Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- The first dinosaur specimen was discovered by Robert Plot in 1676, but not identified as a dinosaur at that time
- Dinosaurs are a group of extinct large reptiles that could walk upright, lived during the Mesozoic Era for over 140 million years
- Sir Richard Owen coined the term “Dinosauria” in 1842, grouping Megalosaurus, Iguanodon, and Hylaeosaurus
- First dinosaur bone, a large femur, found by Plot in Oxfordshire, England in 1676
- Dinosaurs lived on Earth during the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era

Have you ever wondered exactly when dinosaurs were discovered? Well, the first dinosaur specimen was discovered by English naturalist Robert Plot in 1676. The existence of dinosaurs was unheard of at that time.
Although Plot discovered what was later known as the first dinosaur bone discovered, he didn’t know what the bone belonged to.
The first dinosaur bone to be discovered was initially thought to be a bone from a Roman war elephant or a human giant referenced in the Bible.
Later dinosaur fossil discoveries were thought to be large extinct reptiles, but dinosaurs didn’t have a group of their own yet.
It wasn’t until the 19th century that more dinosaur fossils began to pop up around the world. The first dinosaur remains found in North America were discovered in the mid-1800s.
You May Also Like: How Many Rhinos Are Left Today? Learn About The Crisis Facing These Majestic Creatures
What Are Dinosaurs?

Dinosaurs are a group of extinct large reptiles that could walk upright. They roamed the Earth during the Mesozoic Era for more than 140 million years. One of the oldest groups of dinosaurs is believed to have appeared on Earth in the Triassic Period about 251 million years ago.
There’s a common misconception that many of the large reptilian creatures that roamed Earth during the age of dinosaurs are also considered dinosaurs. However, there are several characteristics that set dinosaurs apart from other prehistoric reptiles.
The biggest difference is the upright stance that dinosaurs have compared to other prehistoric and modern-day reptiles. Dinosaurs had a hole in the hip socket which allowed them to walk this way. Other reptiles often mislabeled as dinosaurs didn’t have this feature.
The term dinosaurs was nonexistent until Sir Richard Owen coined the term Dinosauria in 1842. Owen was a well-respected anatomist. He was largely responsible for the splitting of the British Museum, which led to the founding of the Natural History Museum in London, UK.
Based on his studies of three recognized extinct reptile genera, Owen noticed similar characteristics between the fossilized specimens.
Owen grouped together the Megalosaurus, Iguanodon, and Hylaeosaurus genus’ to create the clade Dinosauria. For the first time, these strange and highly unknown extinct reptilian animals were given a category of their own.
When Were Dinosaurs Discovered?
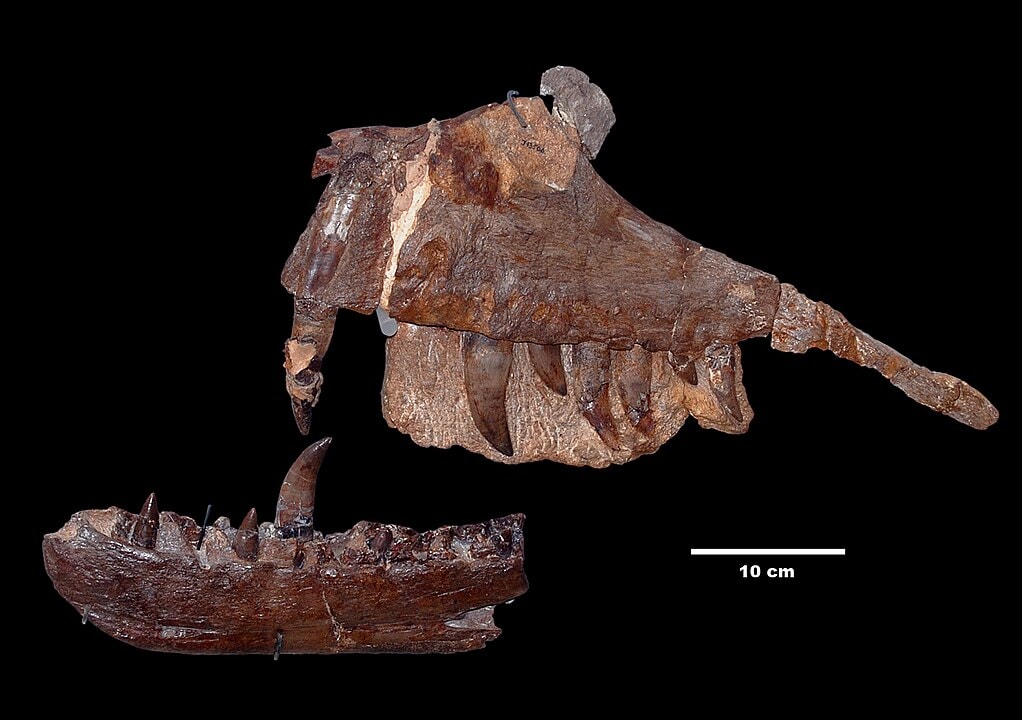

Dinosaur bones were first discovered in 1676 by Robert Plot. The bone was a large femur found at the Taynton Limestone Formation of Stonesfield quarry site in Oxfordshire, England.
Plot and other scholars didn’t know what the bone belonged to. Plot published an illustration of the bone in his book The Natural History of Oxford-shire in 1677.
In his book, Plot described the bone as belonging to a Roman war elephant. He later changed his description and believed the bone belonged to a human giant.
The illustration of the bone reappeared in the publication A System of Natural History by English physician Richard Brookes. He gave the bone the name Scrotum humanum, as it resembled a human scrotum.
A collection of fossils found near Oxfordshire in Stonesfield were described by geologist and paleontologist William Buckland in 1824. The fossil remains were described by Buckland as Megalosaurus.
Although this was the first official scientific description of a dinosaur, it was described as a giant lizard creature rather than a dinosaur. Buckland also believed that Plot’s dinosaur bone belonged to a Megalosaurus.
It’s generally accepted today that Plot’s dinosaur bone belonged to a Megalosaurus. However, the bone went missing a long time ago so its identification cannot be confirmed by modern-day technology.
The First Dinosaur Discovered

A Megalosaurus is deemed the first type of dinosaur discovered and validly named. British geologist and paleontologist Gideon Mantell gave the species its official scientific name, Megalosaurus bucklandii, in his 1827 publication The Geologist of the Southeast of England.
Megalosaurus fossils that Buckland discovered revealed some of the habits and characteristics of the specimen.
The teeth of Megalosaurus showed that it was a carnivorous dinosaur group. Using its bones, it’s estimated that Megalosaurus species were about 40 ft (9 m) long.
Later studies of Megalosaurus bones revealed that these prehistoric reptiles roamed Earth about 170-155 million years ago in the Mid-Jurassic Period.
While scientists and researchers were trying to unravel the mystery of these dinosaur bones, it was largely accepted that they were large extinct reptiles. The idea that these creatures could be categorized separately didn’t come until Richard Owen introduced the clade Dinosauria.
The First Dinosaur Discoveries in North America

The first dinosaur bones found in North America were discovered by American geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden in 1854. Hayden was on an expedition near the upper Missouri River when he stumbled upon fossilized teeth in Montana.
American paleontologist Joseph Leidy described the dinosaur teeth found in Montana in 1856. Leidy described the teeth as being 75 million years old in his report entitled Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia.
Leidy also described one of the most complete dinosaur skeletons discovered in North America in 1858. He gave the creature the scientific name Hadrosaurus foulkii. The mostly intact skeleton was found in Haddonfield, New Jersey by William Parker Foulke.
The public became more aware of the concept of dinosaurs in the 1870s in the midst of the First Great Dinosaur Rush. This period is known for an abundance of dinosaur fossil discoveries, mainly found in Colorado and Wyoming.
A second dinosaur rush occurred in the early 1900s. Scientists conducted large-scale dinosaur fossil hunting expeditions in southern Alberta, Canada.
The discovery of dinosaur remains during the Second Great Dinosaur Rush provided further insight into dinosaur characteristics and behaviors in the late Cretaceous Period.
Timeline of the Age of Dinosaurs

The timeline of when dinosaurs lived on Earth can become clouded as the Jurassic Period is popularly known as the age of dinosaurs. However, dinosaurs also existed in the Triassic and Cretaceous periods of the Mesozoic Era.
The Mesozoic Era is defined as occurring 252-66 million years ago. The end of the Mesozoic Era aligns with the mass extinction of dinosaurs and other living things around 66 million years ago.
Triassic Period

The Triassic Period took place 252-201 million years ago. The climate and landscapes of the Earth were much different in the Mesozoic Era than what we see today.
A mass extinction took place at the end of the Paleozoic Era (541-252 million years ago) in the Permian Period that may have changed the composition of the Earth and the creatures that lived during this period
During the Triassic Period, all of the land on Earth was conjoined into one giant landmass called Pangaea.
The Earth’s tectonic plates began to move in different directions and pulled the land apart. In the late Triassic Period, the diverging plates divided Pangaea into two great landmasses and formed the North Atlantic Ocean.
These land masses became known as Laurasia and Gondwana. Laurasia was made up of North America and Eurasia. South America, India, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica were conjoined as Gondwana.
Reptiles evolved and thrived in the hot, dry climate of the Triassic Period. Polar ice caps didn’t exist during this period. Reptiles were the dominant land creatures.
According to fossil records, the first dinosaurs may have appeared around 240 million years ago.
Some dinosaurs known to live during the Triassic period include Chindesaurus, Coelophysis, Herrerasaurus, Plateosaurus, and Eoraptor.
A mass extinction event occurred at the end of the Triassic Period. It’s still unknown what triggered the event, but theories suggest it could be related to a significant increase in volcanic activity.
Jurassic Period

The Jurassic Period took place between 201-145 million years ago. This period has inspired popular dinosaur movies like Jurassic Park and Jurassic World.
The climate during this period was still warm and resembled tropical conditions. However, climate and weather conditions slightly differed as the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Mexico appeared by the splitting of Pangaea.
Large plant-eating dinosaurs and small carnivorous dinosaurs existed in this period.
Some herbivorous dinosaurs that lived in the early Jurassic Period include:
- Scelidosaurus
- Scutellosaurus
- Vulcanodon
- Yimenosaurus
Early Jurassic carnivorous dinosaurs included:
- Sarcosaurus
- Lophostropheus
- Dilophosaurus
- Cryolophosaurus
Some dinosaurs, such as the Yunnanosaurus, were omnivores. More dinosaurs appeared in the mid to late-Jurassic Period, such as Brachiosaurus, Megalosaurus, and Stegosaurus.
Cretaceous Period

The Cretaceous Period took place between 145-66 million years ago. It’s the last period in the Mesozoic Era. Several changes occurred during this period, including the continuous splitting of the two landmasses into large island continents.
To give you an idea of how different the Earth was, some familiar landscapes in the US like the Rocky Mountains and Appalachian mountains were still mostly underwater. Sea levels were rising and global climate conditions were becoming more mild.
Flowering plants appeared in this period. This allowed various insects, including pollinators, mammals, and birds to evolve. Dinosaurs were still abundant and new genus’ appeared, such as Giganotosaurus, Microraptor, Triceratops, and Tyrannosaurus.
The mass extinction event that occurred 66 million years ago wiped out most of the Earth’s plants and animals. The event was believed to be caused by a meteorite that struck Earth in the Gulf of Mexico.
The meteorite triggered other natural disasters that contributed to the extinction of many species. Any dinosaur species that had not gone extinct in previous periods went extinct during this event.
The Cenozoic Era, also referred to as the age of mammals, began after the Mesozoic Era.
You May Also Like: What Do Wild Rabbits Eat? A Diet Of The Obvious And The Odd
First Types of Dinosaurs Discovered
What we know about dinosaurs comes from fossil evidence. Since many dinosaur fossils may be hiding deep in the Earth below us, we can only go off of what’s already been discovered.
Scientists don’t know what the very first dinosaur was on Earth, but fossil evidence provides some insight into what was alive and when.
Nyasasaurus
Scientists believe that dinosaurs existed prior to the dates of the earliest dinosaur fossil records available.
The fossil of possibly a true dinosaur species, Nyasasaurus parringtoni, was discovered in the 1930s. Found in Tanzania, this discovery has pushed the date of the earliest dinosaurs back by at least 10 million years.
The species may put the appearance of the earliest dinosaurs around 243 million years ago or more.
A 2013 study published by paleontologists in The Royal Society Publishing described the species.
The paleontologists describe N. parringtoni as possibly the earliest member of the clade Dinosauria, or a closely related taxonomic group.
If N. parringtoni isn’t a true dinosaur, some scientists believe that it’s a very close relative that could be linked to the origin of dinosaurs.
One theory is that this species may be a missing piece that connects dinosaurs with a common ancestor called silesaurids.
The discovery of Nyasasaurus may be important for the study of dinosaur fossils in Argentina and Brazil. Paleontologists and dinosaur researcher Professor Paul Barrett have unearthed early dinosaur fossils in the Ischigualasto Formation.
The fossils are characterized as recognizable dinosaurs. Professor Barrett suggests that since they’re already recognizable, this could mean the origins of dinosaurs are even later than previously believed.
Herrerasaurus
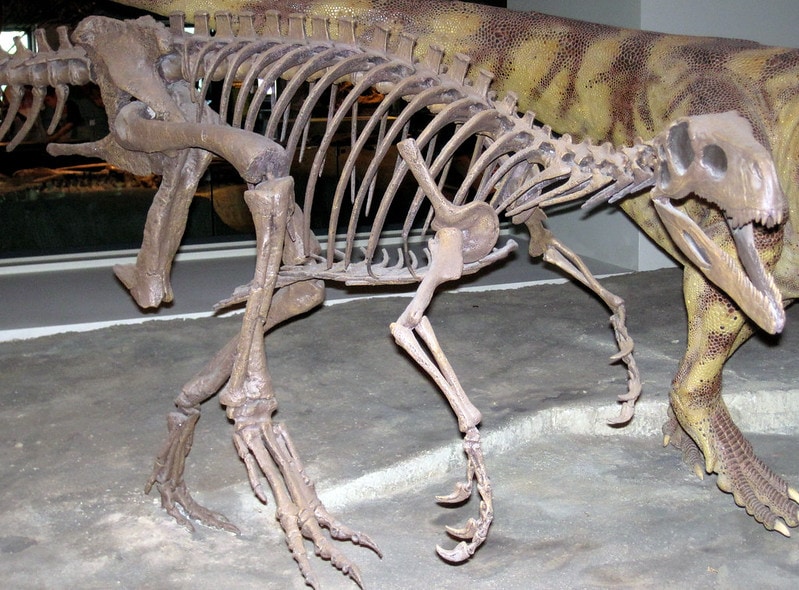

Herrerasaurus dinosaurs were small and carnivorous. They lived in the late Triassic Period about 228 million years ago.
The first fossils belonging to this genus were found in the Ischigualasto Formation of Argentina. It was described by Osvaldo Reig in 1963.
The skeleton originally discovered by Victorino Herrera wasn’t complete enough to identify what the species looked like. However, the discovery of additional bone fragments and a skull in 1988 helped piece this dinosaur together.
These dinosaurs were bipedals with long tails and small, grasping hands. Based on fossil evidence, this description matches what scientists think resemble most early dinosaur species.
Eoraptor
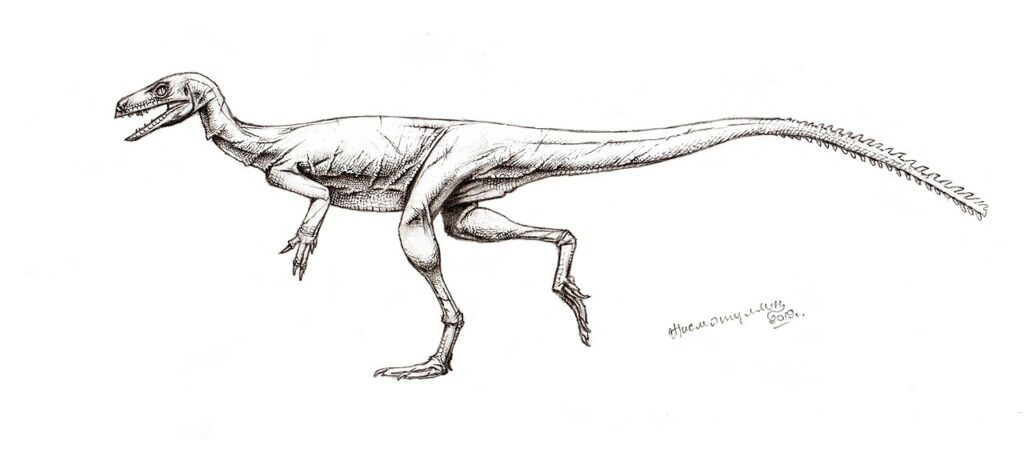
Eroraptors were small, carnivorous dinosaurs that averaged about 3.3 ft (1 m) in length. The first Eoraptor fossil was found by paleontologist Dr. Paul Sereno during an expedition in Argentina in 1991.
Eoraptors lived in the late Triassic Period around 228 million years ago. Its size and bipedalism reflects characteristics of early dinosaur species.
There is some debate on whether Eoraptors are considered true dinosaurs. They don’t have some of the main traits of any dinosaur group. Some believe that it’s actually a close relative in the clade Archosauria. This group includes dinosaurs.
Pisanosaurus

Pisanosaurus is one of the oldest known dinosaurs closely related to birds. This genus is referred to as bird-hipped dinosaurs because they have a different hip bone arrangement than other dinosaurs.
In the late 19th century, scientists divided dinosaurs into two clades: Saurischians and Ornithischians. Saurischians have a reptile-like pelvic structure.
Pisanosaurus lived in the late Triassic Period around 227-221 million years ago. The first fossil was discovered in the Ischigualasto Formation in 1962. It was first described in 1967 by Rodolfo Casamiquela.
How Are Dinosaur Fossils Studied?
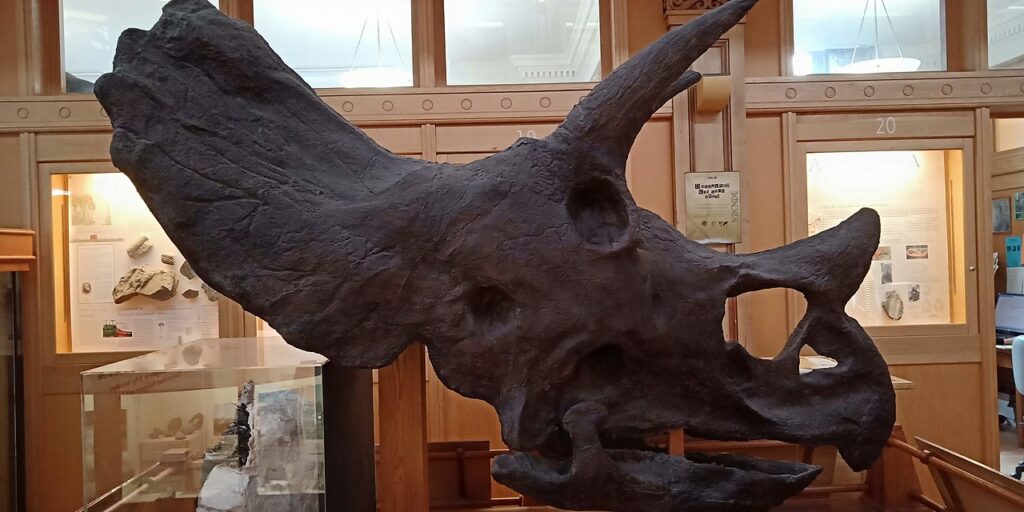

Scientists study dinosaurs by examining fossil evidence. This could include complete dinosaur skulls, bone fragments, teeth, soft tissue impressions, footprints, and more.
Body fossils and trace fossils are two groups scientists use to categorize fossil evidence. Body fossils include remains of dinosaurs. Trace fossils, such as footprints, give scientists insight on the activity of dinosaurs.
Finding complete skulls or fully intact dinosaur skeletons is rare. One common method used to date fossils is identifying the date of the rock the fossil was found in. This can be done by studying the layers of sedimentary rock.
It’s uncommon for such large creatures to turn into fossils. There are several elements needed for something to turn into a fossil.
The mass extinction event that wiped out all of the dinosaurs may have helped fossilize these prehistoric reptiles.
Paleontologists are scientists that study fossils. When fossils are brought into a lab, a fossil preparator carefully removes surrounding material from the fossil. Various substances like adhesive are used to help keep the fossil intact.
Paleontologists go to areas where dinosaur fossils are likely to be found and conduct fieldwork. Microscopes are often used to look at dinosaur bones. Much like tree rings, dinosaur bones have growth lines inside that help scientists determine its age.
Fun Facts
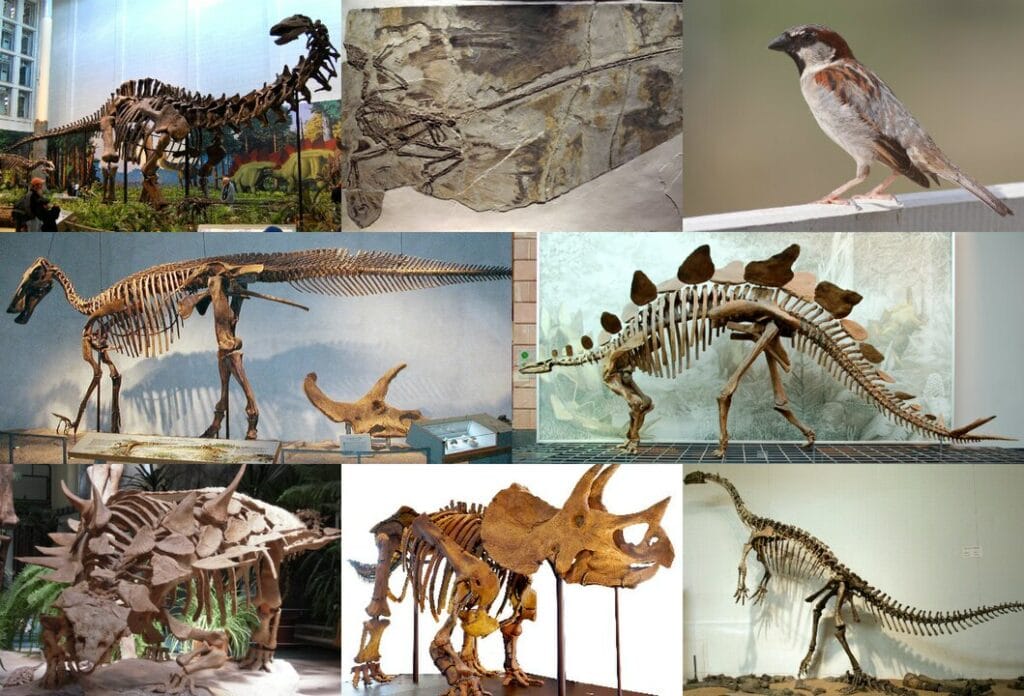

Pterodactyls aren’t dinosaurs.
Pterosaurs, or commonly known as pterodactyls, actually aren’t dinosaurs!
This is a common misconception because these prehistoric reptiles lived in the age of dinosaurs. Although closely related, pterodactyls don’t have some of the key anatomical structures that dinosaurs have.
The first pterosaur fossil was found at a limestone quarry in Germany in the mid-18th century. It was described by Georges Cuvier as a flying reptile after decades of debate on the creature.
Birds are the closest living relative to dinosaurs.
There are several types of characterizations used to distinguish different dinosaurs. One of these characterizations includes two groups consisting of avian and non-avian dinosaurs.
Our modern-day birds evolved from small, non-avian theropod dinosaurs. Birds are considered avian dinosaurs. The oldest bird fossils found are about 150 million years old, which means birds existed during the late Triassic Period.
Many dinosaurs had feathers.
For years scientists thought that dinosaurs had reptile-like skin. However, scientists have discovered that many dinosaur species had feathers.
Birds are the only living things on Earth that have feathers. Several well-preserved dinosaur fossils including features of feathers have been found in the Liaoning Province of China.
Dinosaurs may have evolved to possess feathers because they’re useful for many things. Some dinosaurs may have had less feathers than others, making this feature less likely to appear in fossils.
You May Also Like: Complete Guide To Different Types Of Leaves With Pictures And Leaf Names
When were dinosaurs discovered FAQs

What existed before dinosaurs?
Before dinosaurs appeared in the Triassic Period, there were other living organisms on Earth in the Permian Period. This was the last period in the Paleozoic Era.
The Permian Period took place between 299-252 million years ago. Animals that lived during this period included reptiles and ancestors to mammals called synapsids.
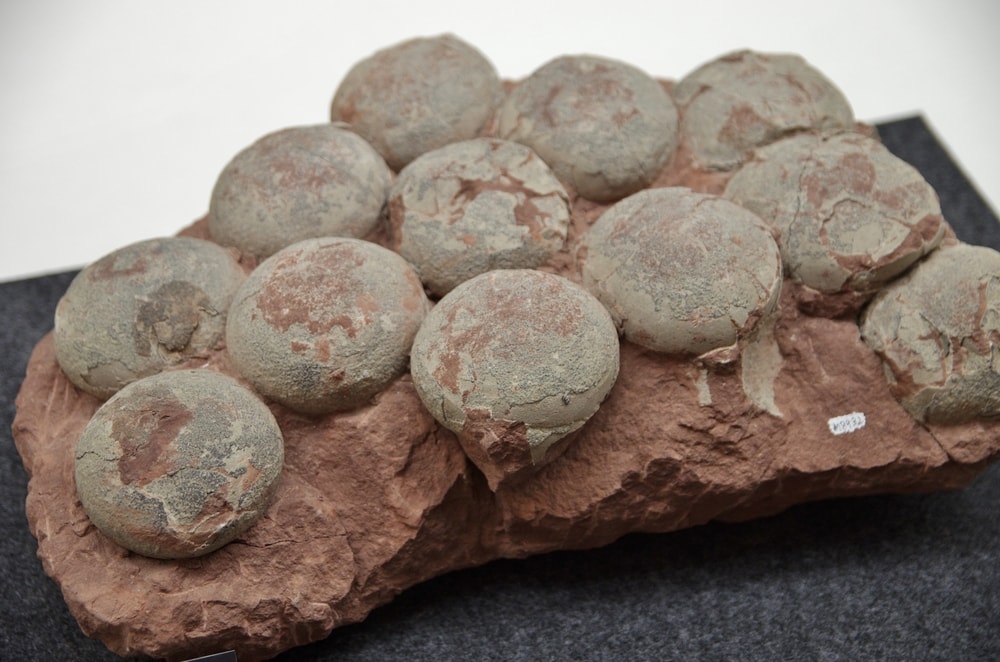
How is a dinosaur born?
One of the common traits of all true dinosaurs is their reproduction process. All dinosaurs laid eggs.
Dinosaurs were also known to have a fast maturing rate. Based on fossil evidence, scientists have determined that dinosaurs experienced a teenage growth spurt just like humans.
Their rapid growth from a small hatchling to some adult species weighing thousands of pounds is unlike any modern-day animal.
How big were dinosaurs on average?
The size of dinosaurs varied widely. There were some dinosaurs that were as small as a chicken. Other large dinosaurs, like Titanosaurs, were massive.
Patagotitan was a type of titanosaur that averaged a length of 123 ft (37.5 m) long! They weighed around 63 tons (57 tonnes)!
Medium-sized dinosaurs weighed less than 1,000 pounds (454 kg) to upwards of 10,000 pounds (4,536 kg).









