Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Green anacondas are the heaviest snakes in the world, with females weighing up to 550 pounds (250 kg) and reaching up to 39 feet (12 meters) in length.
- They are native to South America and mostly found in Brazil’s Amazon River Basin and the Orinoco Basin in Columbia.
- Green anacondas are opportunistic feeders, preying on birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians, and mammals.
- Their conservation status is listed as “Least Concern” by the IUCN Red List.
- Although there are several tales of their ability to eat humans, there is little to no evidence of green anacondas actually doing so. Green anacondas can still be dangerous due to their large size and muscle strength, but these snakes don’t go out of their way to attack humans.

share this image on your site
<a href="https://outforia.com/green-anaconda/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/green-anaconda-infographics-0922-683x1024.jpg"></a><br>green anaconda <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>Have you ever wondered what the largest snake in the world is? The green anaconda is the heaviest snake in the world. It can also get pretty long, but the reticulated python wins the record for the longest snake.
Green anacondas are giant constrictor snakes. They’re sacred to some but feared by many due to their large size. Continue reading to learn more about these gigantic snakes!
Green Anaconda Classification

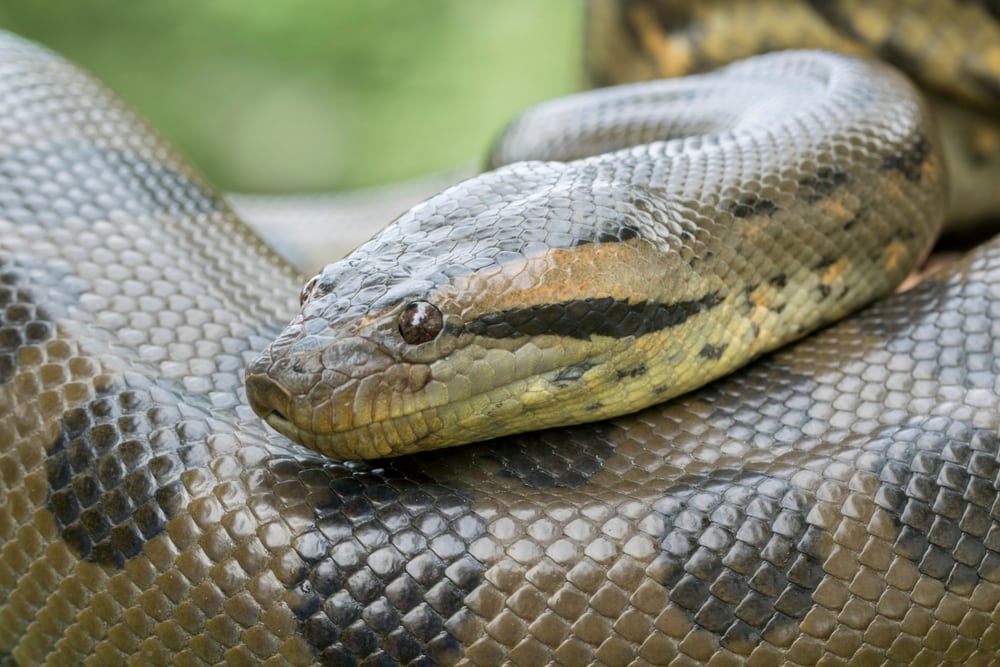
The green anaconda (Eunectes murinus) is a reptile that belongs to the Squamata order. This includes snakes, lizards, and legless squamates called amphisbaenians. Snakes are classified under the Serpentes suborder.
Several snake species and families fall under the Serpentes suborder, one being the Boidae family. Known as boas, the green anaconda belongs to this group. Boas are constrictor snakes that aren’t venomous.
Green anacondas are in the Eunectes genus. This includes three other anaconda species native to South America.
Characteristics and Appearance

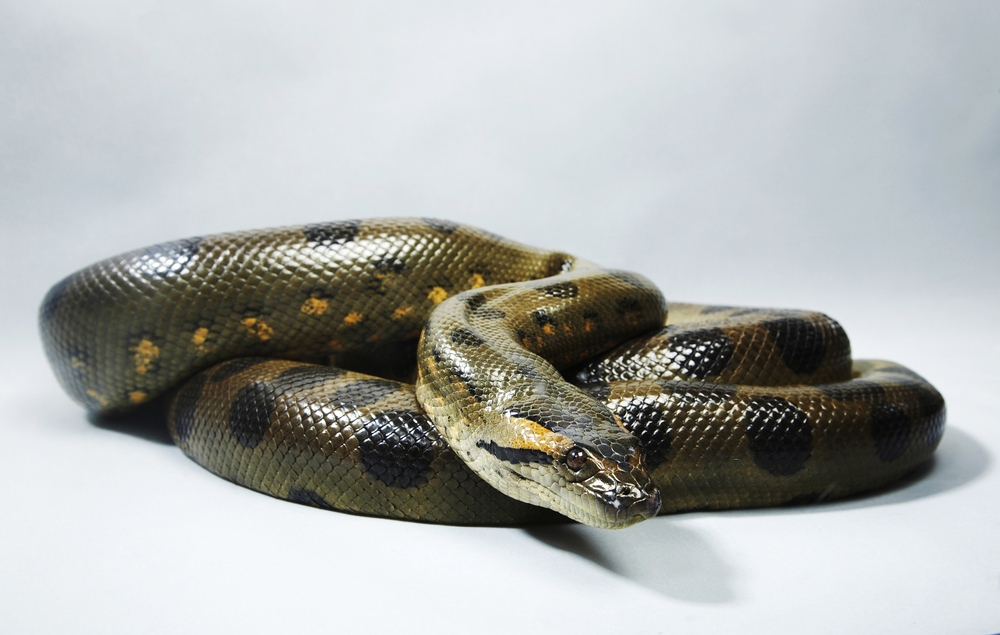
Green anacondas are the heaviest snakes in the world. This is because larger females can weigh up to 550 pounds (250 kg). Males are typically much smaller than females.
Their weight comes from their large diameter. These snakes can have a diameter of up to 12 inches (30.5 cm).
The average length of a male anaconda is about 10 ft (3 m). Females average lengths up to 20 ft (6m). However, females can grow much larger, with some reported up to 39 ft (12 m) in length.
Green anacondas blend in well amongst dense vegetation in their natural habitats. They’re olive green to brown in color with oval-shaped dark brown or black spots along their spine. On each side, they have yellow spots outlined with dark brown or black.
They have large heads, with their eyes and nose located more on the top than sides. This allows them to see and breathe while swimming or wading in water.
Geography and Distribution
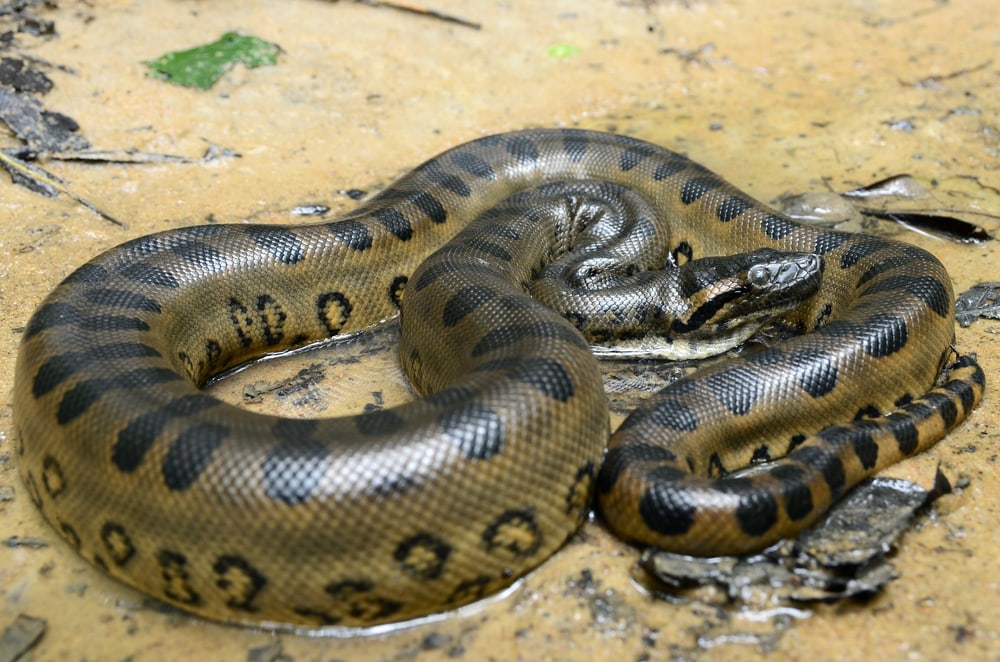
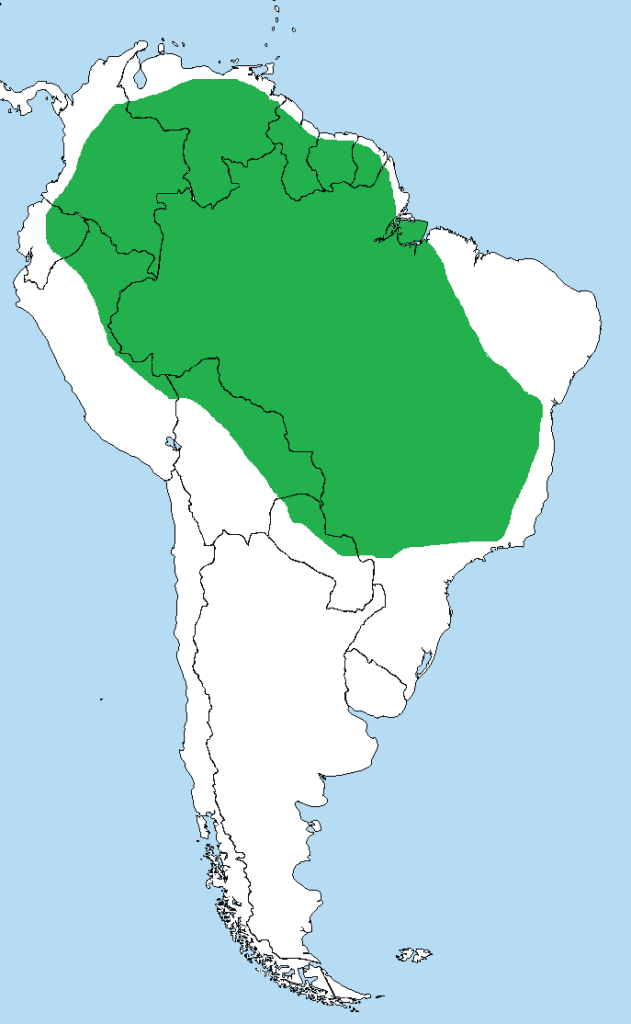
Green anacondas are native residents of several South American countries. They’re most common in Brazil’s Amazon River Basin and the Orinoco Basin in Columbia. They can also be found in Venezuela in the Llanos grasslands.
Other populations are found throughout several South American countries, including:
The green anaconda mostly inhabits the lowlands of these areas. They prefer wet environments, and flooding lowlands are considered their ideal habitat.
Green anacondas have been introduced to Florida. However, the green anaconda population is much smaller than South America’s. Sightings of these snakes in Florida are not very common.
There have been few reports of green anacondas in central and north central Florida.
You may also like: 50+ Snakes In Florida: ID Guide With Facts, Photos, Chart And More
Habitat and Range
By Gossipguy – Own work / CC BY-SA 4.0 / Wikimedia commons
Green anacondas are semi-aquatic snakes. They live in areas that are well-saturated. They can mostly be found swimming in slow-moving freshwaters.
In Venezuela, they live in grasslands. In other parts of South America, they inhabit rainforests and tropical savannas.
Since these giant snakes like to live near water, they need to adapt during the dry season. They migrate to other areas in their range to find water. If they’re unable to find water, they use mud to bury themselves.
A green anaconda’s home range is fairly small. Their range can be as small as 0.10 sq. mi (0.25 sq. km). Their range is slightly larger in the wet season. It can be about 0.14 sq. mi (0.35 sq km).
Females inhabit lowlands during breeding season. Males and non-breeding females stay in higher elevations during the wet season.
You may also like: 39 Fascinating Amazon Rainforest Animals, Birds & Insects
Diet and Food Habits
The size of a green anaconda works to its advantage. These snakes can eat things up to half their own mass.
They’re opportunistic feeders and can eat a wide variety of animals, including:
- Birds
- Fish
- Reptiles
- Amphibians
- Mammals
They’ve been known to eat large animals like capybaras and caimans. Green anacondas have a special characteristic that allows them to detach their jaw. This helps them to fit larger prey into their mouth.
Larger prey can allow green anacondas to last weeks or even months without another meal. Females typically eat a large meal after mating, so they won’t have to eat again until she gives birth.
The green anaconda has a slow metabolism. This allows it to go longer periods without getting hungry. Breeding females have a faster metabolism, so they will eat more often.
A green anaconda hunts by ambushing its prey. Once captured, they use their sharp teeth to bite into it. As constrictors, they use their body to coil around their prey. Then, they suffocate it before swallowing it whole.
Behavior
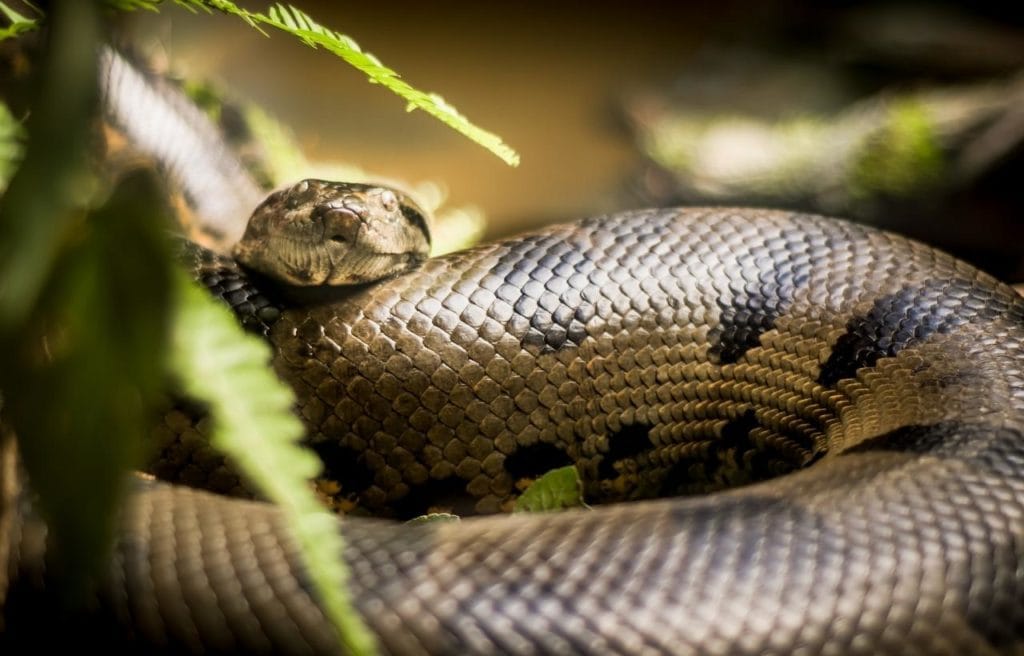

Green anacondas are most active in the evening to keep cool while they migrate. They can travel long distances within short periods.
Suppose green anacondas can’t find water or mud to cover themselves during the dry season. In that case, they resort to a state of dormancy. This state can last throughout much of the dry season.
To stay cool, green anacondas have a unique adaptation. They have the ability to adjust their exposure to the sun. They do this by changing the amount of surface area that’s exposed. By doing so, they regulate their own body temperature.
Green anacondas use chemosensory abilities for communication. This means they can detect chemical signals and pheromones from other species. They use their forked tongues to sense any chemical presence.
They can also sense predators using their pit organs and vibrations. Anacondas can detect other animals through heat using their pit organs on the upper lip.
Mating and Reproduction
Green anacondas are polyandrous. This means that females mate with more than one male during breeding season. Breeding occurs between March and May.
When mating season arrives, males seek out females and form groups. Sometimes these groups can consist of up to 13 male snakes.
The males form a ball-like mass around the breeding female to mate. Each male tries to mate with the female by coiling around her to find her cloaca.
Females mate with many males in the aggregation. But, they are selective when choosing a mate. Large females and large males typically mate with each other. This mating process can last for weeks.
After mating, a female sometimes eats one of the males. This is done to give her a larger meal so she won’t have to eat during the gestation period.
Females produce eggs, which incubate inside their bodies. This is known as being ovoviviparous. Females incubate the eggs for about seven months. Then, they give birth to live young in shallow waters.
The size of a female green anaconda’s clutch can depend on her size. The average clutch size is usually between 20 to 40 young. The largest litter ever recorded was 82.
Baby green anacondas aren’t given any support after birth. They’re fully independent once born.
You may also like Do Snakes Have Bones? Flexible Danger Noodles And Their Spectacular Skeletons
Population and Conservation Status

The conservation status of green anacondas is of least concern, according to the IUCN Red List. Many green anaconda populations live in protected areas. This prevents the hunting and capture of the species.
Green anacondas are protected by Cites Appendix II as a part of the Boidae family. This includes certain regulations in relation to international trade.
Even though they’re not threatened, restrictions placed on international trade help keep populations healthy.
More research is needed to determine their current population trend.
Threats and Predators
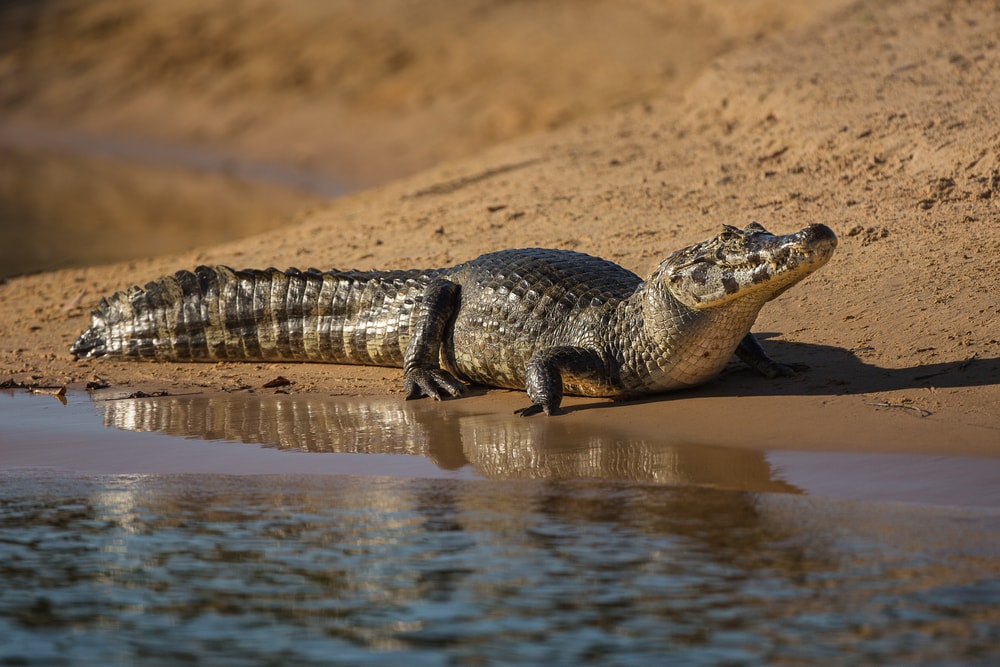

Female green anacondas don’t have any predators. They’re considered apex predators at the top of the food chain. Males and young green anacondas do have predators, though.
Caimans are common predators of smaller anacondas. When threatened, anacondas will either retreat or coil up. When retreating, they either hide in mud or slither into water to escape the threat.
If unable to escape, anacondas will coil up to protect their head. Coiling when cornered is also a sign that an anaconda is ready to strike if necessary.
Other threats to green anacondas include humans. People often kill green anacondas for their body parts or out of fear. They’re also captured for the international pet trade. Despite CITES Appendix II regulations, green anacondas are still captured and illegally traded.
Another human threat to green anacondas is habitat destruction. These snakes like dense vegetation. Deforestation disrupts their habitat and even results in destruction.
You may also like: Wildlife Trades: Live Animal Trades Analyzed
Green Anaconda Ecological Role
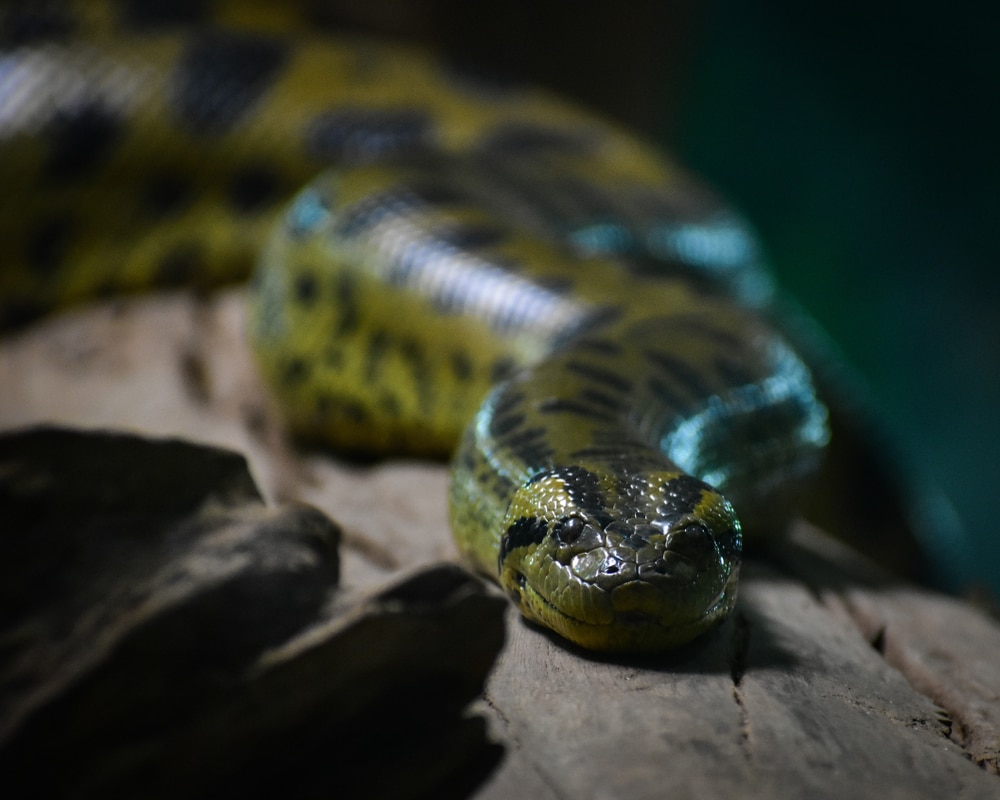

Green anacondas help regulate prey populations within their ecosystem. Younger anacondas and smaller males serve as a food source for larger animals.
Due to their varying diet, anacondas help control the large animal populations that may not have other predators.
You may also like: 12 Different Types Of Ecosystems And Why They Are Important
How Dangerous is a Green Anaconda?
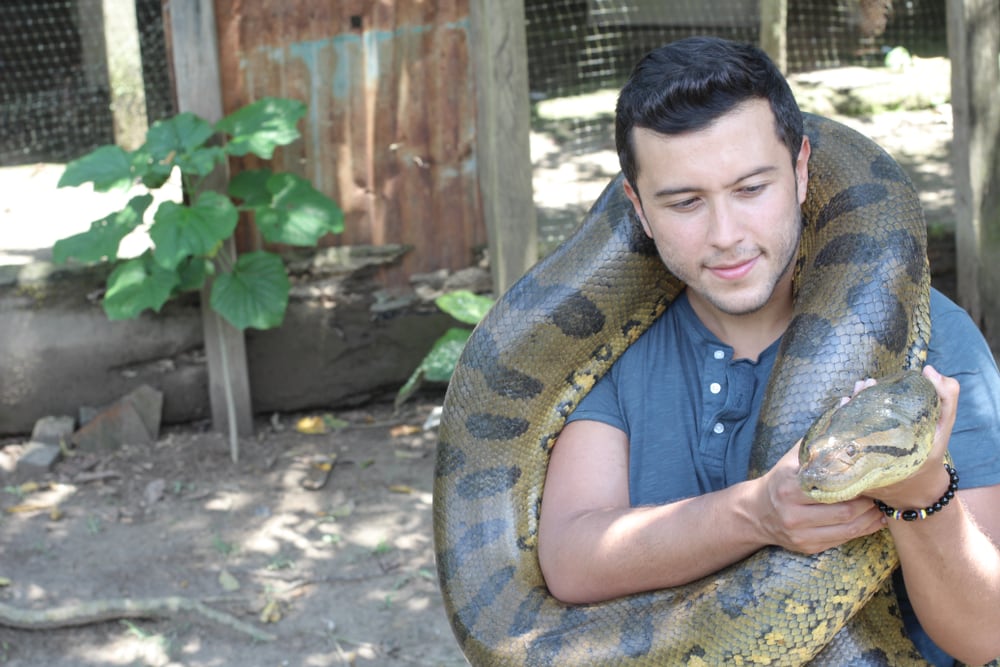

Green anacondas can be dangerous due to their large size. Alongside sharp teeth, their special senses allow them to detect animals nearby.
Their constricting abilities are also dangerous because of their muscular strength. They can coil around large prey to suffocate them.
Although there are several tales about green anacondas eating humans, there isn’t evidence to support this. Anacondas can be dangerous to humans, but these snakes don’t go out of their way to attack humans.
Their range in South America is also located away from urban areas.
People who keep anacondas as pets do run the risk of these snakes’ natural abilities. If owned as a pet, it’s important to handle it with extreme caution.
You may also like: 21 Different Types Of Rattlesnakes Species: Pictures And Guide
Fun Facts about Green Anaconda
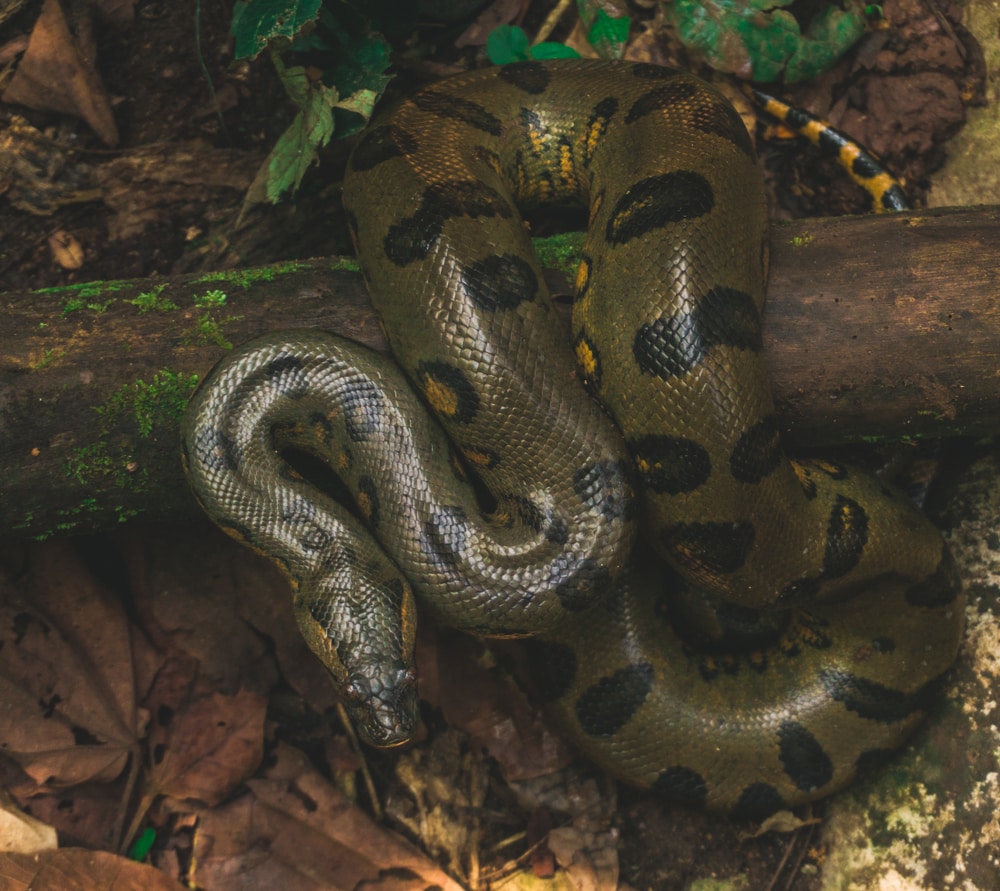

👉🏼 Green Anacondas are Thought to Have Spiritual Properties
Some indigenous groups in South America believe that green anacondas have spiritual properties. These snakes are often captured and used for medicinal or ritual purposes.
Some of the illnesses that green anacondas are used for include:
- Inflammation
- Infection
- Thrombosis
- Rheumatism
👉🏼 Green Anacondas are on the Prohibited Species List of Florida
Along with several python species, green anacondas are on Florida’s prohibited species list. This means that a special reptile license is needed to own this snake.
The green anaconda is considered a high-risk, nonnative reptile in Florida. It was added in 2021, along with several other species.
👉🏼 Baby Anacondas are More Aggressive
Baby green anacondas are known to be more aggressive than adults. They bite more frequently because they’re more vulnerable to predation. Mortality rates for babies and smaller males are higher due to their size.
👉🏼 Green Anacondas Give Birth to Larger Young Than Most Snakes
Baby green anacondas are much larger when born than the average snake. At birth, they average a weight of almost half a pound (200 grams). They’re born at about 27 inches (68 cm) in length.
👉🏼 The Size of a Green Anaconda Can Depend on its Habitat
Green anacondas that live in river basin habitats tend to be larger than those found in savannas. This is thought to be because of prey availability. Prey might not be as available during dry seasons in savannas.
River-dwelling anacondas tend to have more abundant food sources. This allows them to reach greater lengths and weigh more.
You may also like: All 25 Types Of Crocodile Species: ID Guide With Facts And Pictures
Green Anaconda FAQs
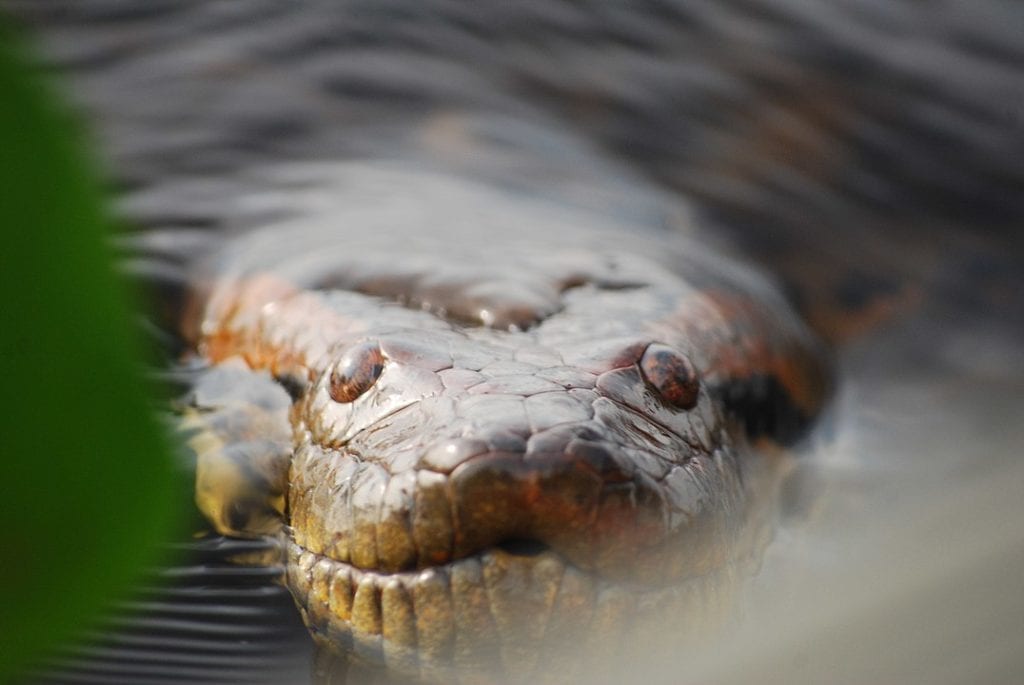

Can green anacondas eat humans?
Green anacondas have the ability to eat humans, but it’s a very rare occurrence. There is actually little to no evidence of green anacondas eating humans. Since they live solitary lives in areas with low human populations, it’s extremely rare for green anacondas to eat a human.
Are green anacondas good pets?
Green anacondas aren’t practical pets for your average pet owner. These snakes can get very large and need a proper enclosure to develop healthily.
This snake would not be a good pet for a child or anyone under the age of 18. Although they can be calm creatures, their size should be respected.
Is a green anaconda snake poisonous?
No, green anacondas are not poisonous. They belong to the Boidae family. This family consists of nonvenomous constrictor snakes.
What eats an anaconda?
Adult female anacondas don’t have any predators. But small males and baby green anacondas can be eaten by larger predators. Some of these predators may include caimans or jaguars.
What is the biggest anaconda ever found?
The biggest anaconda ever recorded weighed in at 500.5 pounds (227 kg) and reached a length of almost 28 ft (8.43 m). Its diameter was 3.6 ft (1.11 m).
More from Outforia
Learn more about these other amazing snake species!










