
Unlike most of the animals that live in the ocean, whales are mammals. This means that they have lungs and need oxygen to breathe. If a whale were to sleep the way that humans do, they would probably drown.
A whale’s entire brain doesn’t shut down while it’s sleeping. Instead, half of its brain will stay conscious so that the whale can breathe and look out for predators.
This may seem exhausting to us because a whale never truly falls asleep like we do. But, it’s a good way for the whale to get much needed rest while staying safe.

share this image on your site
<a href="https://outforia.com/how-do-whales-sleep/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/how-do-whales-sleep-infographic-1222-683x1024.jpg"></a><br>how do whales sleep <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>Where Do Whales Sleep?
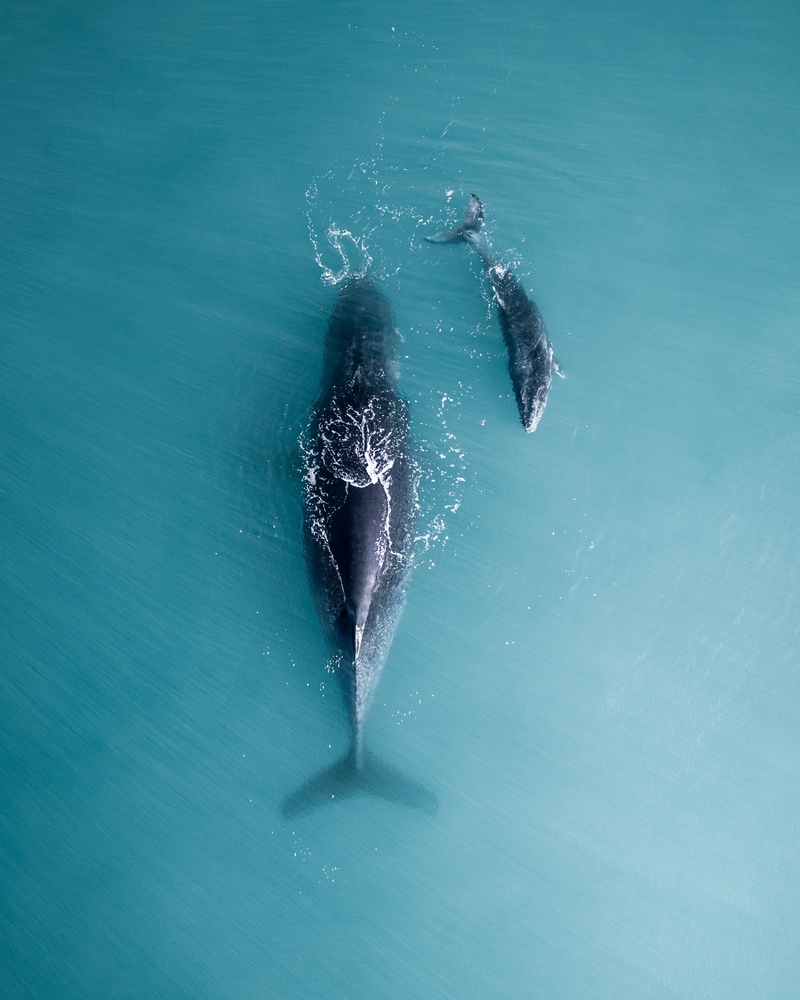

In general, whales stay at the surface or close to the surface of the water while they’re sleeping. This allows them to easily come up for air when needed.
Whales are also very buoyant because of the amount of blubber in their bodies. This helps them continue to float while sleeping without worrying about sinking. Most whales will continue to swim with their pods while asleep, but some whales, like the sperm whale, can rest in place. You will even see some whales sleeping vertically.
How Do Whales Breathe When They Sleep?

Whales don’t breathe the same way that humans do, so they don’t sleep the same way either.
As humans, we are involuntary breathers. We don’t need to be awake to tell our bodies to take in oxygen, it just does it on its own. This is why we’re able to sleep for long periods of time without thinking anything of it. Our bodies just keep breathing for us.
How Do Whales Sleep Without Drowning?

If whales were to just fall asleep the way humans do, their bodies would not keep breathing and they would drown. In order to breathe, a whale needs to be “conscious”. This doesn’t mean that they need to be fully conscious, though. It simply means that at least one part of their brain needs to be “awake”.
If whales breathed involuntarily like humans do, they would likely drown during their day-to-day swimming. Obviously, it would not be good to be swimming underwater when your body decides to take a breath.
Whales don’t breathe like humans, but they don’t breathe like fish either. Whales do not have gills, and cannot respire using water. It is very important, then, that they remember to take intermittent breaths even while asleep.
Whales also have respiratory systems that are significantly larger than that of other mammals. Their lungs are specialized and allow them to breathe in more air at one time than would be possible for a human.
Not only can they take in more oxygen, but they can utilize more of the oxygen that they take in. Researchers think that whales can use up to 90 percent of the total oxygen they breathe in. Conversely, humans can only use about 15 percent of the total oxygen they breathe in.
The extra oxygen helps to transfer blood to their vital organs. It also helps them hold their breath much longer than is possible with most mammals.
Not only can whales use the majority of the oxygen that they take into their bodies, but they can even monitor the amount of oxygen in their body. If they are running low on oxygen, they have the ability to shut down some of their vital systems temporarily. Shutting these areas down allows them to utilize oxygen and blood flow where it’s needed most.
You may also like: Learn About The 21 Majestic Types of Whales Roaming on the Ocean: With Chart, Images, Classification and More!
What Happens To A Whale’s Brain When They Sleep?

How whales sleep is really interesting. A sleeping whale’s brain is still aware of what’s going on around them. This allows them to remain at the surface of the water so that their blowhole can take in air.
How this works is that most whales will sleep with half their brain shut off. This is a process called, “unihemispheric slow-wave sleep”. This gives one side of their brain a chance to rest and reset. The other half of the brain is awake to keep the whale breathing.
Also, the eye opposite to the side that is awake will remain open and alert. This can help whales protect themselves from predators, and allows them to keep an eye on the other members of their pod.
After about two hours, the brain will switch which side of the brain is resting. Switching every few hours allows the whale’s whole brain to receive an adequate amount of rest.
Brain Structure
It’s no secret that whales have some of the biggest brains in the world. For example, orcas have the second largest brain in the animal kingdom when compared to their body size. To give you some perspective, an orca’s brain is about the size of a basketball and can weigh up to 15 pounds/6.8 kilograms.
Many researchers believe that some whales, like orcas, are capable of cognitive thinking in addition to feeling emotion. Believe it or not, but their brains are more complex than human brains in some ways.
The part of the brain that controls emotions, the limbic system, is more developed than the limbic system of humans.
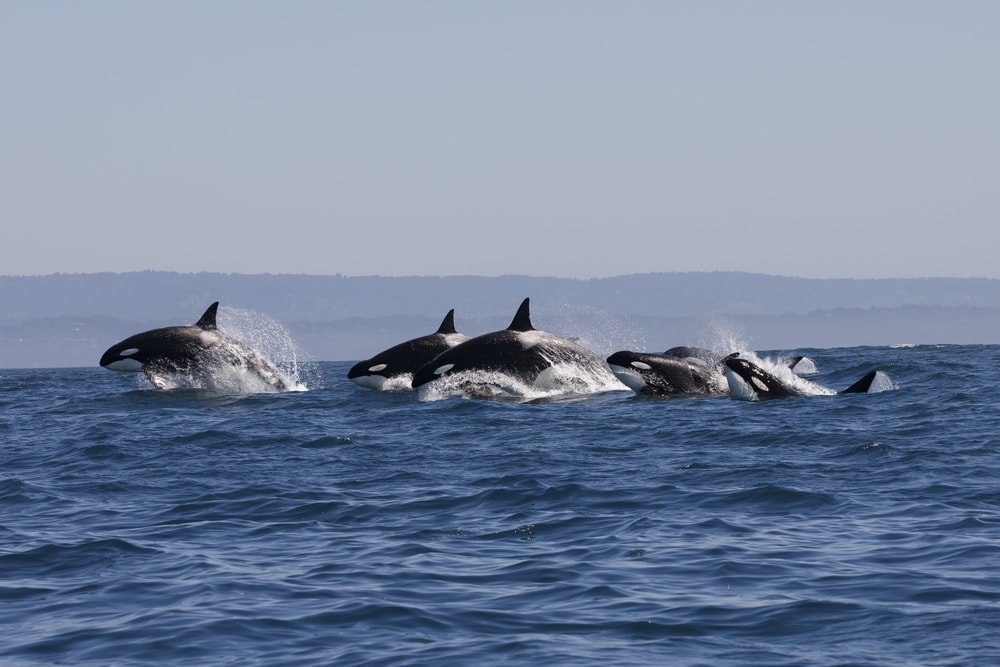

There is an entire system in an orca’s brain that humans do not have — the paralimbic system. The paralimbic system is a lobe made of tissue that is found next to the limbic system. This is a whole extra lobe that humans don’t have! This is the part of the brain that researchers suggest might allow for cognitive thinking.
Orcas live in social family pods, and they respond very emotionally to their family members. When an orca becomes injured, its fellow orcas will respond with such complex emotion that isn’t even seen in humans. Because of this, researchers believe that the paralimbic system allows orcas to have a sense of self as well as create special bonds with their pod members.
You may also like: Learn More About The 25 Adorable Types of Dolphins: Complete with Chart, Images, Facts, and More!
What Happens To A Whale’s Body When They Sleep?
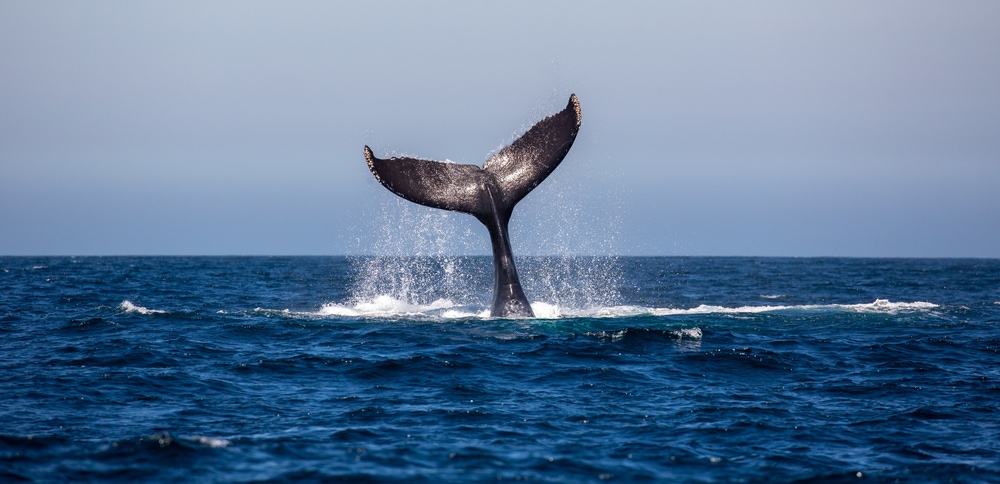

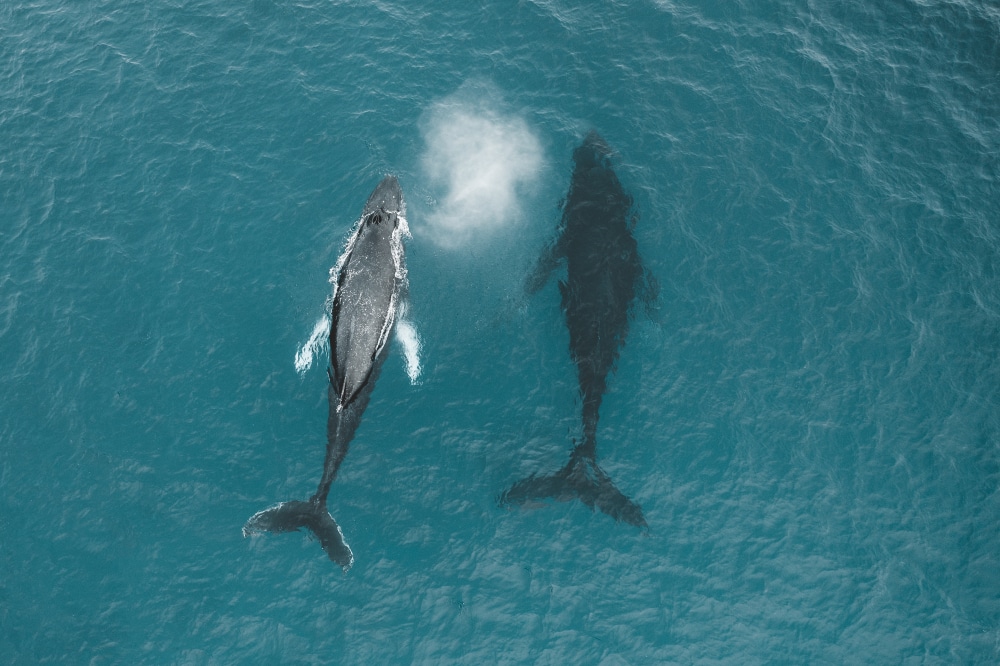
Because a whale only shuts down half of its brain while it’s sleeping, the whale doesn’t need to stay in one place. In fact, many whales will continue to swim side by side with their other pod members even while asleep. The half of the brain that is awake reminds them to take a breath every time they swim to the surface.
By continuing to swim, it’s a lot easier for the whale to take breaths. They simply swim up to the surface when they need to breathe.
Besides that, swimming while sleeping likely helps them regulate their body temperature. Whales need to keep their body temperature within a certain range. In water, a body loses heat much faster than it does in air. A whale likely needs to keep moving to keep its body temperature up.
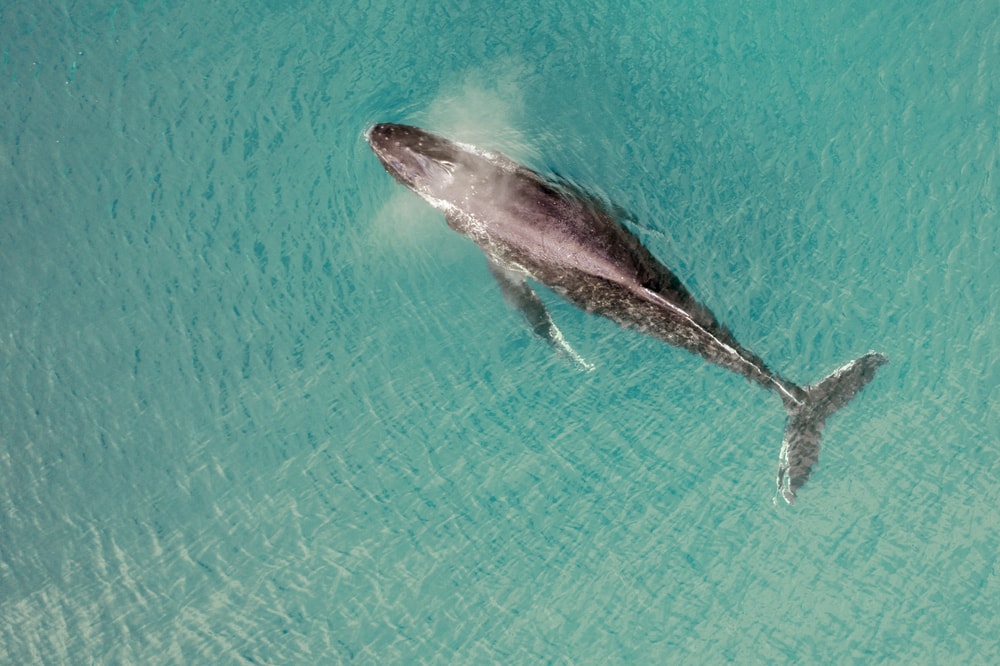

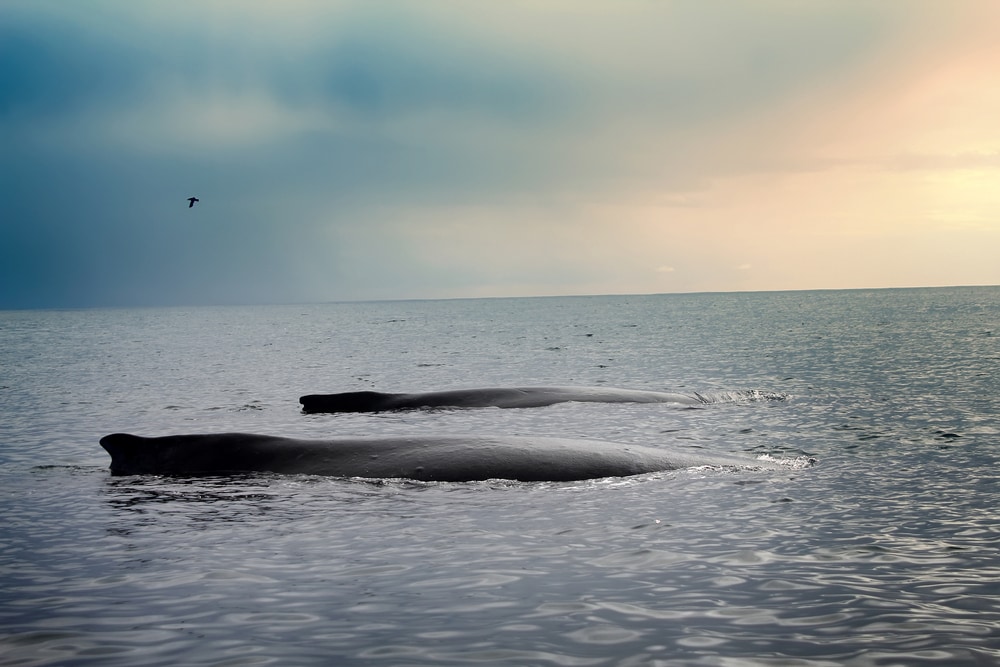
When they don’t want to swim, whales may choose to sleep floating still near the surface. Smaller whales are less likely to do this because they can only sustain it for a few minutes at a time. It’s much more likely in large whales like Blue Whales and Sperm Whales who can hold their breath longer.
When floating at the surface, you may notice the whale positioned how it is when it swims: horizontally. Some people refer to this sleeping position as “logging”. The whales are so still while in this position that they could be mistaken for a log if they weren’t so large.
Another way that a whale might float is by hanging upside down. This may seem unnerving when witnessed by someone who has never seen it before. After all, a completely still, unbreathing whale that is hanging upside down isn’t a normal site. But, this is just how some of them choose to sleep.
You may also like: Learn How Do Sharks Mate and How They Reproduce: Complete With Images, Facts, and More!
How Long Do Whales Sleep?
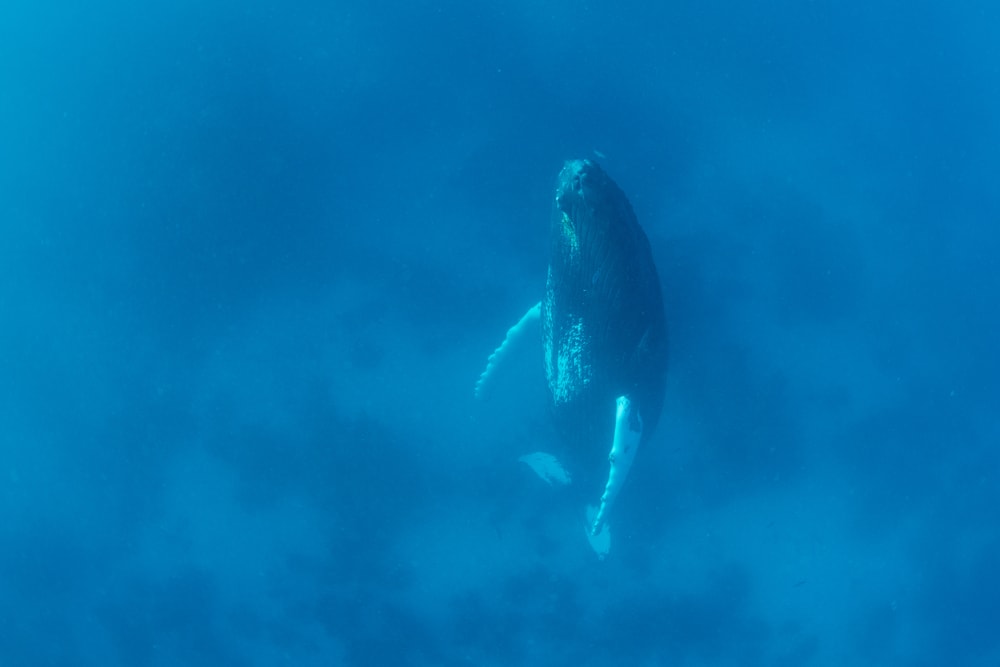

When a whale sleeps and swims at the same time, they can do so for a long time. As I stated above, whales will switch between shutting each half of their brain off about every two hours.
However, if a whale is floating, they can only maintain that for a much shorter time. The sleeping time for a floating whale is generally about 10-15 minutes. Some larger whales can manage to sleep at the surface for up to half an hour at a time. Because of how short these sleeping sessions are, many people refer to them as “cat naps”.
You May Also Like: How Long Can Whales Hold Their Breath? Deep Divers & Master Lungs
Do Whales Dream?

Much is still not known about the sleeping patterns of whales. However, it doesn’t seem like whales go into REM, or rapid eye movement, sleep. REM is the stage that the body must usually enter in order to dream. Without it, it’s unlikely that whales can dream.
However, not all dreaming occurs during the REM stage, so it’s possible that whales might have dreams. The truth is, researchers just don’t have the answer yet.
You may also like: Check out These 25 Ferocious Types of Shark Lurking on the Ocean: With Images, Facts, Chart, More!
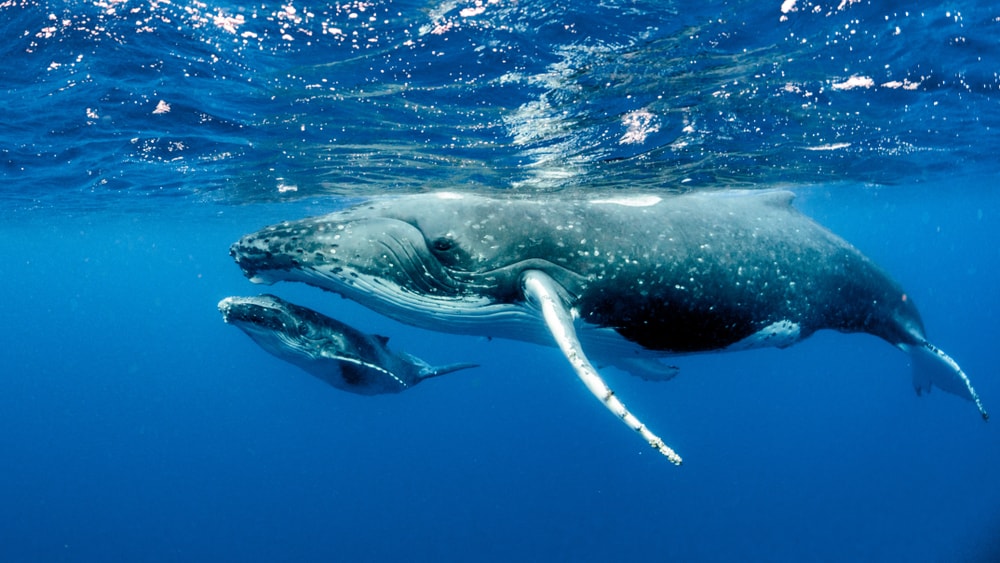
How Do Whale Calves Sleep?
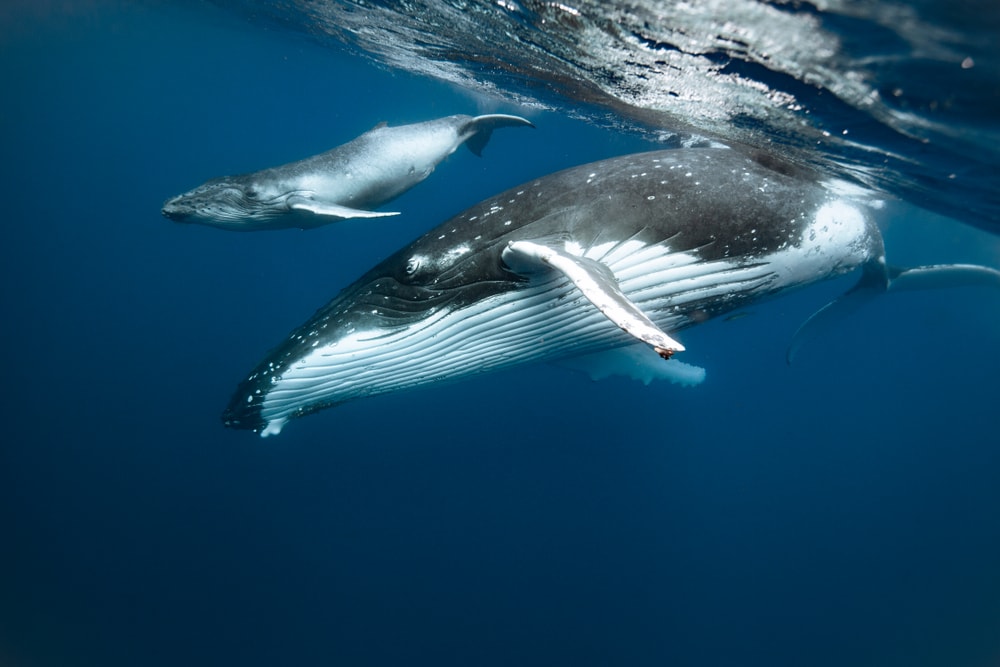

When calves are born, they are born with very little to no blubber. Because of this, they’re not able to float, and their mothers are the only thing preventing them from sinking and drowning. How then, do calves manage to sleep?
It’s actually a pretty interesting process. Calves sleep by what is called “echelon swimming”. Echelon swimming is when the calf will swim behind the mother in her slipstream. A slipstream is a kind of current that is created by the mother’s movement. The calf can effectively rest and sleep inside this slipstream without sinking. They will simply be pulled along behind their mother.
Echelon swimming is important for more than just sleeping, though. Calves are much smaller than adults, and they don’t have much muscle or blubber to store energy. By swimming along behind the mother in her slipstream, the calf is able to gradually build up strength.
You may also like: Learn the Different Species of Sharks You Might See on Maui’s Shores: With Images, Facts, Chart, and More!
How Do Sperm Whales Sleep?
Sperm whales and other large whales have much larger respiratory systems than the smaller whales. Because their lungs are larger, they’re able to hold their breath for a longer period of time. Because they don’t need to come to the surface as often for air, they can sleep while in a stationary position.
These larger lung systems are efficient not just for sleeping. They allow the whale to take in more air, but they also give the whale a higher tolerance for carbon dioxide.
How sperm whales sleep is a lot more interesting than them just being able to take in extra air. Researchers and divers alike have witnessed the unique phenomenon that is sperm whales sleeping.
It seems that when they sleep, sperm whales will sleep together in their pods. This is likely due to protection because the calves are kept at the center of this sleeping “circle”.
What’s more interesting, though, is how they sleep. I already discussed how many whales can sleep while floating. When doing this, most whales will sleep horizontally like a log. Not sperm whales. They will sleep vertically with their heads pointed toward the surface.








