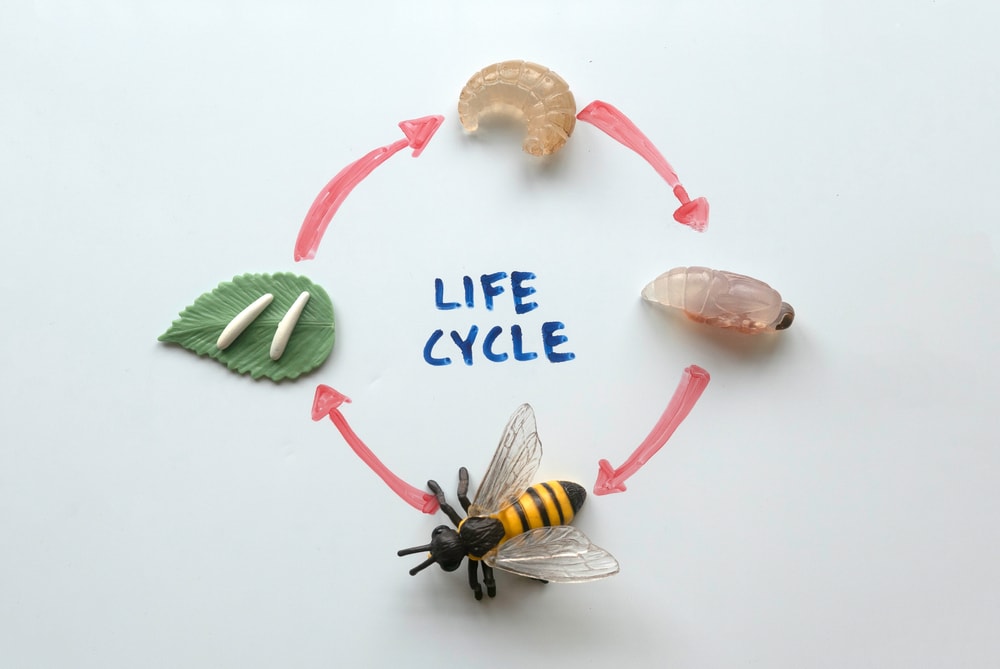
The life cycle of bees is an exciting process that operates like clockwork. As soon as spring begins, you may start to hear them buzzing about full of life.
In fact, their business coined the phrade “busy as a bee” as early as 1392. That’s several centuries of a busy reputation!
But one must wonder: how long do bees live? Luckily, we’ve done our research to answer this question for you!
We’re going to discuss the life cycles of several bee species and talk about some neat bee facts.
What Are Bees?

Bees are insects that belong to the order Hymenoptera. Sawflies, wasps, ants, and bees are part of this order. Bees are then separated into the suborder Apocrita. Within this suborder is the Apoidea superfamily. Apoidea consists of bees and sphecoid wasps.
Within the superfamily, there are seven bee families.
The Apidae family is the largest bee family. It has more than 5,000 bee species! Some of these species include bumblebees, honey bees, and carpenter bees.
Bees are descendants of ancient carnivorous wasps. It’s believed that bees evolved from wasps about 125 million years ago. This was when the first flowering plants appeared. They evolved into bees by eating pollen and drinking nectar to satisfy their hunger.
As of now, there are more than 20,000 bee species buzzing around the world today!
How Are Bees Born?
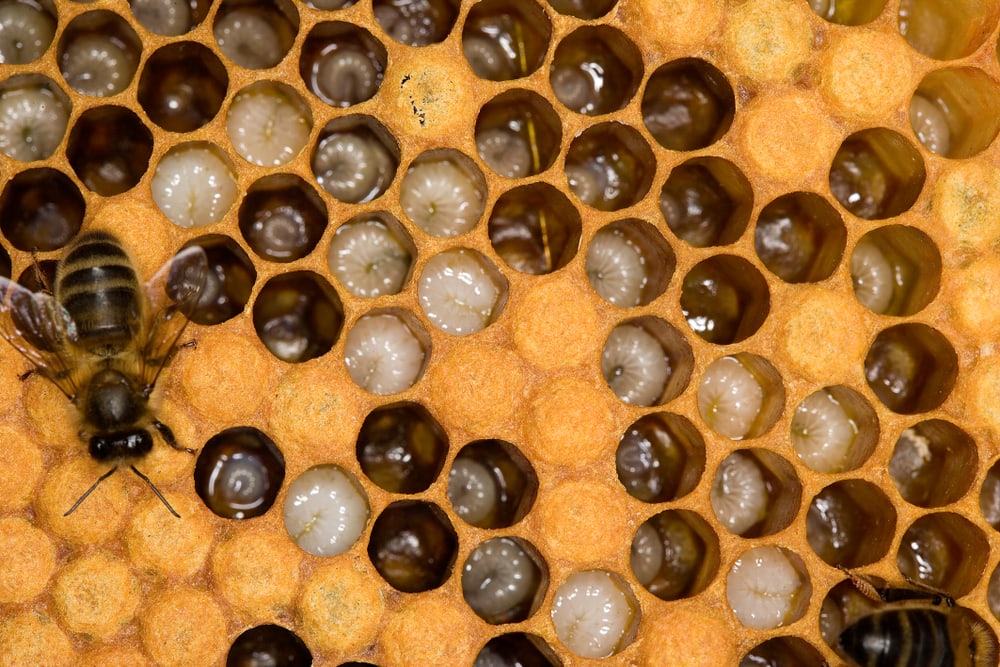

Queen bees lay eggs after finding a suitable nesting site. The egg-laying process depends on the type of bee.
For instance, queen honey bees lay their eggs in a specific section of the beehive. Queen bumblebees typically find a nesting site in a pre-existing cavity.
Larvae emerge from the eggs in about three days. They feed on a mixture of pollen, nectar, and adult bee saliva for nutrition. It takes about 12 days for larvae to complete the feeding stage. After this period, it wraps itself in a cocoon and enters the pupa stage.
In about seven to ten days, bees will emerge from their cocoon. Bees grow into their full size while in the cocoon. Undersized bees may be smaller due to malnutrition or other natural factors.
Once a bee emerges from its cocoon, its wings and exoskeleton will firm up, and it’s ready to get to work!
What Factors Affect a Bee’s Life?

Several factors could affect a bee’s lifespan. Within a bee colony, there are different types of bees. This plays a role in how long the bee will live. Queen bees live longer than female workers or male drone bees.
Harmful factors that affect a bee’s life may include:
- Parasites
- Pesticides
- Viral, fungal, or bacterial infections
- Climate change
- Habitat destruction
Parasites and infections are natural factors that could affect how long a bee lives. Harmful pesticides used to rid plants of insects can also be toxic to bees.
Climate change affects bee lifespans more than you’d imagine. This is due to stressors on habitats, food, and water availability.
Habitat destruction caused by urbanization is another common threat to bees. Extreme weather can also contribute to habitat loss.

SHARE THIS IMAGE ON YOUR SITE
<a href="https://outforia.com/how-long-do-bees-live/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/how-long-do-bees-live-infographic-1-683x1024.jpg"></a><br>HOW LONG DO BEES LIVE <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>How Long Do Bees Live?
Certain bees have longer lifespans than others. Depending on the type of bee and species, a bee might only live for about one month. Worker bees tend to live for about five or six weeks.
Bees that continue to maintain the hive through winter are called wintering bees. Overwintering bees may live as long as six months. A drone bee typically lives for about seven weeks.
How Long Do Queen Bees Live?
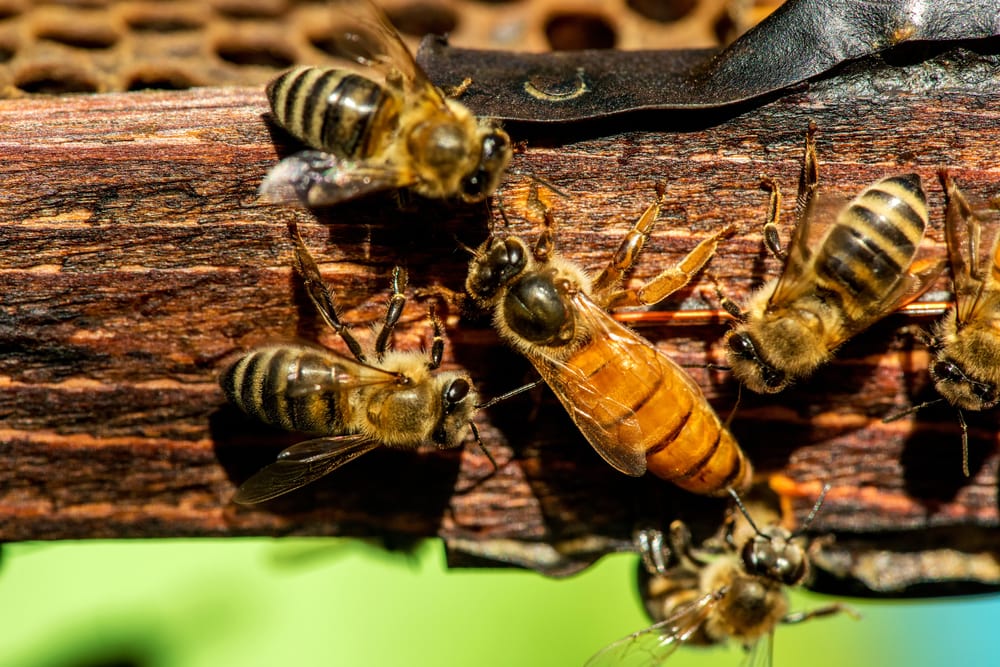

Queen bees live the longest. They generally live for about one year to complete the whole life cycle. Some queen bees can live for two or three years. The typical bee life cycle starts with the queen in early spring. She will emerge from hibernation and begin fueling up on nectar and pollen.
A queen bee will search for a nesting site once she’s gained enough energy from food. She will start laying eggs to make a colony.
Queen honey bees can lay thousands of eggs in their lifetime.
New queen bees are born in the late summer. They mate with a drone bee within a week or two of maturing.
Old queen bees that were born the previous year will die by autumn. The life cycle restarts in the spring with new queen bees.
Bumblebee Lifespan
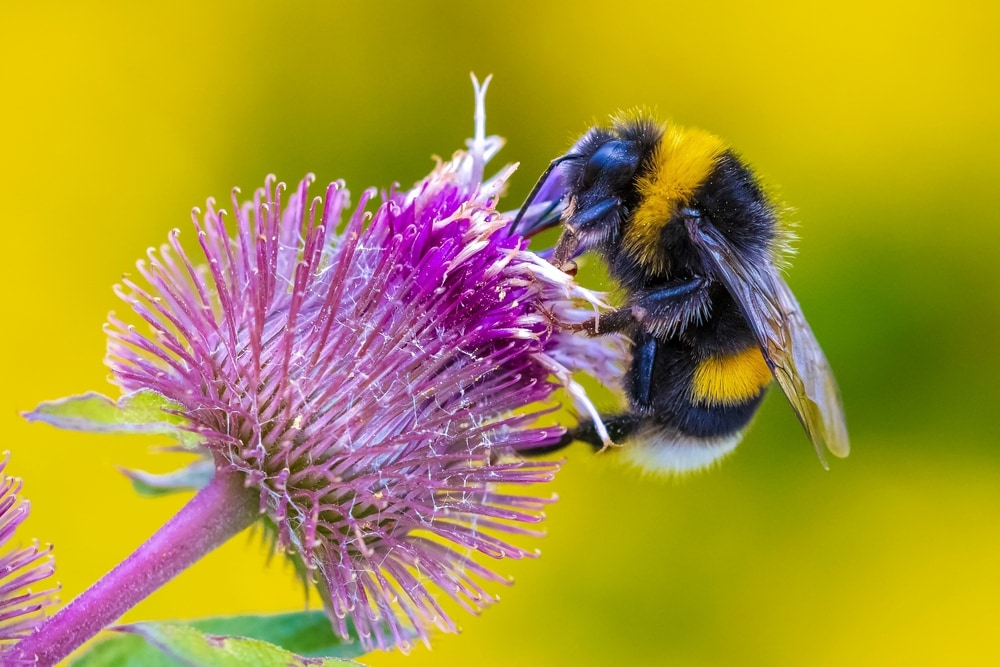

Bumblebees are large, friendly bees. They are primarily black with yellow, white, or orange coloration on their backs.
Bumblebee colonies begin with a queen bumblebee that emerges in the early spring. Unlike honey bees that live in hives, bumblebees nest in the ground. Bumblebee colonies are smaller, averaging about 50 to 400 bees.
A queen bumblebee lays about six eggs in her first brood. These eggs hatch into female worker bees. These bees work for the queen while she focuses on laying more eggs to build the colony. Most female worker bees are sterile and cannot produce offspring.
Queen bumblebees lay both male and female eggs in the late summer. The male bees will then find new queen bees to mate with.
The female bees that are born in late summer become queen bees. They find male bees to mate with before hibernating in an underground site for winter.
Female workers and male bumblebees only live for about one month.
Honeybee Lifespan
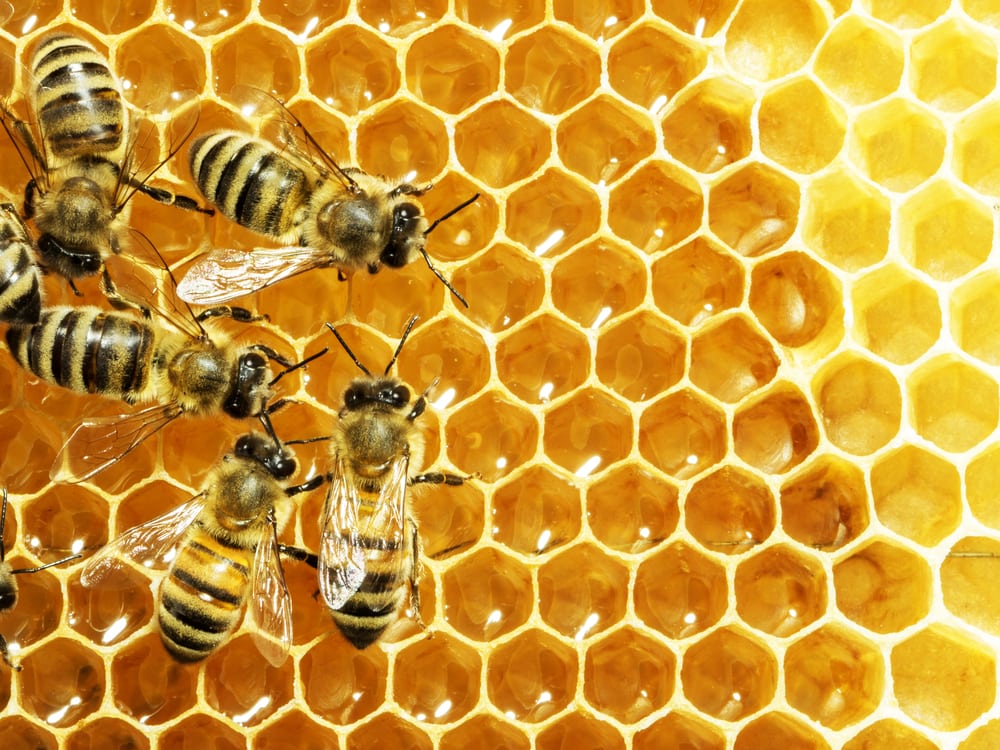

A honeybee’s lifespan is a little different than a bumblebee’s. Honeybee colonies are much larger than other bee colonies. Healthy queen honey bees can lay up to 3,000 eggs per day during the height of egg-laying season.
A honeybee colony consists of female and male bees that have different roles.
Young female worker bees tend to larvae, known as nursing bees. Nursing bees become worker bees once they mature. Worker bees gather nectar and pollen, build honeycombs, and store food.
Male drone bees are born for mating purposes only. Female workers and drones live no more than two months.
Honey bees practice overwintering behavior. This means they don’t hibernate like bumblebees do. Most bees die off during the winter, but younger winter bees can live as long as eight months.
To prepare for winter, worker bees store enough food in the hive. The winter queen bees don’t lay eggs and drone bees don’t mate during winter. They’re forced out of the colony by winter to prevent using up more resources.
When the queen bee dies, she’s replaced with a new queen bee.
Carpenter Bee Lifespan
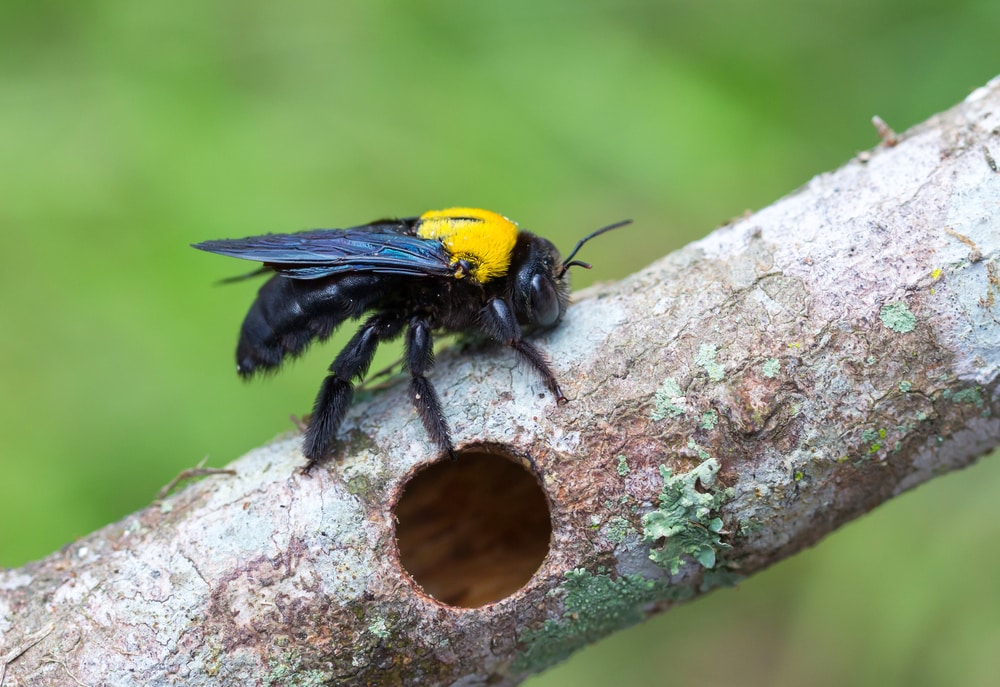

Carpenter bee nests and life cycles are much different than honeybees and bumblebees. Some carpenter bees may be more solitary or social.
Bumblebees and carpenter bees are easily confused. They do have one distinct difference in appearance. Carpenter bees have shiny abdomens while bumblebees have fuzzy abdomens. Carpenter bees are also usually all black, with some yellow on their thorax.
Carpenter bees build nests by excavating tunnels in wood. Nesting sites are used repeatedly every year. A female carpenter bee will not produce nearly as many offspring if she has to build a new nesting site.
All female carpenter bees are capable of reproducing. This means that all female carpenter bees are queen bees. How long these bees live depends on their lifestyle.
If carpenter bees live together in a large nesting site, there is usually a primary queen bee.
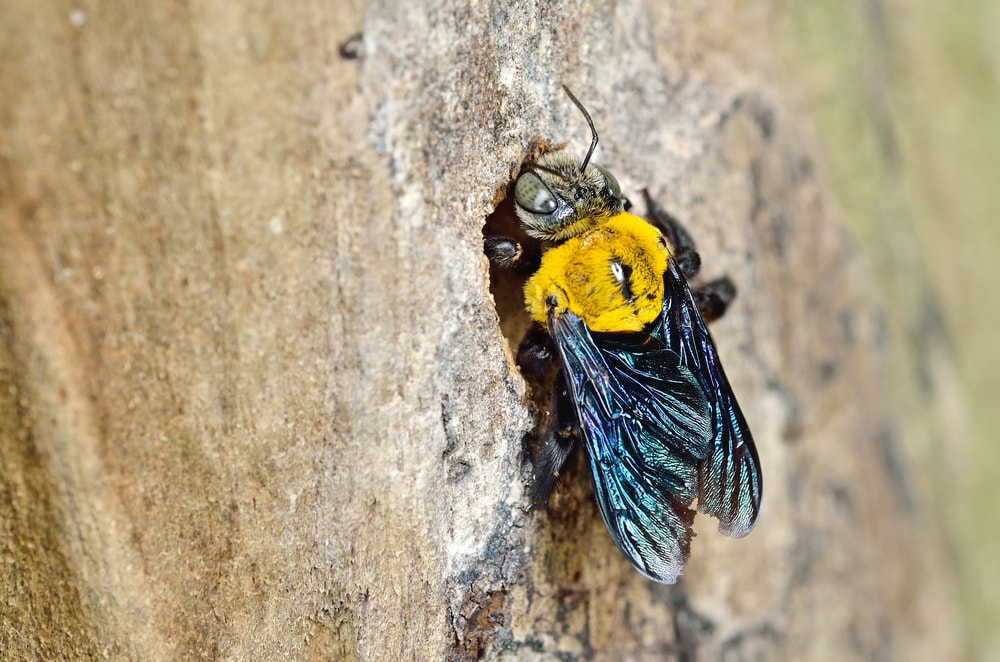

Other females living with a primary queen are called subordinate queen bees. Subordinate queen bees are mainly in charge of protecting the nesting site. The primary queen bee lays eggs, cares for the larvae, and feeds herself.
Healthy subordinate queen bees can live up to three years when living in a group. Most female carpenter bees live for one year.
Male carpenter bees can also live up to one year, but die soon after mating. Bees born later in the summer hibernate in nesting tunnels during winter.
Once spring begins, new female carpenter bees will begin to lay eggs and start a new generation.
Longhorn Bee Lifespan
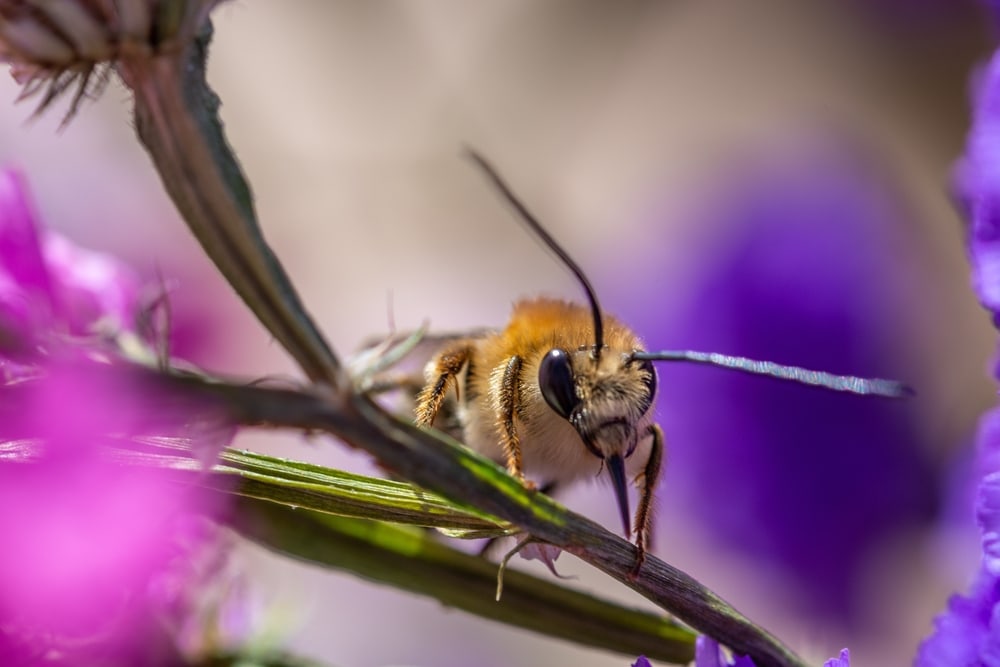

More than 700 subspecies make up the longhorn bee tribe. These bees are named for their long antennae. These bees are typically ground nesters.
Longhorn bees are primarily solitary. Females are known to build their own nests and live alone. Groups of females may be found, but this is uncommon.
Longhorn bees appear in the late spring and early summer. Female longhorn bees build a nest underground to lay eggs and care for larvae. They collect pollen to feed the larvae while they develop underground. Only one or two small broods are produced per generation.
Most adult longhorn bees are only active for about one month. They will find food, build a nest, and reproduce during this time. They’re most active in the late summer and fall months.
The full extent of the longhorn bee lifespan is largely unknown. This is because little research has been done on these bees. It’s also difficult to pinpoint an average lifespan of a long bee because this tribe is very diverse. Females likely live no more than a year, and males die shortly after mating.
You may also like: The Different Types of Stink Bugs You Should Know About with Photos, Infographics, Facts, and more!
How Long Do Bees Live After They Sting?
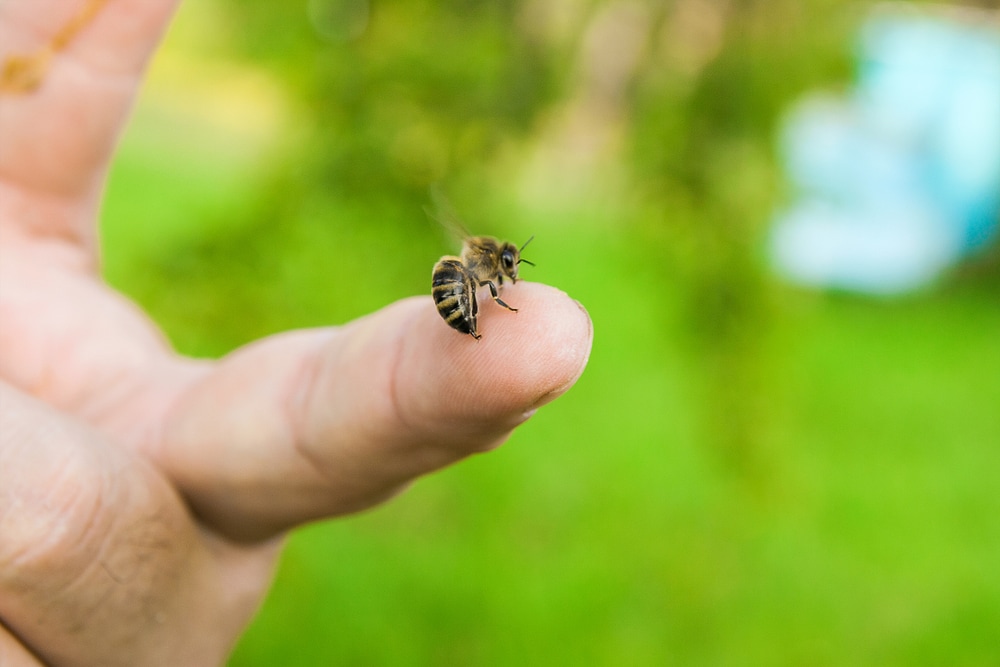

Not all bees die after stinging. Female honey bees are the only bees that die after stinging. Additionally, females are the only bees that have a stinger.
A honey bee dies after stinging because it loses a part of its body when it stings. A bee’s stinger often gets stuck in its victim because it has barbs along its length.
Female honey bees are known to die fairly quickly after stinging. They may survive for only a few minutes or possibly a little longer.
You may also like: What Do Bees Eat? All About The Rich Diet Of A Bee
Importance of Bees to Humans and Nature
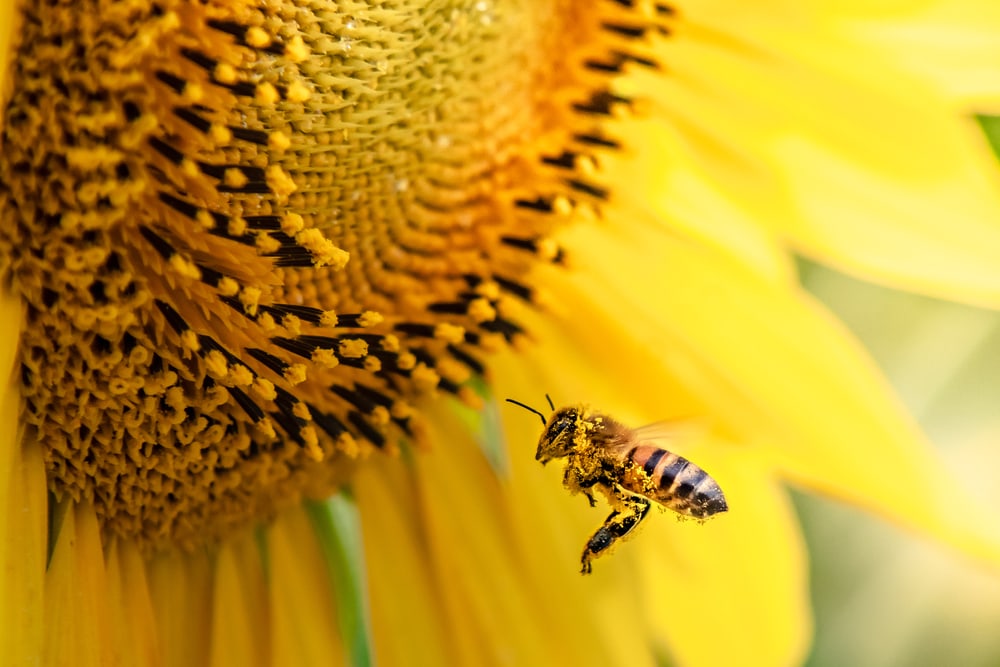

You may have heard the saying, “save the bees!” and there’s a reason for it. Bees are very important to the environment and humans.
Bees are key pollinators. They help carry pollen from one flower to another. This process fertilizes the flowers.
Pollination plays a crucial role in plant reproduction. It’s also important to the abundance of wildlife that depends on plants.
In order to survive, almost all seed plants need pollination. Ecosystems
without our pollinating pals.
If all bees ever went extinct, it’s estimated that humans would only survive for about four years after the fact.
You may also like: 29 Different Types Of Butterflies – Pictures, Chart, Facts And Guide
What Is the Greatest Threat to Bees?
The greatest threat to bees is a culmination of things. Human activity contributes to a large part of bee population decline.
Urbanization, for example, destroys bee habitats. Most pesticides are also toxic to bees. Climate change fueled by greenhouse gas emissions alters plant growth and weather patterns.
Drastic changes in temperatures can also be harmful to fragile ecosystems.
Natural Threats
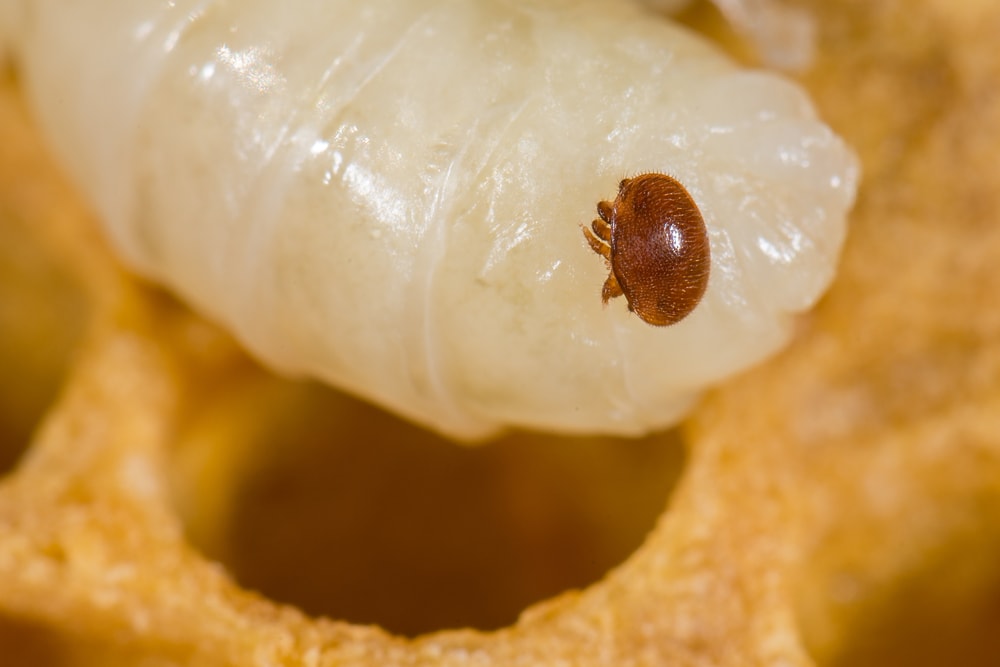

Natural factors like weather events, parasites, and infections affect the lifespan of bees.
Some bee species are vulnerable to certain parasites. For example, the western honey bee is susceptible to the Varroa mite. This can weaken the bee and transmit pathogens.
Bacterial, fungal, and viral infections are another threat to bee colonies. So far, over 20 bee viruses have been recorded throughout history. These infections can spread and kill off entire bee colonies.
Natural weather conditions can impact bees and food sources. Dramatic weather events can reduce food availability.
Man-Made Threats
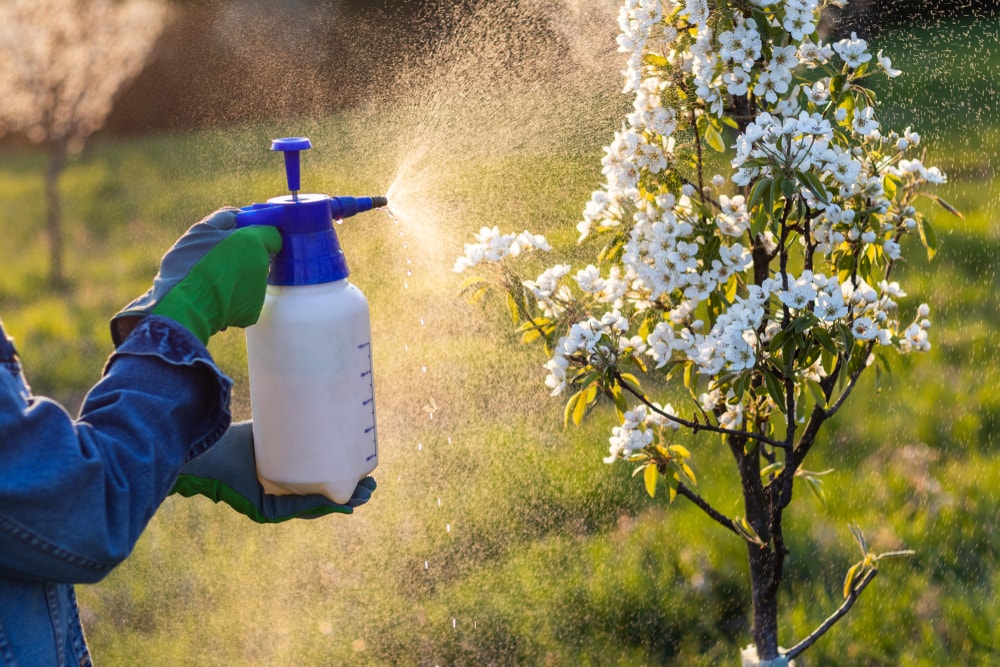

Pesticides and climate change are two major man-made threats to bees. Pesticides can help reduce diseases and control pests, but some are harmful to bees.
The following pesticides are considered very toxic to most bees and other pollinators:
- Carbamates
- Organophosphates
- Chlorinated cyclodienes
- Neonicotinoids
- Synthetic pyrethroids
Other pest preventatives, such as most herbicides, are considered safer for bees.
Climate change can lead to abnormal temperature and humidity changes. Some bee species are sensitive to humidity and very high or low temperatures. If climate change worsens, this can be detrimental to bee populations.
Urbanization largely diminishes bee populations through habitat destruction. It also depletes food sources. Air pollution from cars and factories can also affect a bee’s lifespan.
You may also like: How Long Do Butterflies Live? Not As Long As You’d Think!
Fun Facts About Bees

1. Bees Can Be Found Almost Anywhere
Bees can be found on every continent except Antarctica. Bees can even be found in the Arctic! The Arctic tundra is home to the Arctic bumblebee. This species can withstand harsh, cold conditions.
2. Bees Communicate Through Chemicals
Bees can communicate using pheromone chemicals. Queens, workers, drones, and broods are examples of bees that give off pheromones.
3. Bees Will Dance to Alert Other Bees
Bees will dance to communicate something to other bees. One dance involves a “waggle” movement to tell other nearby bees about a good flower spot. Bees will do a round dance by walking back and forth in a circle to let other bees know there’s a flower patch nearby.
4. Honey Bees Visit Many Flowers in One Trip
Worker honey bees spend a lot of time foraging for food. Honey bees visit anywhere between 50 to 100 flowers in just one foraging trip.
FAQ

Do bees sleep?
Yes, bees do sleep! Depending on the species, bees in colonies often take turns resting and sleeping. Some species may sleep up to six hours a day.
What’s the longest living bee?
The longest-living bee is the queen bee in most species. Queen bees must live long enough to nest, lay eggs, and establish a colony.
How old is the oldest bee?
The oldest bee is an ancient wasp in the middle of transitioning to a bee. It is called Melittosphex burmensis. It’s from Myanmar, and its body was preserved in amber from 100 million years ago.
Do king bees exist?
King bees do not exist. Male bees exist, but their only purpose is to mate with a queen bee to help build a colony.
What happens if a queen bee dies?
The worker bees will quickly find a replacement if a queen bee dies. Bees will choose a specific larva to become the new queen. The larva is fed a special substance called royal jelly to nourish it into becoming a queen.
How long can a bee live without food?
Bees can’t survive very long without food. A bee can die if it does not consume nectar, pollen, or water for a few hours. Some bees may be able to survive up to a day without food.
Can a queen bee survive on her own?
Most queen bee species cannot survive on their own. A queen bee typically needs worker bees to care for her while she is busy laying eggs. Drone bees are required to mate with queen bees to build a colony and continue the next generation.