Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Temperate grasslands, characterized by grasses as dominant vegetation, are impacted by a variety of factors including temperature variations, precipitation levels, wildfires, and grazing by animals.
- These biome types cover 25% of the global landmass and can be found in regions such as Western Europe, parts of the US, and mountainous regions in Japan.
- Temperate grasslands are created through a medley of conditions including a temperature range of 0°C to 18°C annually, dominance of grasses as vegetation, and distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Grazing animals help maintain grasslands by eating stems, leaves, and flowers, trampling the vegetation and through nutrient transfer via their dung.
- Different regions have unique names for these grasslands, such as “puszta” in Hungary, “downs” in Australia and New Zealand, and “pampas” in Argentina and Uruguay.
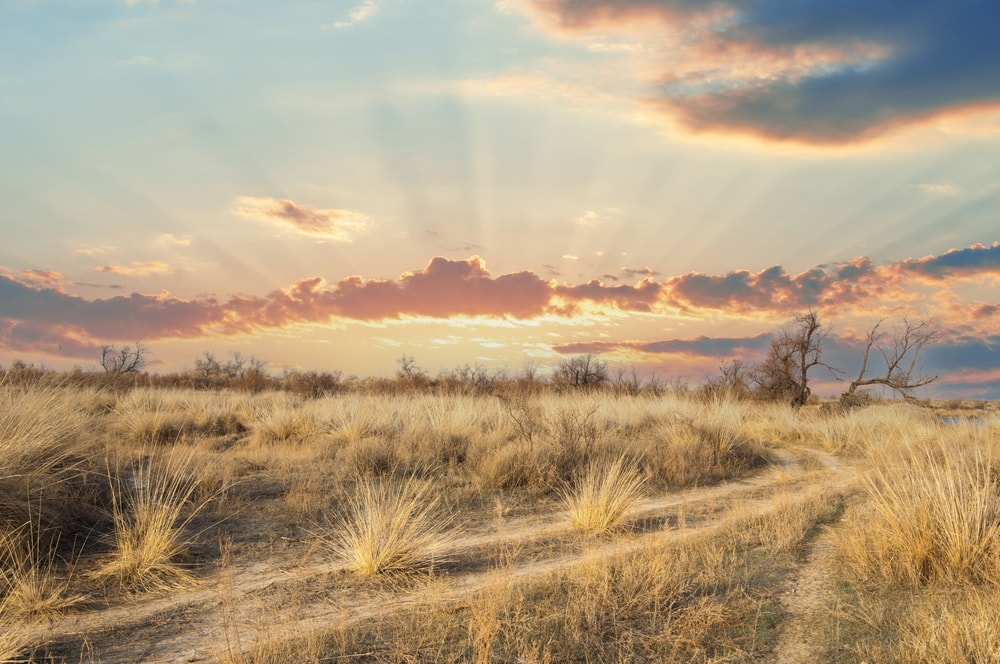

Temperate grassland is a type of biome characterized by grasses as the dominant vegetation. Temperatures vary drastically, with warm or hot summers and cold winters. Most often, there is a wet and dry season.
Temperate and tropical grasslands exist on 25% of the landmass across the world. You’ve probably walked in temperate grassland if you’ve ever visited Western Europe, England, The West and East USA, or mountainous parts of Japan.
So what lives here, and how does it survive? How important are grasses?
What is a Biome?
A biome is a community of plants and animals in a specific climate and topographical region. Topographical means the type of land the community is on, whether it be montane or desert, wetland or tundra.
There are 26 different types of biomes in all.

Share This Image On Your Site
<a href="https://outforia.com/temperate-grassland/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/temperate-grassland-infographics.jpg"></a><br>Temperate grassland Infographic by <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>What Does Temperate Mean?

Temperate regions of the world are found north and south of the dry zones. The dry zones are found north and south of the tropics. In a temperate climate, the coldest month averages between 0°C and 18°C. Their warmest month averages above 10°C.
Temperate regions include:
- Most of Western Europe
- UK
- East China and some parts of Japan
- West and East USA
Temperate regions have distinct wet and dry seasons. How cold, wet, or hot this is is variable. These last factors subdivide temperate grasslands further. For instance, Mediterranean grasslands are temperate grasslands, but they are characterized by mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers.
This subtropical grassland is in Paphos, near Cyprus.
You May Also Like: A Colorful Exploration: 22 Incredible Types Of Coral And Their Beauty
How is a Temperate Grassland Created?
Temperate grassland is a biome with these features:
- It’s in a temperate region of the world, with a temperature range of 0°C to 18°C annually.
- The dominant vegetation is grasses
- It has definite wet, cold, and dry, hot seasons. The temperature of these can vary.
There are a few factors that combine to create a situation ideal for grassland to develop. These are rainfall levels, grazing by animals, and wildfires.
Rainfall in Temperate Grasslands
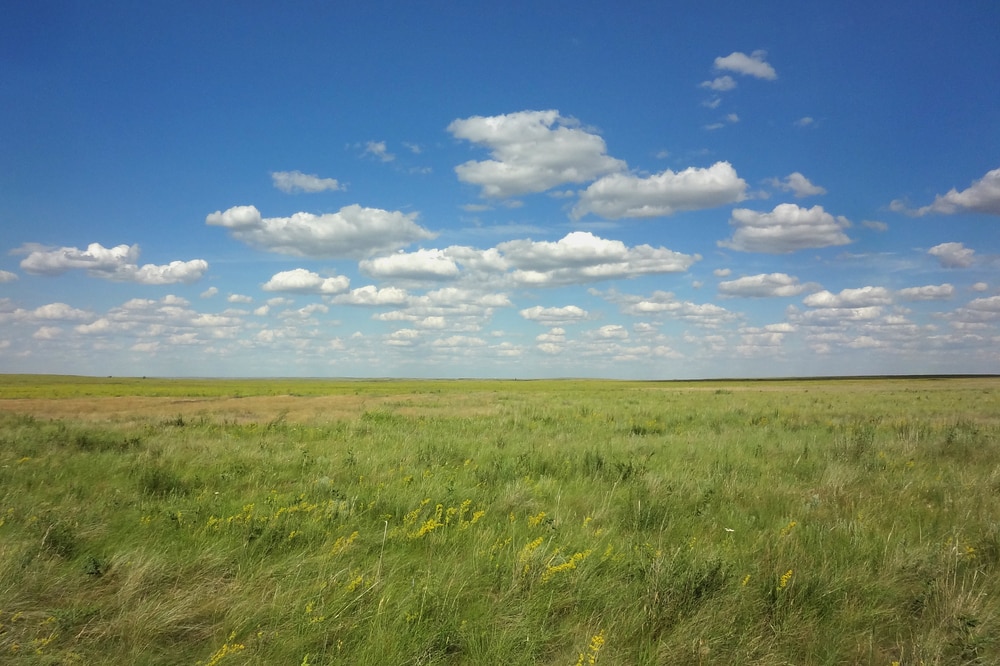

The precipitation levels of the world’s grasslands are in the range of 19.7-35.4 in (500-900 mm) per year. This includes tropical grasslands like the African veldt, which has a very rainy season and a very dry season.
Temperate grasslands receive an average of 19.7-34.6 in (500-880 mm) of rainfall per year.
This amount of rainfall is enough to sustain grasses but not enough to sustain trees. It’s this factor, plus the occurrence of fires in the region, that creates the grassland environment.
Wildfires and Grasslands
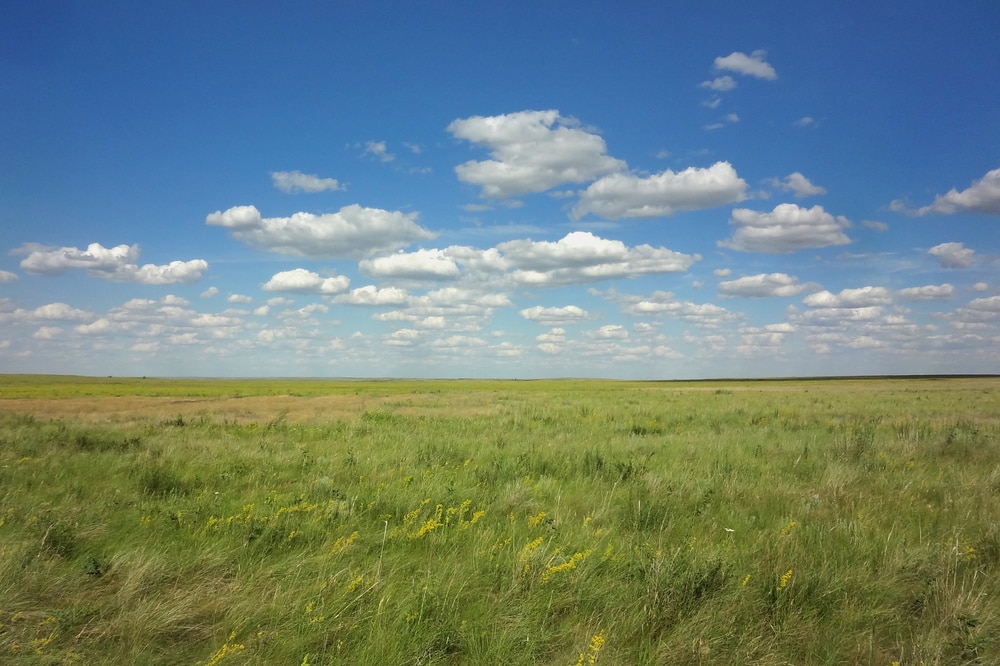

Fire is not always a bad thing. Fires start naturally in dry grassland from lightning strikes. They can also be started by native peoples wanting to clear land for grazing or enrich the soil for farming.
Wildfires halt the progression of grassland into shrubland and forest. Grasses are better adapted to survive fires than trees. They grow back quickly. Bison from the Little Bighorn Battlefield area of the US even prefer grass from previously burned areas.
You’ll notice that many of the world’s grassland areas, such as the prairies of the USA, are in areas with frequent natural thunderstorms.
Together with our human tendency to burn out forested areas for grazing and agriculture, you’ll see how areas of temperate grassland are created.
You May Also Like: All About The 4 Types Of Volcanoes+ Formation, Eruption, And Facts
Grazing and Grasslands

Herbivorous grazing animals help to create and maintain grasslands. They can be domestic or wild; it doesn’t matter; the effect is the same.
So sheep, cattle, and horses keep grassland from turning back into forest. So do deer, bison, and non-ungulates like prairie dogs.
- Defoliation. Grazing animals eat stems, leaves, and flowers above the ground. These plants are herbaceous anyway, dying down to their roots in the winter and then regrowing. The plants that aren’t herbaceous, like shrubs and trees, will not grow back from grazing.
- Trampling by grazing animals stops tall plants from gaining a foothold.
- Nutrient transfer. Herbivore dung returns some of the nutrients to the soil, creating patches of richer ground. The grazing animals retain some of the nutrients.
Temperate Grasslands Around the World
Temperate grasslands across the world are known by many names. In Hungary, they’re called “puszta.” In New Zealand and Australia, they’re known as “downs.” In South America’s Argentina and Uruguay, they are “pampas.”
Here are some famous grasslands you may want to visit:
Theodore Roosevelt National Park, High Plains, US
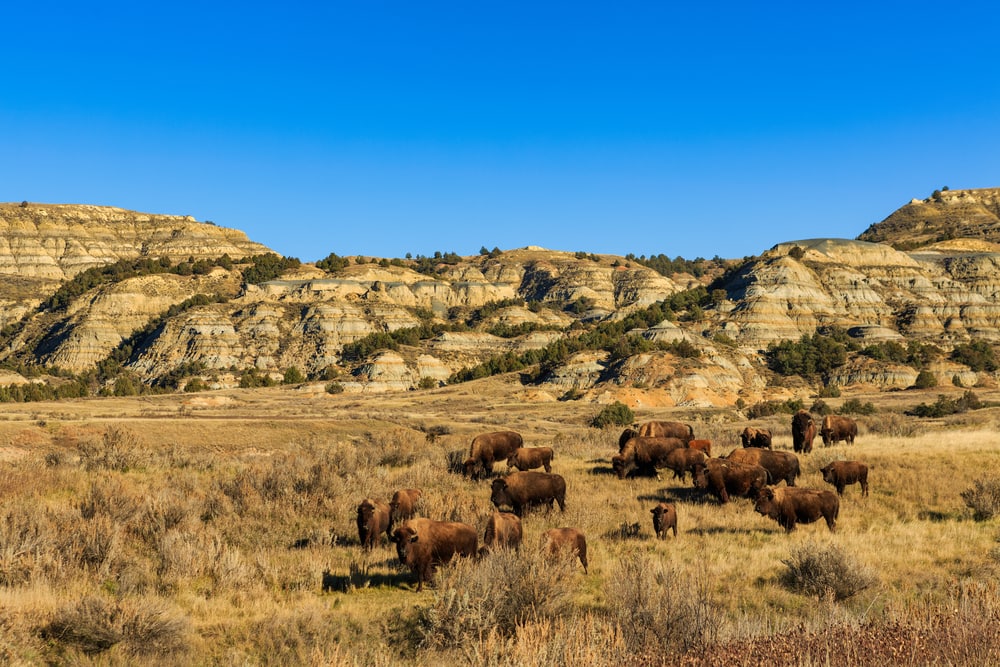

This national park is named after America’s famous president. He loved to visit the park in his youth, when he was known as ‘Teddy.’ It contains rolling grasslands, rock formations, and hills. The Little Missouri River cuts through it.
There are lots of bison here. Bison were driven to the brink of extinction during the struggle between white settlers and native Americans, but now their populations have recovered.
You can camp at one of the two campgrounds or sleep in a hotel. The best way to see this vast park is by vehicle.
Gungahlin Grassland Reserves, Australia
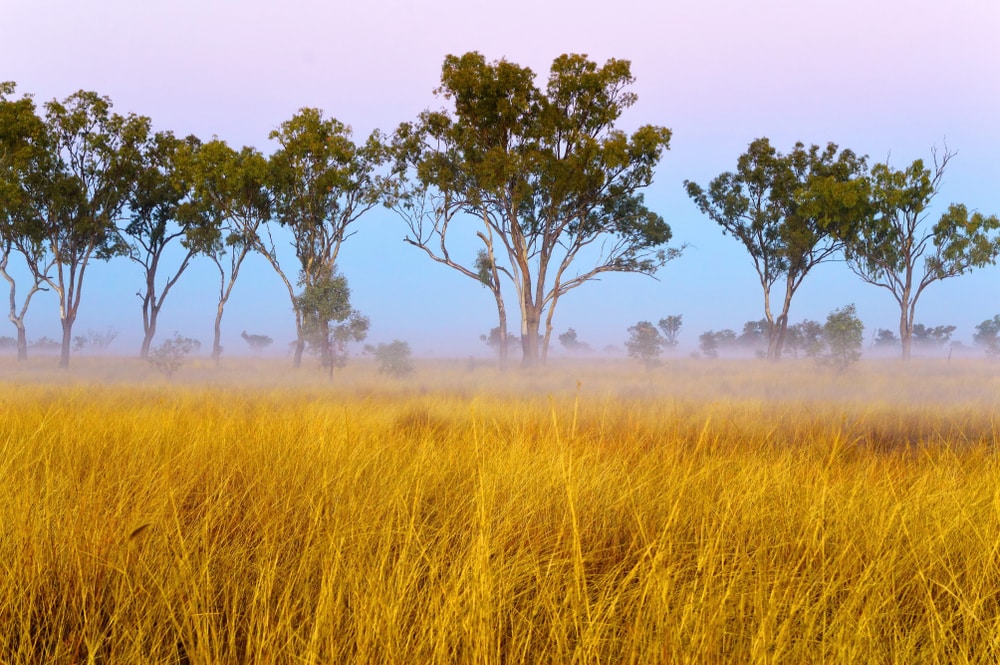

Temperate grassland accounts for just 0.5% of Australia’s landmass. When white settlers first arrived, there were large areas of natural grassland. Most of these have now been turned into agricultural land.
Perennial tussock grasses, shorter grasses, moss, and lichens cover the Australian grassland landscape. You can find the rare Ginninderra Peppercress and the Button Wrinklewort here.
Animal life is diverse, with the Golden Sun Moth (Synemon plana), the Grassland Earless Dragon (Tympanocryptis pinguicolla), and the Striped Legless Lizard (Delma impar).
The Dunlop Nature Reserve is another grassland nature reserve you can visit. Grasses have even been transplanted here from other threatened areas. The photo shows Albinia National Park in Queensland.
Great Himalayan National Park, Himachal Pradesh, India
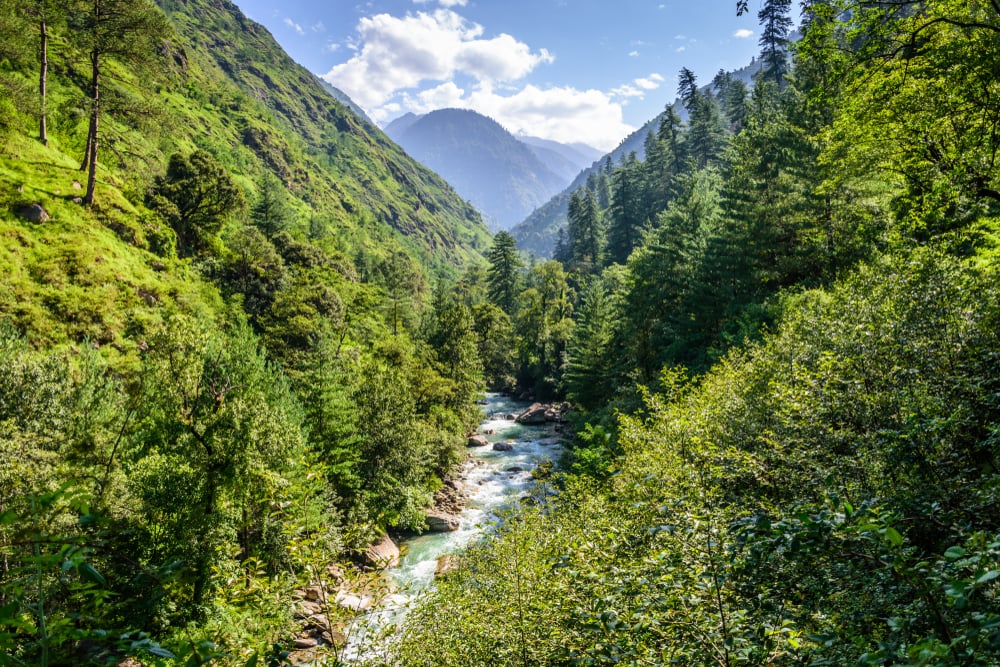

The GHNP was awarded UNESCO World Heritage Site status in 2014. It is rich in biodiversity. It spreads across four valleys, each with its own flora and fauna. It encompasses both temperate and alpine ecosystems.
Plant life includes rare orchids like the Himalayan Marsh Orchid (Dactylorhiza hatagirea) and the Monkey Orchid (Calanthe tricarinata).
As for birds, you can find the spectacular Western Horned Tragopan. This rare pheasant is known locally as the “jujurana,” or “king of birds.” The Bharal, or Greater Blue Sheep (Pseudoisnayaur), climbs rocky areas.
Fun Facts

- The Eurasian steppe covers one-fifth of the distance around the world. That’s big—very big.
- The Great Himalayan National Park is on a boundary between two very climatically different regions: the Oriental to the south and Palaearctic to the north.
- The American Bison has been the national mammal of the USA since 2016.
- Many chalk grassland flowers can only grow in nutrient-poor, calcareous soil. If the soil is too rich, it encourages the growth of competitor plants instead.
You May Also Like: 15 Different Types Of Terrain You Should Know About: Complete Guide
Temperate Grassland FAQs

Are grasslands a temperate ecosystem?
There are not only temperate grasslands but also tropical grasslands like savanna. Grassland is not defined by temperature; it is more defined by the amount of rainfall, herbivore grazing, and the number of wildfires.
Is tundra a type of grassland?
Although tundra contains grasses, they are not the dominant vegetation. Mosses and lichens are more prevalent. There is more rainfall in tundra regions, and the moisture stays around longer due to the cold. So, tundra is not grassland.
What’s the difference between savanna and temperate grassland?
Savanna grasslands have a long dry season and receive rainfall only a few months of the year. Temperate grasslands have more rainfall over a longer period and lower, more variable temperatures. The soil in temperate grassland is richer.
What sort of plants are forbs?
Forbs include Legume (bean and pea family) plants and Compositae (daisy family) plants. Most wildflowers come from this category.