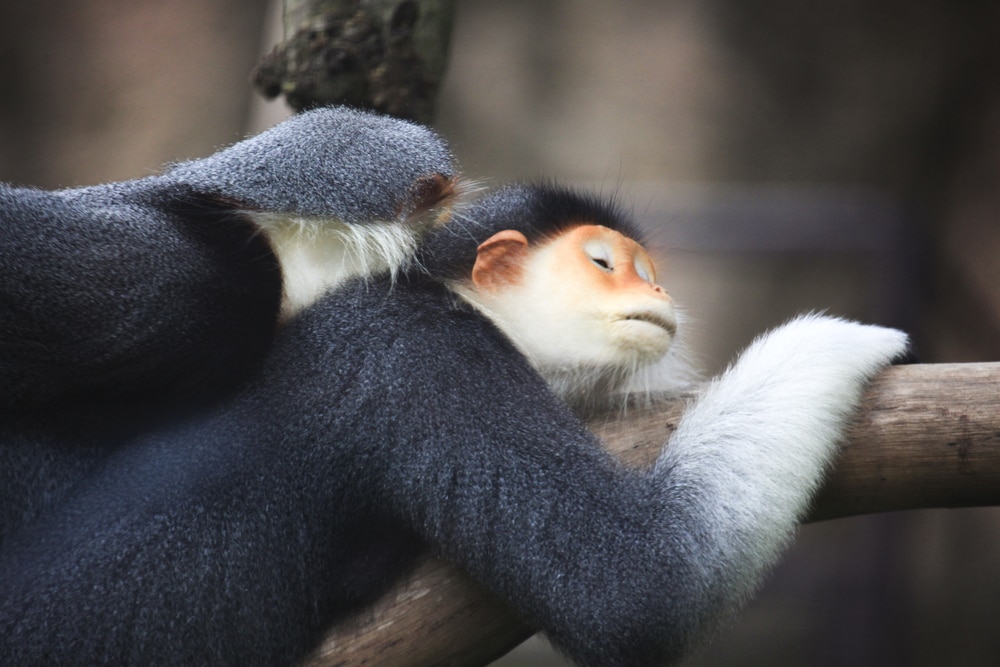

Interestingly, it’s usually the female that makes the first move. This unique characteristic sets them apart from many other animal species, where the male typically initiates the courtship ritual.
Once the mating process is successful, a single offspring is born after a gestation period. The parental care and upbringing of the young monkey then play a significant role in its growth and development.
Lifespan of the Red-Shanked Douc
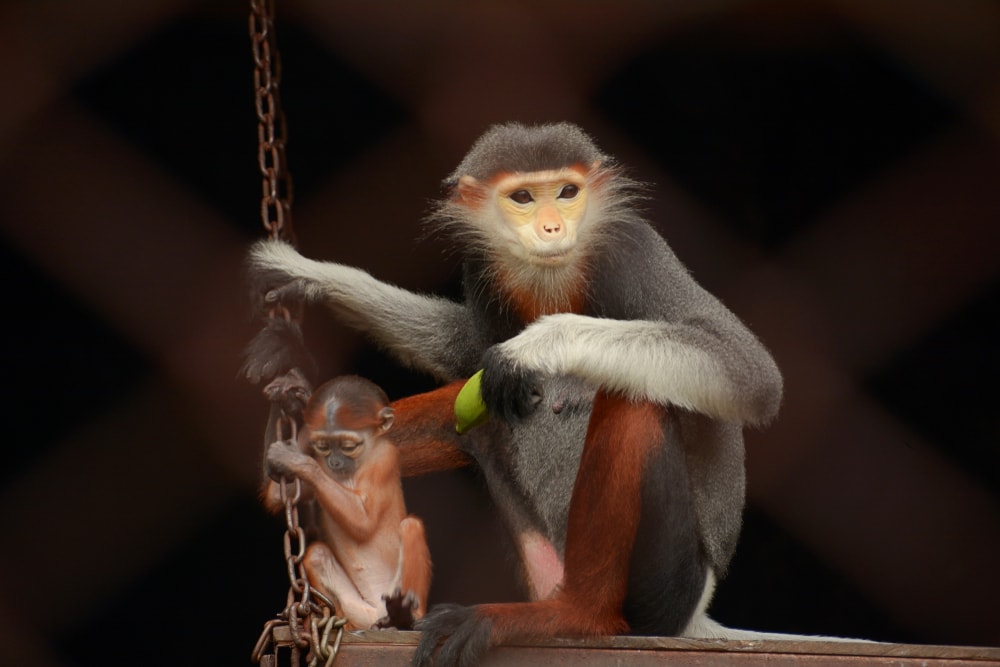

Interestingly, their lifespan is relatively long for a monkey. In the wild, these Old World monkeys typically live up to 25 years. However, note that various factors can impact their longevity, such as habitat, diet, and reproductive success.
By consuming a varied diet, they can effectively meet their nutritional needs to sustain a healthy and long life.
Furthermore, their social behaviors and gregarious nature contribute to their survival. They actively engage in grooming and connecting with their group members, boosting their immunity and improving their overall well-being.
While their lifespan may be extended in captivity due to controlled environments, conservation efforts focus on protecting these creatures in the wild.
Population Status
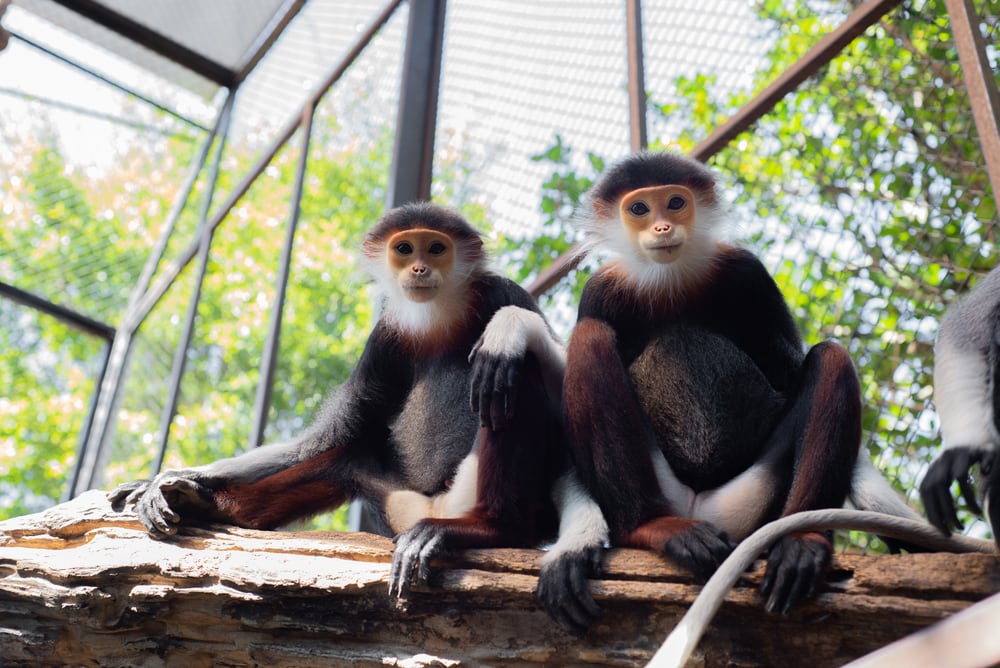

A significant part of the red-shanked douc population can be found in Laos. It’s where the Nakai-Nam Theun National Protected Area is home to approximately 4,420 groups of this species, followed by the Hin Namno National Protected Area.
Unfortunately, exact population numbers are still unknown, adding to the challenge of assessing their overall status.
Similarly, the other two douc species, black-shanked douc (Pygathix nigripes) and gray-shanked douc (Pygathix cinereus), are also experiencing a decline in population numbers. They are currently listed as endangered and critically endangered, respectively.
You may also like: The 7 Smallest Monkeys in the World: Pictures + Facts
Ecological Niches and Their Importance
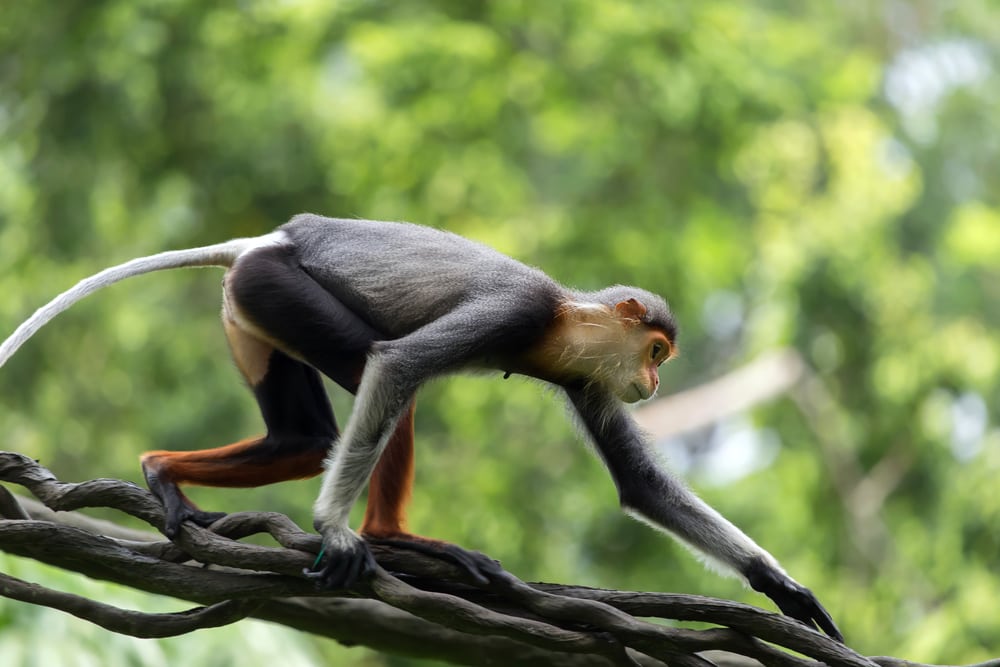

In this context, the term ecological niche refers to the unique role that a species plays within its environment.
As these monkeys inhabit specific geographic locations, they help balance the ecosystems in which they live.
They contribute to maintaining a stable ecosystem by consuming certain plants and fruits and dispersing seeds. In turn, this promotes natural growth and regeneration, preserving the region’s biodiversity.
Thus, preserving this species becomes vital not only for the health of their local ecosystems but also for the overall biodiversity in its native countries.
As an integral part of their native ecosystems, losing the red-shanked douc could cause a domino effect, ultimately impacting a wide range of other species that rely on the same environment for their survival.
Threats to the Red-Shanked Douc
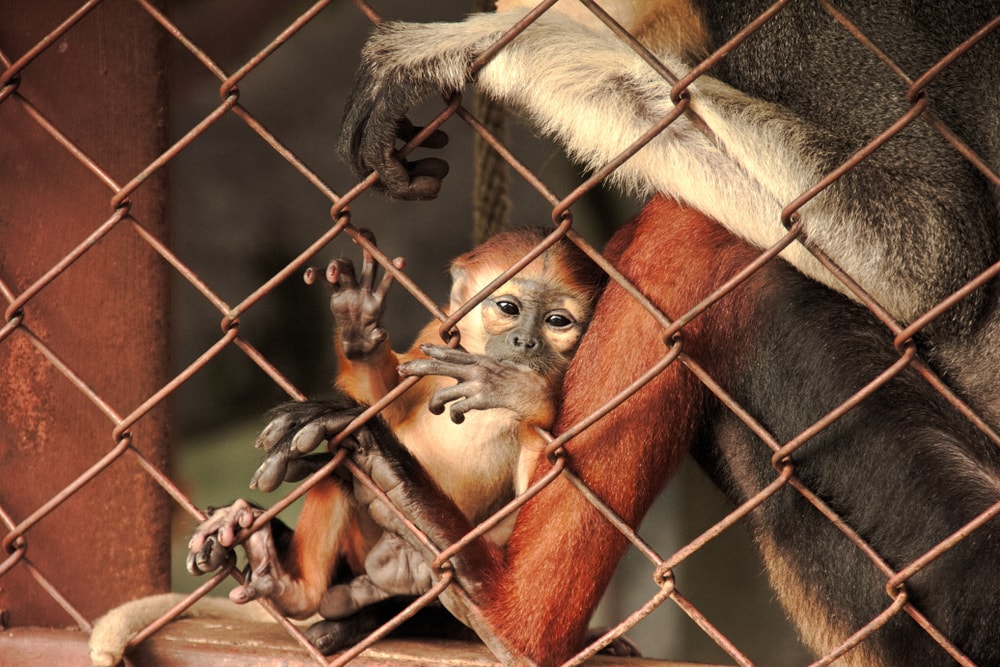

This particular douc species is currently facing significant threats to its survival. Habitat loss, hunting, and illegal pet trades are a few of the most substantial threats they face today.
As forests are cleared for agriculture, infrastructure development, and logging, the douc’s natural habitat is disappearing, making it difficult for them to find food, shelter, and avoid human interaction.
Aside from that, they are often hunted for their meat and bones, which are believed to have medicinal properties.
Additionally, they are often captured and illegally sold in the pet trade, putting further strain on their already dwindling population.
Conservation Status and Efforts

The red-shanked douc is currently classified as endangered on the IUCN Red List, with their population having declined by 50-80% over the last 30 years. The main threats to their survival include habitat loss, hunting, and the pet trade.
One notable effort to protect the species is the establishment of nature reserves. World Land Trust has played a significant role in creating safe spaces for this species and many others by supporting the creation and expansion of protected areas in their native habitat.
In addition to preserving their habitat, various organizations are actively involved in douc conservation.
The New England Primate Conservancy, for example, is dedicated to the conservation of primates like the red-shanked douc. Through research, education, and advocacy, they strive to ensure the species’ survival in their native habitat.
Collaborations between local communities, governments, and non-governmental organizations are also fundamental to protecting the species.
Red-Shanked Douc FAQs

What are the main adaptations of red-shanked doucs?
They possess elongated limbs and a prehensile tail that helps them expertly maneuver through the forest canopy.
Their distinct fur also helps them camouflage among the foliage while communicating with other members of their group.
What are the predators of the red-shanked douc?
Red-shanked doucs face a variety of predators in the wild, including large birds of prey and large carnivorous mammals, such as the leopard and the clouded leopard. However, the most significant threat to their survival is human interference in their habitat.
Can red-shanked doucs be kept as pets?
No, red-shanked doucs should not be kept as pets. As critically endangered species, it is crucial to preserve their wild populations and maintain their natural living conditions. Additionally, as highly social creatures, they have complex physical, social, and psychological needs that are difficult to replicate in a domestic setting.









