Outforia Quicktake: Key Takeaways
- Cirrocumulus clouds are high clouds that occur between 20,000-40,000 ft (6,096-12,192 m) and are composed of ice crystals.
- They appear as tiny white cotton balls in rows across the sky, and are associated with cold and fair weather.
- There are four types of cirrocumulus clouds: stratiformis, lenticularis, floccus, and castellanus.
- They form due to turbulent vertical currents and can be created by contrails from airplanes.
- Cirrocumulus clouds are different from cirrus and cirrostratus clouds in their ability to hold liquid precipitation and their formation based on weather patterns.
Several different types of clouds come in many shapes and sizes. They’re also indicators of various types of weather.
Clouds are categorized into four main groups. These groups include cirro-form, cumulo-form, strato-form, and nimbo-form.
Cirrocumulus clouds are in the cirro-form category. They look like tiny white cotton balls that appear in rows across the sky. Follow along to learn more about the unique characteristics of cirrocumulus clouds, how they form, and what they mean for the weather.
SHARE THIS IMAGE ON YOUR SITE
<a href="https://outforia.com/cirrocumulus/"><img style="width:100%;" src="https://outforia.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Cirrocumulus-infographics-12012022.jpg"></a><br>Cirrocumulus <a href="https://outforia.com">Outforia</a>What Are Cirrocumulus Clouds?
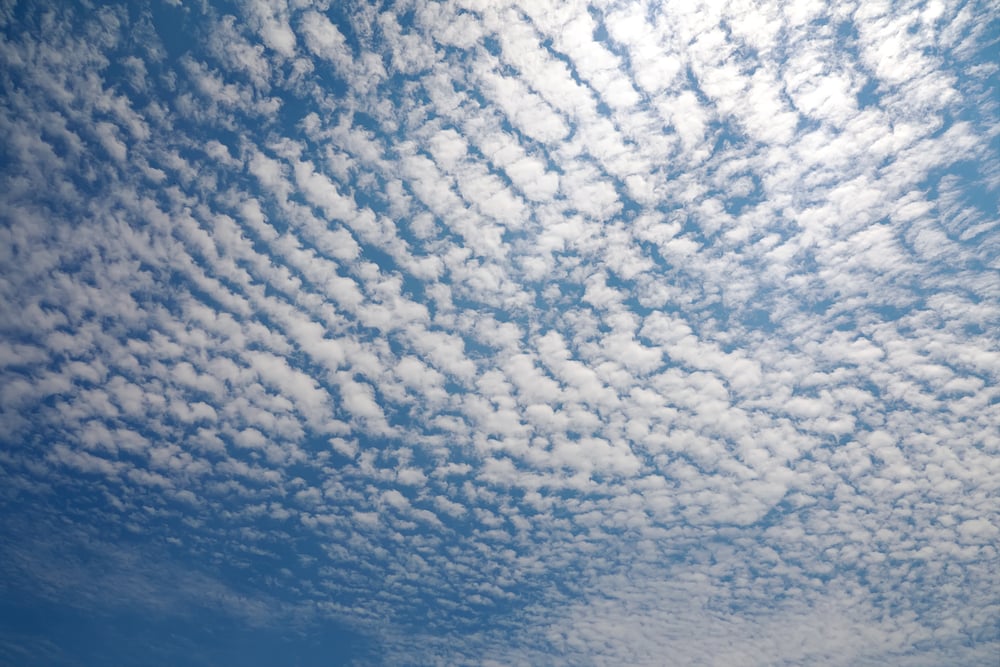

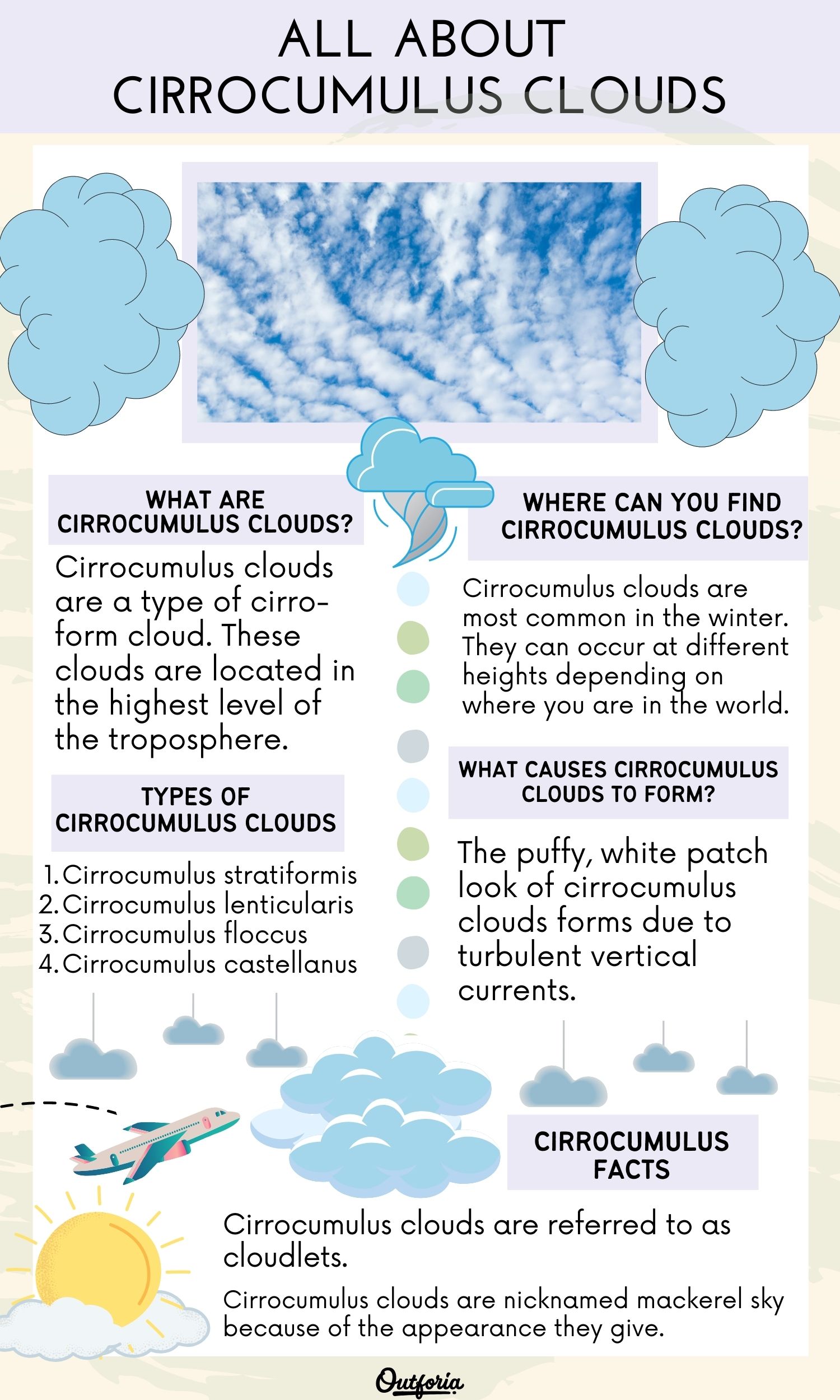
Cirrocumulus clouds are a type of cirro-form cloud. British chemist and amateur meteorologist Luke Howard categorized the four main types of clouds. He introduced the four cloud categories in his Essay of the Modifications of Clouds in 1803.
These clouds are located in the highest level of the troposphere. The troposphere is the lowest layer of the Earth’s atmosphere. It’s where most types of clouds form because it’s the wettest atmosphere layer.
Cirrocumulus clouds are referred to as high clouds because they occur between 20,000-40,000 ft (6,096-12,192 m).
Clouds at this level in the troposphere are mainly composed of ice crystals. Cirrocumulus can also occur where mid-level clouds are between 6,500-20,000 ft (1,981-6,096 m). Mid-level clouds include altostratus, altocumulus, and cumulonimbus.
You May Also Like: 12 Different Types Of Ecosystems And Why They Are Important
What Do Cirrocumulus Clouds Look Like?
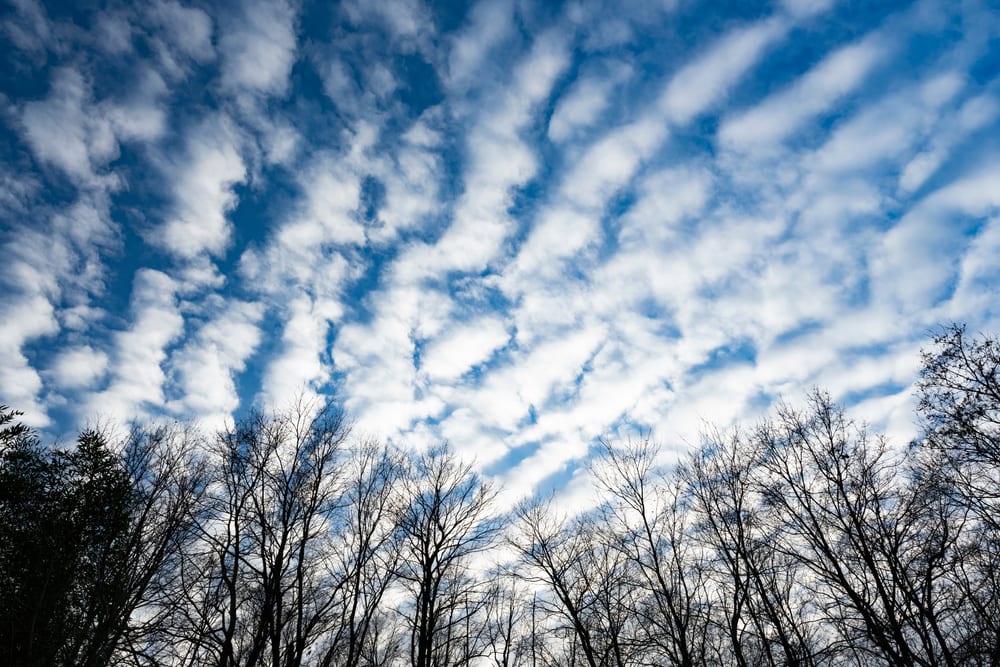

Cirrocumulus clouds are mainly white but can sometimes be light gray. Cirrocumulus clouds present in the high level of the troposphere are white. This is because they’re mainly composed of ice crystals in the form of grains. The drastic drop in temperature at this high altitude creates granulated ice crystals.
Many of the tallest mountain peaks in the world have snow on them due to the drastic temperature drop at very high altitudes.
The boundary separating the troposphere and the stratosphere layer above is called tropopause. The average temperature at the tropopause is about -60 degrees Fahrenheit (-51 C).
Cirrocumulus clouds that form at a lower level can be gray. They become gray as more precipitation builds up in the cloud. It causes the cloud to become denser when it contains liquid precipitation rather than solid ice crystals.
When you extend your arm and hold your finger up to the sky, cirrocumulus clouds are no larger than your finger. These clouds are no more than 656 ft (200 m) thick. They’re small, round clouds that have a puffy appearance. Cirrocumulus clouds occur in rows that extend across the sky.
Where Can You Find Cirrocumulus Clouds?
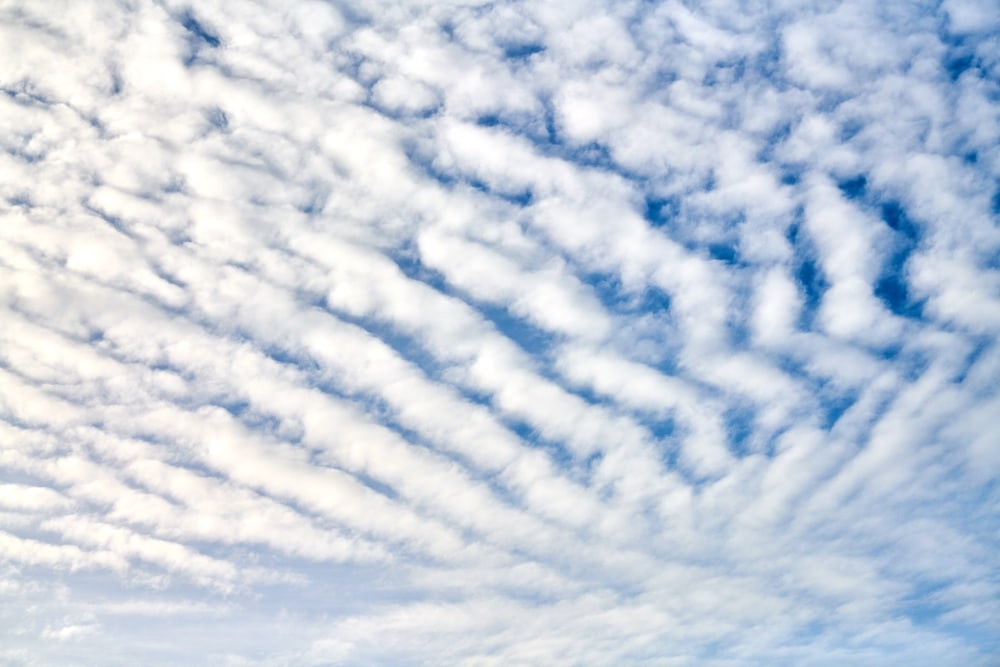

Cirrocumulus clouds are most common in the winter. They can occur at different heights depending on where you are in the world. This is because the height of the troposphere varies with latitude.
For example, the troposphere is thinner over the poles. It’s higher at the equator. Seasons also affect the height of the troposphere. It’s thinner in the winter than during the summer.
Cirrocumulus clouds are associated with cold and fair weather. Therefore, they can be common in places that experience colder weather more often. They can still develop in warmer areas depending on the conditions in the upper level of the troposphere.
What Are Microbursts?
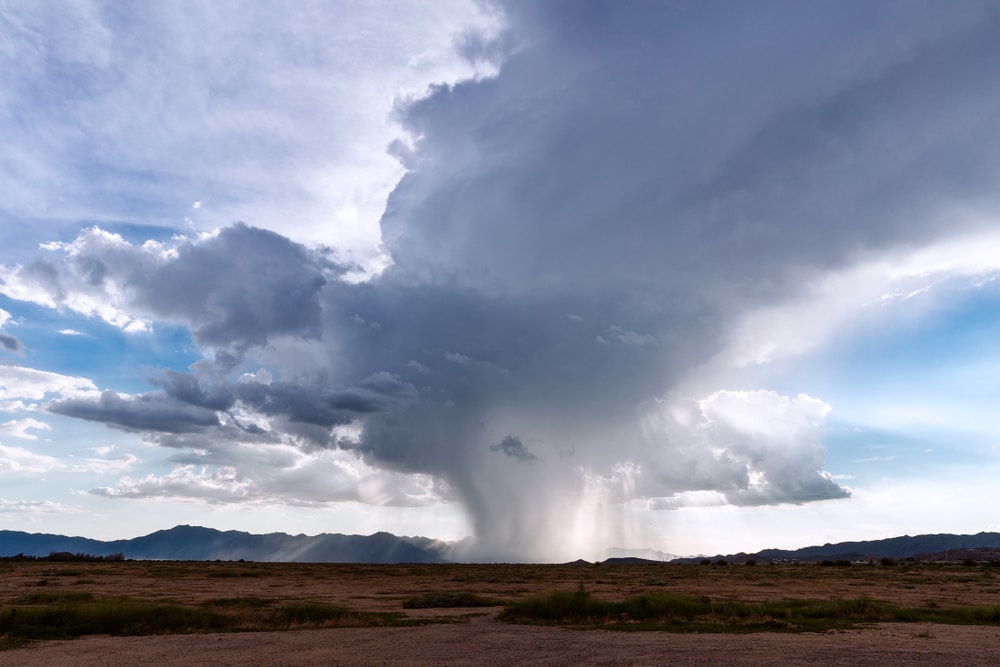

Microbursts are the result of water droplets or hailstones being suspended and released. Precipitation is developed, and warm air rises, carrying the precipitation with it. This is known as an updraft. Microbursts are created by strong updrafts when a thunderstorm develops.
The updraft can suspend large amounts of precipitation in the upper part of a thunderstorm. As precipitation begins to fall from the storm cloud, it drags air down, creating a downdraft.
When an updraft is weakened, it can’t provide enough support to hold large amounts of precipitation. This causes all the precipitation to plummet rapidly to the ground. The point where a microburst hits the ground receives the most damage.
Microbursts cause heavy precipitation and high winds in concentrated areas. Surrounding areas can be affected because the winds and precipitation spread as they reach the Earth’s surface.
Wind speeds of a microburst hitting the ground can reach up to 100 mph (161 kph). A microburst can cause major damage to structures and trees. Microbursts can be predicted about 6-12 hours before they’re expected to develop.
Types of Cirrocumulus Clouds
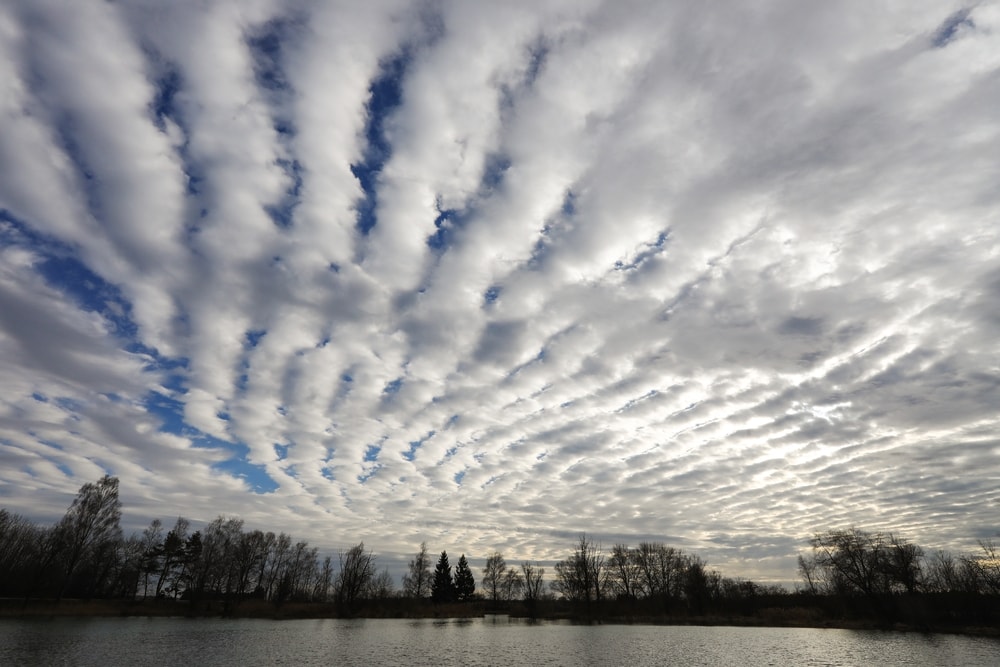

There are four sub-types of cirrocumulus clouds. They are characterized by their different appearances. The four types of cirrocumulus clouds include:
- Cirrocumulus stratiformis
- Cirrocumulus lenticularis
- Cirrocumulus floccus
- Cirrocumulus castellanus
Stratiformis refers to clouds being spread out in a horizontal sheet or layer. Along with cirrocumulus, it can also apply to altocumulus and stratocumulus clouds. Cirrocumulus stratiformis clouds are more spread out. They resemble a long sheet of small puffy clouds in consecutive rows.
Cirrocumulus lenticularis clouds have a unique lens-like shape. The term lenticularis refers to clouds with a lens or almond shape, which is elongated. They resemble the shape of lenticular clouds but look more thin and delicate.
Cirrocumulus floccus clouds are puffy with wispy tails. They sometimes appear with virga. Virga are visible trails of precipitation that evaporate before it reaches the ground.
Cirrocumulus castellanus clouds form due to atmosphere instability at the cloud level. They form turrets, defined as small towers on top of larger ones. These clouds form as they rise from the base of a cloud when air rises due to latent heating.
What Causes Cirrocumulus Clouds to Form?
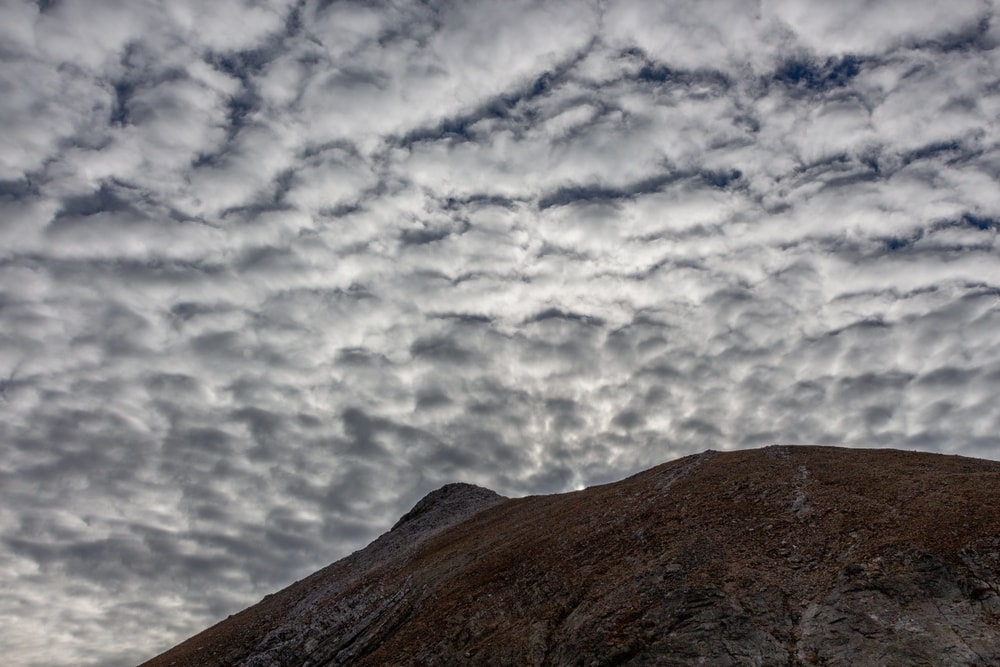

The puffy, white patch look of cirrocumulus clouds forms due to turbulent vertical currents. Turbulence refers to the irregular motions of air as a result of vertical currents.
Vertical currents are created when air converges and diverges at various levels in the troposphere. When vertical currents occur, they can cause irregularities in the motions of air.
Airplanes avoid areas in the troposphere with extreme turbulence because it causes the plane to be tossed around. Light turbulence is less dangerous and violent.
If turbulent vertical currents meet with a layer of cirrus clouds, it can create cirrocumulus clouds.
Cirrus clouds are light and wispy. When they’re mixed up by irregular motions of air, it creates tiny cotton ball-like shapes that become cirrocumulus clouds.
Contrails can also create cirrocumulus clouds. Contrails are the vapor trails that airplanes leave behind in the sky. If you’ve ever noticed the white trail flying planes leave behind, you’ve seen contrails.
The streaks of contrails can spread out and become different types of clouds. Cirrocumulus, cirrus, and cirrostratus clouds can be created by contrails.
What Kind of Weather Is Associated With Cirrocumulus Clouds?
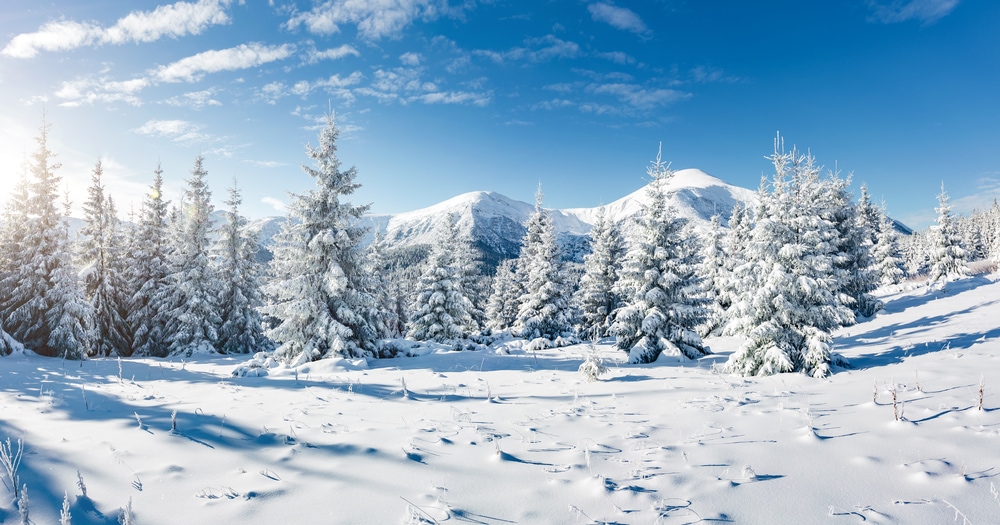

Cirrocumulus clouds indicate cold and fair weather. Due to their height in the sky, any precipitation they may create doesn’t reach the ground. Cirrocumulus clouds can sometimes be an indicator of stormy weather later on. However, stormy weather isn’t caused by cirrocumulus clouds.
The lifespan of cirrocumulus clouds is also very short. They can appear and disappear within minutes. Cirrocumulus clouds are usually a transition phase between cirrostratus and cirrus clouds.
You May Also Like: 24 Types Of Natural Disasters That You Need To Know
Cirrus, Cirrostratus, and Cirrocumulus: What’s the Difference?
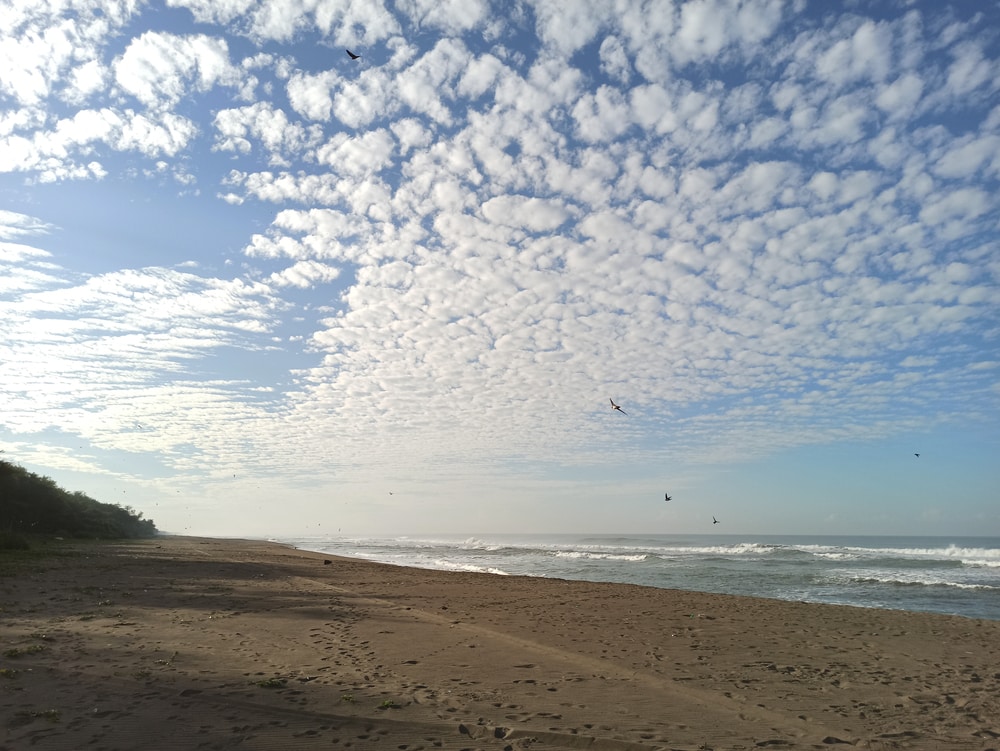

Cirrus and cirrostratus clouds are found in the same upper troposphere as cirrocumulus clouds.
Cirrus clouds are wispy, layered clouds that can appear patchy. They’re very white and look light and delicate. These clouds can take on the vibrant colors of a sunrise or sunset.
Similar to cirrocumulus clouds, cirrus clouds can also form through contrails. However, cirrus clouds are only composed of ice crystals. They don’t contain any liquid precipitation, unlike some cirrocumulus clouds.
Cirrus clouds can also form when dry air ascends into the atmosphere. They appear due to water vapor turning directly into fine granules of ice crystals. Any precipitation from cirrus clouds doesn’t reach the ground. These clouds are associated with warm fronts.
Cirrostratus clouds are smooth, layered clouds that cover large parts of the sky. Similar to cirrus, cirrostratus can also appear wispy and light.
Cirrostratus clouds often appear at the front of weather systems. This makes them a good short-term weather predictor. They form due to air slowly ascending and don’t produce precipitation.
Cirrocumulus clouds share many similarities with cirrus and cirrostratus clouds. However, cirrocumulus clouds do have the ability to hold liquid precipitation. Cirrus and cirrostratus clouds are usually always composed of ice crystals. They also form differently based on varying weather patterns.
Fun Facts
Cirrocumulus clouds are referred to as cloudlets.
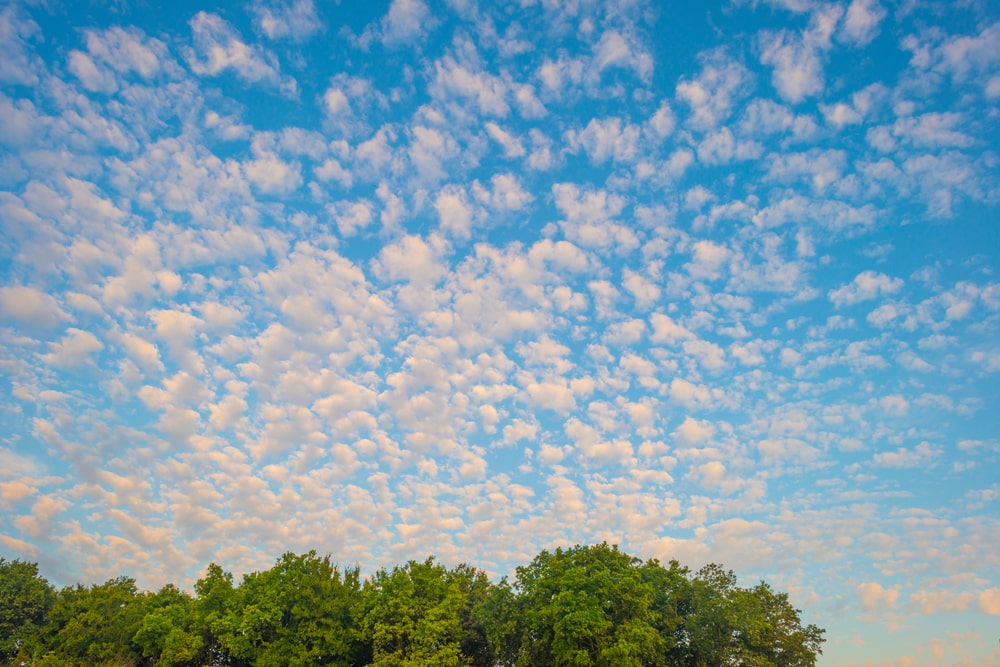

The small, cotton-like clouds of cirrocumulus that form in groups are called cloudlets. The nickname is fitting because cirrocumulus clouds are shaped like cumulus clouds. Cumulus clouds are larger and very fluffy and white. They often appear in clear blue skies. These clouds are associated with nice weather.
Volcanoes and wildfires can cause clouds to form.
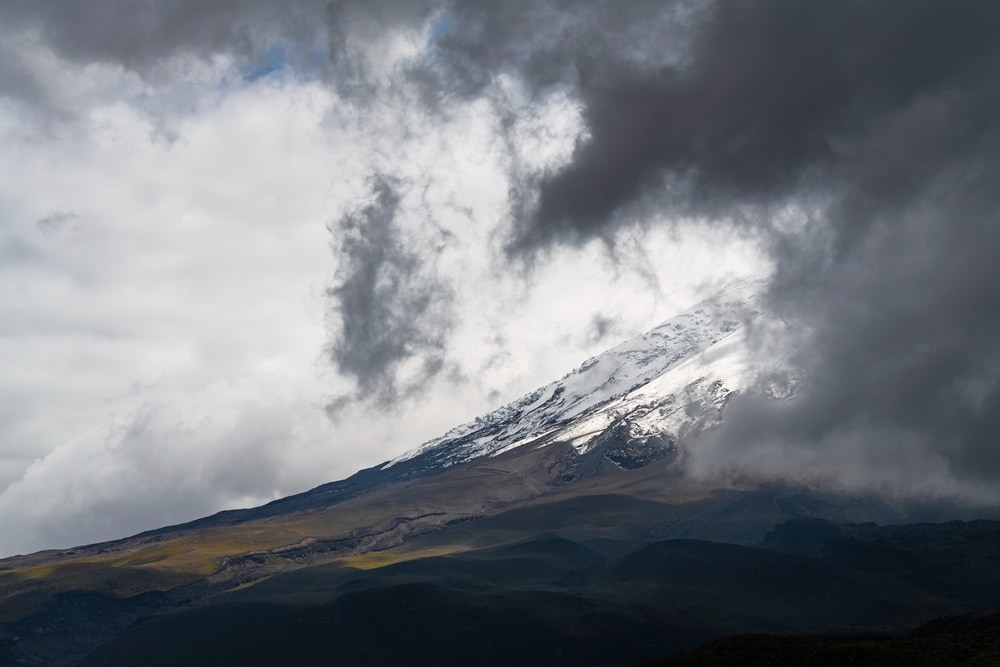

The intense heating of the Earth’s surface caused by volcanoes and wildfires has the ability to create cloud formations. These clouds are called flammagenitus clouds. They’re also referred to as pyrocumulus clouds.
It can also create thunderstorm clouds if enough water vapor is in the atmosphere. These clouds are known as pyrocumulonimbus.
Clouds are white because of the sun.
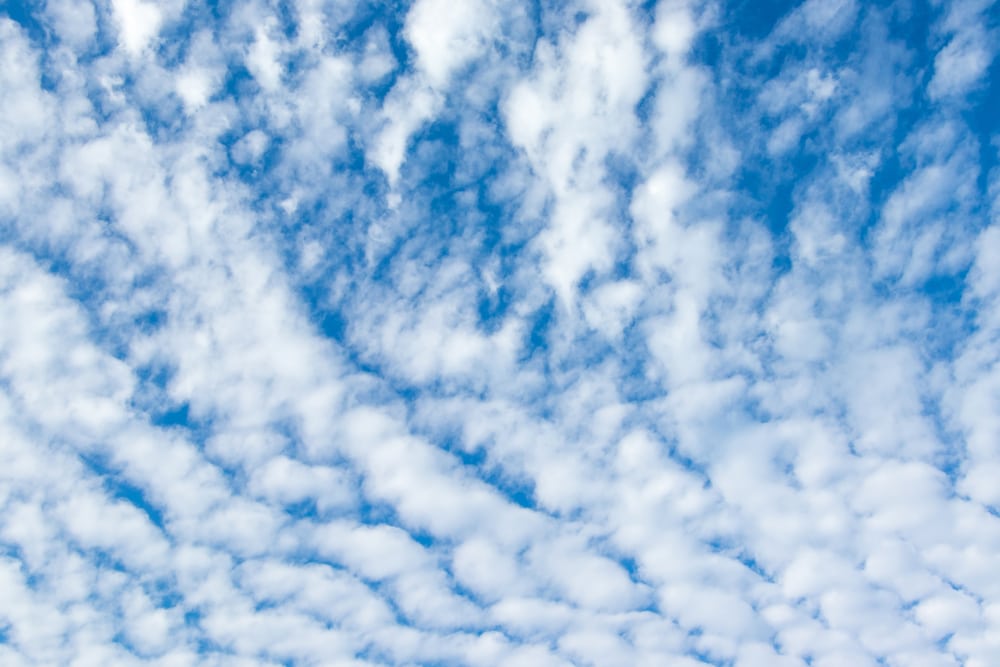

As sunlight casts down on clouds, the light scatters amongst the water droplets or ice crystals. When sunlight interacts with the water or ice particles in a cloud, it remains white.
Gray clouds are denser and heavy than white clouds because they hold larger amounts of precipitation. Sunlight isn’t able to pass through as easily in lighter clouds. This gives them a gray appearance.
More than half of the Earth is usually covered by clouds.

Scientists and researchers have determined that 67% of the Earth’s surface is usually covered by clouds at any given time. Years of satellite data were collected and analyzed to discover how much cloud coverage the Earth has. Other studies also determined that 30% of skies over land are cloud-free. It was also determined that 10% or less of the sky is clear over oceans.
You May Also Like: What Causes Tides?
Cirrocumulus FAQ

Why are cirrocumulus clouds called mackerel sky?
Cirrocumulus clouds are nicknamed mackerel sky because of the appearance they give. Since the clouds form in patch-like rows, it sometimes resembles the look of fish scales.
What is the fluffiest type of cloud?
Cumulus clouds are the fluffiest clouds. They usually have a flat base. The upper half of cumulus clouds have round arches across the top.
These clouds show that fair weather is in the forecast. However, they can turn into dark gray and fluffy cumulonimbus clouds. Cumulonimbus clouds are a sign that thunderstorms are on the way.
What is the most dangerous type of cloud?
Rotating cumulonimbus clouds can be considered one of the most dangerous types of clouds. These clouds are referred to as supercells. They can create dangerous weather conditions. Heavy rain, lightning, high winds, and tornadoes can come from supercells.
Is it safe to fly into cirrocumulus clouds?
Unlike virga clouds, cirrocumulus clouds aren’t dangerous to fly into. They form in stable air conditions, despite being created as a result of turbulent vertical currents. Commercial airplanes usually fly at an altitude of 30,000 ft (9,144 m) or higher.
If you’re flying through layers of cirrus clouds, it’s likely the plane you’re in is leaving behind cirrocumulus clouds.









