Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Goblin sharks are a rare deep-sea shark species, primarily found off the coast of Japan
- Known for their distinct, extendable jaws, long snout, and jagged teeth
- Goblin sharks employ their jaws to hunt fast-moving prey in low-light ocean depths
- Little is known about their behavior, reproductive cycle, or precise life span due to their rarity
- Listed as Least Concern by the IUCN; not targeted by fishermen and have no significant market value
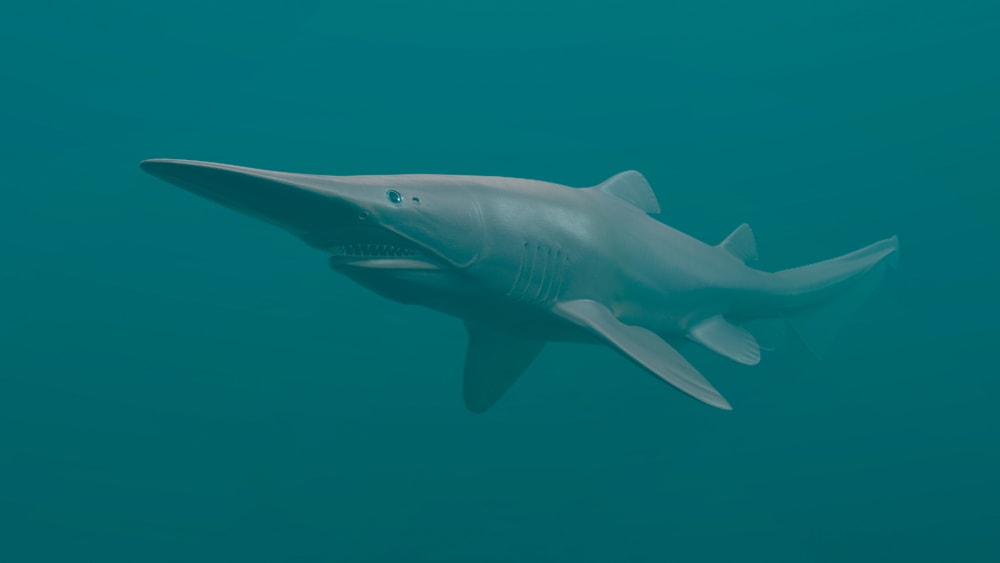
Deep in the earth’s oceans, where sunlight cannot reach, lurks a horrifying predator. Sporting a long snout and extendable jaw filled with jagged teeth, the goblin shark (Mitsukurina owstoni) is one of the strangest deep-sea beasts in the ocean.
Researchers know little about these startling sharks. But their strange appearance has caught the attention of researchers and shark enthusiasts alike.
Put on your diving equipment and say goodbye to sunlight; we’re taking a deep dive with goblin sharks to learn about their habitat, behavior, special adaptations, and more.
Characteristics
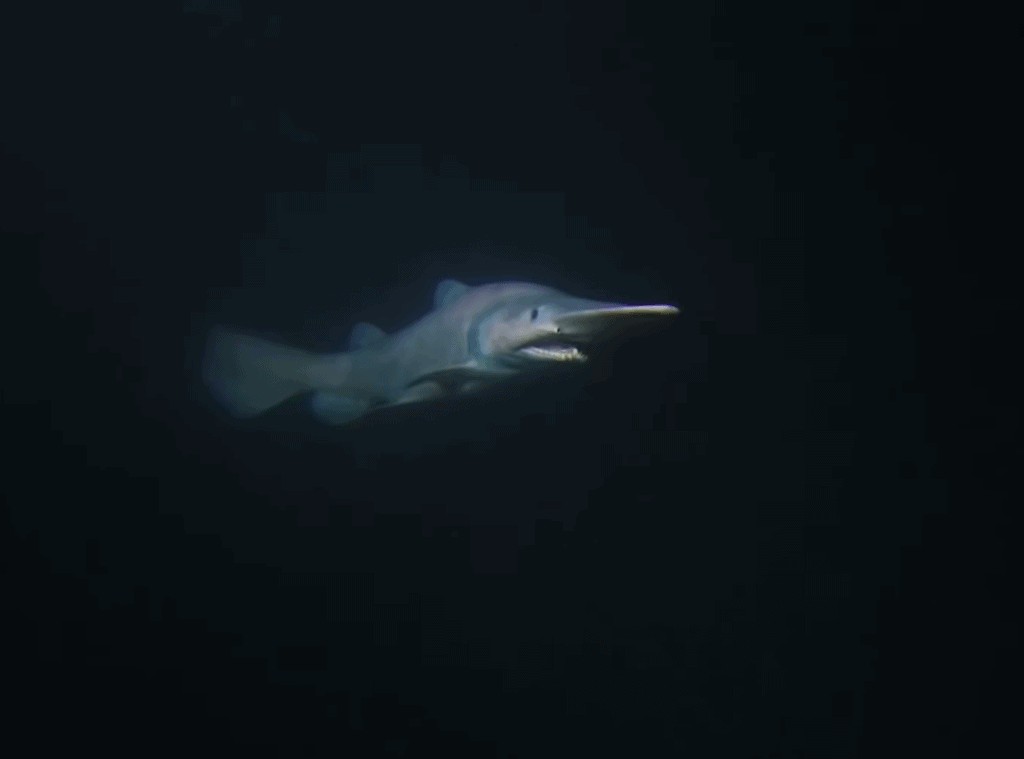

First, let’s address the elephant in the room. What are goblin sharks, and why do they look like that?
To start, they’re a species of deep-sea shark that live throughout the earth’s oceans. They’re especially common off the coast of Japan.
Well, common might be a bit of a strong word. In the 118 years that we’ve known about this species, only 50 individuals have been officially recorded. And in 2008, Japanese scientists filmed the first goblin shark recorded in its natural habitat. So, these sharks are quite a rare find.
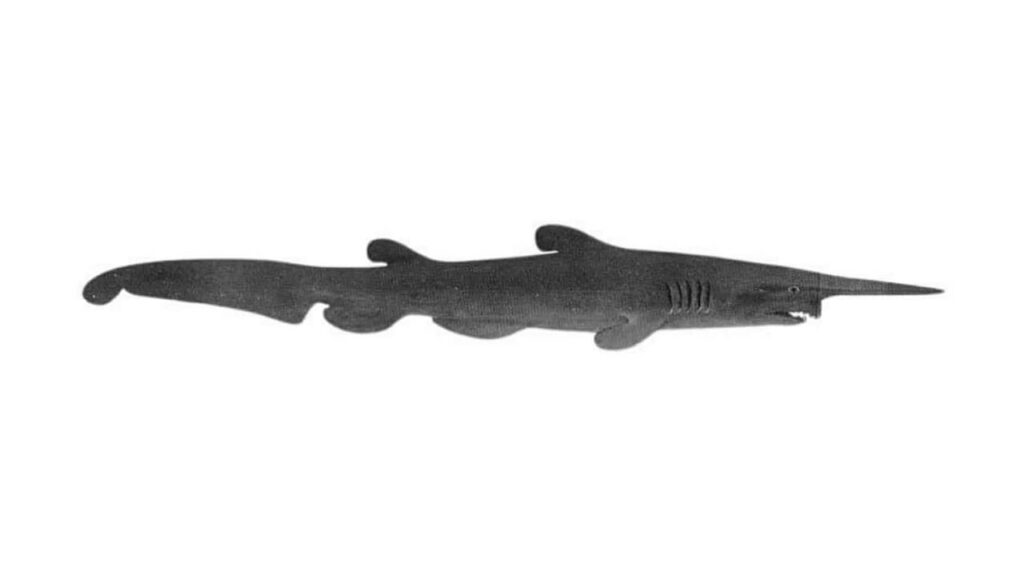
Goblin sharks are pinkish-gray and can reach lengths of 11 feet (3.4 m). However, one specimen captured in 2000 supposedly measured 20 feet long (6 m).
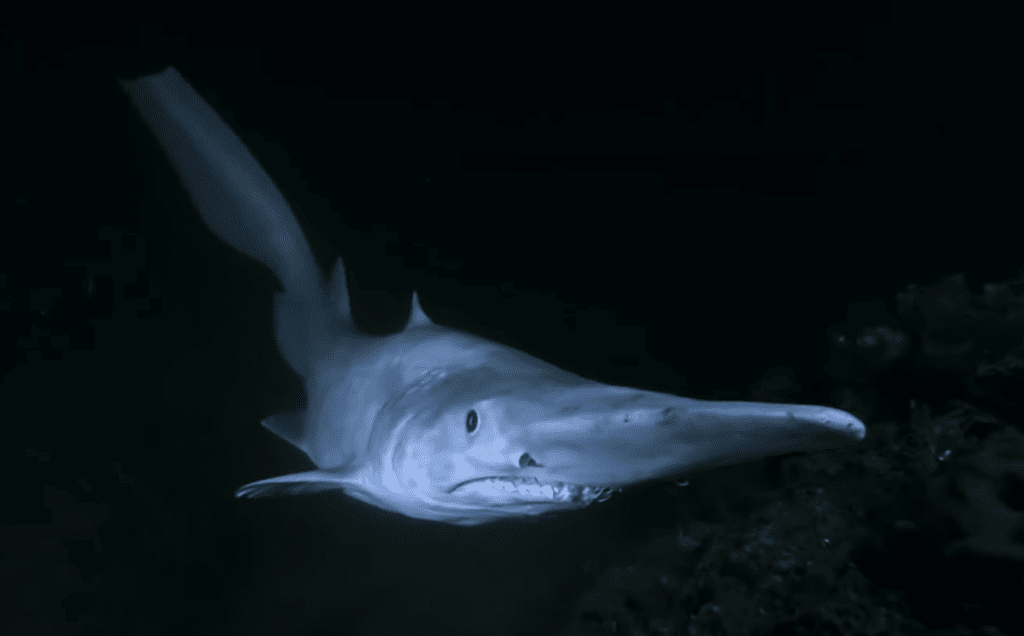
Their most distinguishing feature is their long snout, called a rostrum. Their rostrum is covered in sense organs that detect electrical currents produced by other fish. This helps them locate prey in the low light of the deep sea.

In addition to their rostrums, goblin sharks have long tails and protruding jaws. Their jaws also act as a hunting aid. They can shoot their jaws forward at speeds of 3.1 meters per second (10 ft/s). That’s faster than most snakes can strike!
Goblin sharks are slow-moving. Having such a fast and far-reaching jaw gives them an advantage when hunting prey faster than them.
Goblin sharks also have long, jagged teeth that look very different from standard shark teeth. They protrude out of the mouth even when closed, adding to their unsightly appearance.
Extendable Jaw

Let’s take a closer look at a goblin shark’s extendable jaw.
Researchers break down the movements of the goblin shark’s jaw into four phases. First is the resting phase. Next is the expansive phase, the compressive phase, and finally, the recovery phase.
The resting phase is the goblin shark at its most ordinary. This is their standard swimming and exploring phase. Even so, the mouth hangs slightly open as if in anticipation for prey to swim by.
The expansive phase is when a goblin shark locates food and shoots its jaw toward it. Their mouth opens a staggering 111 degrees wide.
For comparison, human mouths can only open to 50 degrees wide. So if you had a jaw like a goblin shark, your chin could rest on the top of your ribcage without lowering your head.
Next is the compressive phase, when the jaws close around their prey. The jaws make up nearly 10% of a goblin shark’s total length at the max extension.
As one writer puts it, “stick your lips out as far as they can go. Now imagine them 7-10 inches (18-25 cm) farther out than you can muster. That’s what it’s like for a goblin shark.”
Lastly is the recovery phase, when the jaw slides back into place, ideally with a tasty morsel inside it.
Keep in mind that this whole process takes less than a second to complete. I would hate to be an unlucky fish on the wrong side of those jaws.
If you’d like to see a goblin shark’s jaws in action, check out this video here:
You may also like: A Deep Dive into the 25 Types of Sharks (Names, Chart and Pictures)
Range and Habitat
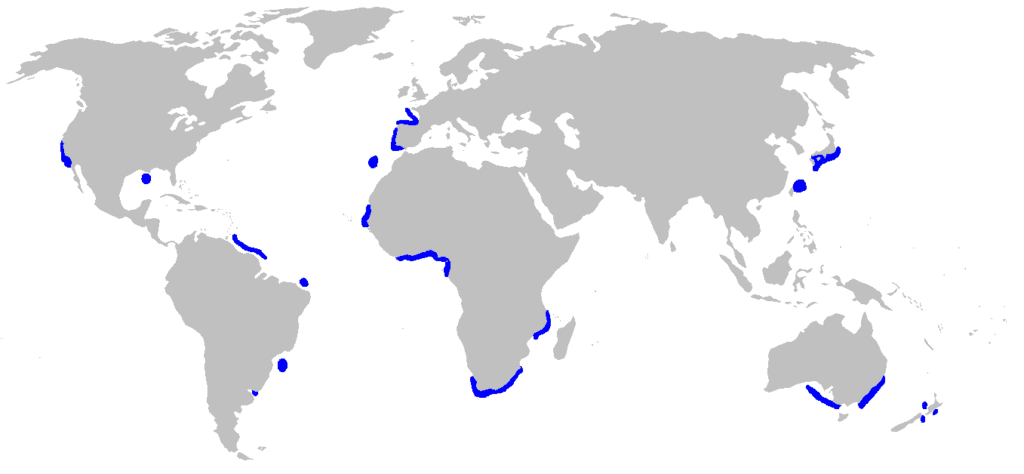
By Yzx (talk)This file was derived from: BlankMap-World-noborders.png – Own work using:IUCN / CC BY-SA 3.0 / Wikimedia commons
Goblin sharks live at depths between 130 and 4,265 feet (40-1,300 m). As previously mentioned, most goblin shark sightings are reported in the waters around Japan.
That said, they have been found elsewhere, too, including the coast of southern California and the Gulf of Mexico.
Goblin sharks live in nutrient-scarce environments. Because of this, their bodies seem poorly developed. For example, they have reduced skeletons, soft even for a cartilaginous skeleton.
In addition, muscle mass is hardly formed, and their fins are floppy and small. All of these features suggest that goblin sharks are slow-moving and sluggish.
That said, they are suited for their specific environments. For example, their rostrum helps them locate prey. In addition, their detachable jaw allows them to capture food without spending too much energy.
Also, despite living in low-light environments, goblin sharks can and do use their eyes. However, their eyesight is weak compared to their rostrum’s sensory capabilities.
You may also like: Are Sharks Mammals: Where Do Sharks Fit in the Classification of Animals?
Diet and Hunting
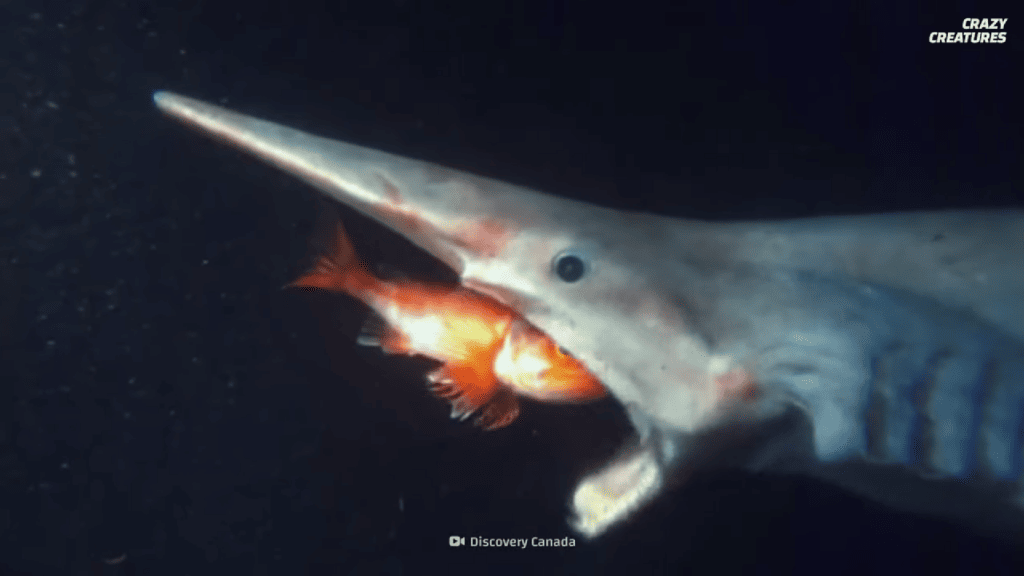

Goblin sharks primarily feed on fish, including angler fish. They also feed on shellfish and might even scarf down some squid when they can catch them.
Little is known about how goblin sharks hunt because so few have been studied in their natural habitats. However, they are thought to be ambush predators rather than active hunters.
Goblin sharks are low-density creatures with large, oily livers. These characteristics help them float through the water without exerting too much energy.
Using their rostrum to detect prey, they float toward their target with minimal movement to avoid detection. Then, once they’re close enough to their prey, their jaws extend forward instantly, engulfing the prey whole.
You may also like: Do Sharks Have Bones? Diving Into the Mystery of Shark Anatomy
Behavior and Relationship With Humans

Aside from feeding habits, little is known about goblin shark behavior. However, because they live at such depths, it’s safe to say they are little threat to humans.
The first writings on goblin sharks were published in 1910 by Dr. I Hussakof. He described the shark as “grotesque” and commented on its “curiously elongated nose.” Since then, goblin sharks have fascinated humans because so little is known about them.
Some live specimens were captured in Japan and brought to aquariums. Unfortunately, the specimens died shortly after they arrived at the aquariums.
Besides researchers and the occasional fisherman, interactions between goblin sharks and humans are rare. Perhaps that’s for the best. And you can rest easy knowing that you won’t bump into these “grotesque” creatures when swimming at the beach.
You may also like: Ancient Predators: How Long Do Sharks Live?
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Little is known about goblin sharks’ life cycle or how they reproduce. No pregnant females have been observed or studied.
However, researchers believe they share similar reproduction characteristics to sharks like thresher sharks. They are considered viviparous, meaning babies develop within their mother’s womb rather than in eggs.
The smallest recorded goblin shark was 32 inches (81 cm) long. This is likely their size at birth, but the exact length isn’t known.
Males reach sexual maturity when they are around 8 feet long (2.4 m). It’s unknown when females are able to reproduce.
It’s also unknown how long goblin sharks live for, but some researchers believe they can live anywhere between 16 and 60 years.
You may also like: How Do Sharks Mate? It Might Surprise You
Conservation Status

The exact population estimates for goblin sharks are unknown. However, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists goblin sharks as a species of Least Concern.
Fishermen don’t target goblin sharks as they have no real market. This means that goblin shark populations are spared from overfishing. That being said, they are often found tangled in fishing nets, and accidental catches aren’t uncommon.
In one instance, in 2003, over 100 goblin sharks were unintentionally captured by fishermen. Why so many goblin sharks were in one area is unknown, but the event did come right after a major earthquake which might have some correlation.
The captured goblin sharks were either sold for meat or released. Unfortunately, no researchers were present to record them, hence why only 50 are said to be officially recorded.
Also, goblin shark meat can be consumed by humans. Sometimes goblin shark’ jaws are sold as collector’s items as well.
Even so, fishing poses little threat to goblin sharks, and for now, their populations appear stable. It’s a good thing too. It’d be a shame if such a unique creature went extinct, even if they are scary to look at.
You may also like: Are Mermaids Real? Exploring Ocean Myths And Legends
FAQ

Why do goblin sharks look so weird?
Because they’re a product of their environment. They live in low-light, high-pressure environments and they need to adapt in order to survive there.
Their rostrum is an advantageous adaptation because it helps them navigate the dark waters of the deep sea. Their extendable jaws help them catch prey that would be too fast to chase. Finally, their soft, fleshy bodies help them withstand the intense pressures of deep waters.
If it wasn’t for these adaptations, they couldn’t survive in their habitat. So, just because they’re ugly looking, it’s for their own good because it helps them survive.
And anyway, who are we to judge? They’d probably think we’re pretty weird looking as well.
Why are goblin sharks called living fossils?
Goblin sharks are called living fossils because they remained virtually unchanged from their ancient relatives. They are the only living member of the shark family Mitsukurinidae, and are thought to have existed for at least 125 million years.
How did goblin sharks evolve?
Goblin sharks evolved from a family of ancient sharks called Mitsukurinidae.
They are believed to be the most basal member of the order Lamniformes which includes other sharks like great whites. Basal means that they are the most primitive member of their order, making them “living fossils.”
More from Outforia
Be amazed by these other shark species!
Shark species from different states!
Sharks in Florida | Sharks in Hawaii | Sharks in Maui | Sharks in Lake Michigan









